* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roller Coaster - Pennsylvania State University
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
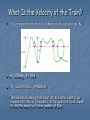
Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy Sang Yun Lee In Woo Song Song Kwang Seok Potential and Kinetic Energy in a Roller Coaster The ride often begins with a chain and motor exerting a force on the train to lift it to the top of a very tall hill. At the top of the hill, the train possess a potential energy. Potential energy is dependent upon the mass of the object and the height of the object. ( Work = mgh2 - mgh1 ) As it descends the first drop, it loses much of this potential energy. Instead, it subsequently gains kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is dependent upon the mass of the object and the speed of the object. ( Work = 1/2mv22 – 1/2mv12 ) Thus, its original potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy. As the ride continues, the train is continuously losing and gaining height. Whenever it gains a height, there is a loss of speed as kinetic energy is transformed into potential energy. Whenever it loses a height, there is a gain of speed as potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy. Mechanical Energy in a Roller Coaster As potential and kinetic energy are happening at the same time, mechanical energy is applied. ( Work = (1/2mv22 – 1/2mv12) + (mgh2 - mgh1) ) From a Real Roller Coaster… Incredible Hulk Universal's Islands of Adventure Orlando, Florida I rode this one when I went to Orlando this spring break. So..I want to investigate further… It is brought up to 110 feet(33.5m), and the first drop is 105 feet(32m). Its mass is 300kg and can hold 32 riders per train. If I assume the average mass of a normal person as 55kg, the total mass is 2060kg. What Is the Velocity of the Train? If I just simply stretch the rail in 1 dimension, the rail looks like this… m = 2060kg, h = 32m W = 2060*9.8*32 = 646016Nm This amount of energy that is put into the roller coaster car remains with the car throughout its trip down the track. I want to find the velocity of roller coaster at 25m. 646016 = mgh + 1/2mv2, at h = 25m 646016 = 2060*9.8*25 + ½*2060*v2 646016 = 504700 + 1030*v2 141316 = 1030*v2 137.2 = v2 v = 11.7m/s In the picture, the roller coaster reaches 25m at four different positions (blue dots). Therefore, the roller coaster has the same velocity, 11.7m/s at any 25m. The Origin of Roller Coaster The origin of the Roller Coaster dates back to the Russian Ice Slides built in the 17th century in Russia. The structures were built out of lumber with a sheet of ice several inches thick covering the surface. Riders climbed the stairs attached to the back of the slide, sped down the 50 degree drop and ascend the stairs of the slide that laid parallel to the first one. The History of Roller Coaster It is known that by 1817 two coasters were built in France called the Russes a Belleville and Promenades Aeriennes, both of which featured cars that locked to the track in some manner. Bellville's ride was the first coaster to lock the cars by having the axles slide into a groove cut in the track. First Looping Roller Coaster The French Centrifugal Railway, the world's first looping roller coaster with a 13-foot diameter loop was imported to France from England. Today’s Roller Coasters Physics and Roller Coasters Roller Coaster designer must use knowledge of kinematics to build a roller coaster. What kind of physics are there in roller coasters? - Pretty much all! Potential, kinetic, and mechanical energy, gravitation, free fall, projectile motion, centripetal acceleration, friction, centrifugal acceleration, and so on. Based on my basic knowledge of physics, I want to concentrate on potential and kinetic energy, which are the most important terms to consider in building a roller coaster. Conclusion At the same height, a roller coaster has the same velocity wherever its position is. However, it is not that simple thing to think about its velocity at certain points only based on the knowledge of potential and kinetic energy. The reason is that there are also friction, brake, and acceleration to consider its velocity. Roller coasters can not be exited without the knowledge of physics. As far as the safety and recreation of passengers are concerned, physics is the most fundamental and important notion in building roller coasters as well.