* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
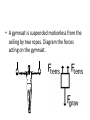
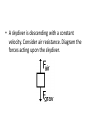
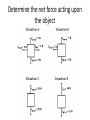
• Please turn in your week 6 accountability sheet and pick up week 7. • If you did not bring your workbook, share with a table partner. REVIEW: Newton’s first law • Sometimes referred to as the law of inertia • “An object at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.” Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • What’s that mean? • This is equilibrium! equal magnitude, opposite direction • Now consider a book being pushed to your right… • Unbalanced forces cause Accelerations These pics are called Free Body Diagrams Drawing Free-Body Diagrams • “diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation” • Use vector arrows • Example: Our first free body diagram • A book is at rest on a tabletop • A gymnast is suspended motionless from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the gymnast. • An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air resistance. Diagram the forces acting on the egg as it is falling • A flying squirrel is gliding (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Diagram the forces acting on the squirrel • A rightward force is applied to a book in order to move it across a desk with a rightward acceleration. Consider frictional forces. Neglect air resistance. Diagram the forces acting on the book. • A rightward force is applied to a book in order to move it across a desk at constant velocity. Consider frictional forces. Neglect air resistance. Diagram the forces acting on the book. • A college student rests a backpack upon his shoulder. The pack is suspended motionless by one strap from one shoulder. Diagram the vertical forces acting on the backpack. • A skydiver is descending with a constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Diagram the forces acting upon the skydiver. • A force is applied to the right to drag a sled across loosely packed snow with a rightward acceleration. Diagram the forces acting upon the sled. • A car is coasting to the right and slowing down. Diagram the forces acting upon the car. Determining the Net Force • A. B. C. • net force is the vector sum of all the forces that act upon an object (“Where is the imbalance?”) • Figuring out the net force: Ask yourself these questions: In what direction and of what magnitude is the imbalance? Determine the net force acting upon the object The net force is known for each situation. However, the magnitudes of a few of the individual forces are not known. Analyze each situation individually and determine the magnitude of the unknown forces.