* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Calculating Work - Northern Illinois University
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
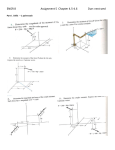
Calculating Work The Joule Work is force acting over a distance, and has units equal to units of force times units of distance. • With 1-dimensional constant force and distance, W = F Dx The unit of work is the joule (J) = 1 N m. Constant Force Lifting an object requires a constant force equal to gravity, F = mg. mg Dx = h The work done by the lifter is W = F Dx = mgh. -mg mg The work done by gravity is W = - F Dx = -mgh. -mg Using the Scalar Product Dx F A man is letting a 300 kg piano slide 4 m at constant velocity down a 30° incline while exerting a 400 N force on the horizontal. What work does he do? • The component of the force is (400 N)(cos 30) = -350 N • Negative since it is opposite the displacement • The work is (-350 N)(4 m) = -1400 N m = -1400 J Variable Force The force applied to a spring increases as the distance increases. The work must be calculated over each separate interval. The work increases over a small interval as the force increases. F Dx Area under a Curve Separate the total distance into steps Dx. The product within a small step is the area of a rectangle F Dx. The total equals the area between the curve and the x axis. F Dx Work on a Spring F=kx For the spring force the force makes a straight line. The area under the line is the area of a triangle. 1 Fs x 2 1 Ws (kx) x 2 1 Ws kx2 2 Ws x Integral Form of Work The work can be found by taking the area under any force curve. F This technique in calculus is the integral. W F||dx W F dr x next