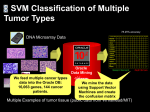
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to XML
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to XML CS348 Information System Guest Lecture Hazem Elmeleegy Outline What is XML? Syntax of XML Document DTD (Document Type Definition) XML Schema XML Query Language XML Databases Oracle JDBC Introduction to XML XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language XML was designed to describe data. XML tags are not predefined unlike HTML XML DTD and XML Schema define rules to describe data XML example of semi structured data Building Blocks of XML Elements (Tags) are the primary components of XML documents. Element FNAME nested inside <AUTHOR id = 123> element Author. Element <FNAME> JAMES</FNAME> Author with <LNAME> RUSSEL</LNAME> Attr id </AUTHOR> <!- I am comment -> Attributes provide additional information about Elements. Values of the Attributes are set inside the Elements Comments stats with <!- and end with -> XML DTD A DTD is a set of rules that allow us to specify our own set of elements and attributes. DTD is grammar to indicate what tags are legal in XML documents. c XML Document is valid if it has an attached DTD and document is structured according to rules defined in DTD. DTD Example <BOOKLIST> <BOOK GENRE = “Science” FORMAT = “Hardcover”> <AUTHOR> <FIRSTNAME> RICHRD </FIRSTNAME> <LASTNAME> KARTER </LASTNAME> </AUTHOR> </BOOK> </BOOKS> Xml Document And Corresponding DTD <!DOCTYPE BOOKLIST[ <!ELEMENT BOOKLIST(BOOK)*> <!ELEMENT BOOK(AUTHOR)> <!ELEMENT AUTHOR(FIRSTNAME,LASTNAM E)> <!ELEMENT FIRSTNAME(#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT>LASTNAME(#PCDATA) > <!ATTLIST BOOK GENRE (Science|Fiction)#REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST BOOK FORMAT (Paperback|Hardcover) “PaperBack”>]> XML Schema Serves same purpose as database schema Schemas are written in XML Set of pre-defined simple types (such as string, integer) Allows creation of user-defined complex types XML Schema RDBMS Schema (s_id integer, s_name string, s_status string) XMLSchema <xs:schema> <xs:complexType name = “StudnetType”> <xs:attribute name=“id” type=“xs:string” /> <xs:element name=“Name” type=“xs:string /> <xs:element name=“Age” type=“xs:integer” /> <xs:element name=“Email” type=“xs:string” /> </xs:complexType> <xs:element name=“Student” type=“StudentType” /> XML Document and Schema </xs:schema> <Students> <Student id=“p1”> <Name>Allan</Name> <Age>62</Age> <Email>[email protected] </Email> </Student> </Students> XML Query Languages Requirement Same functionality as database query languages (such as SQL) to process Web data Advantages Query selective portions of the document (no need to transport entire document) Smaller data size mean lesser communication cost XQuery XQuery to XML is same as SQL to RDBMS Most databases supports XQuery XQuery is built on XPath operators (XPath is a language that defines path expressions to locate document data) XPath Example <Student id=“s1”> <Name>John</Name> <Age>22</Age> <Email>[email protected]</Email> </Student> XPath: /Student[Name=“John”]/Email Extracts: <Email> element with value “[email protected]” Oracle and XML XML Support in Oracle XDK (XML Developer Kit) XML Parser for PL/SQL XPath XSLT Oracle and XML XML documents are stored as XML Type ( data type for XML ) in Oracle Internally CLOB is used to store XML To store XML in database create table with one XMLType column Each row will contain one of XML records from XML document Database Table: Database Row : XML Document XML Record Examples <Patients> <Patient id=“p1”> <Name>John</Name> <Address> <Street>120 Northwestern Ave</Street> </Address> </Patient> <Patient id=“p2”> <Name>Paul</Name> <Address> <Street>120 N. Salisbury</Street> </Address> </Patient> </Patients> Example Create table prTable(patientRecord XMLType); DECLARE prXML CLOB; BEGIN -- Store Patient Record XML in the CLOB variable prXML := '<Patient id=“p1"> <Name>John</Name> <Address> <Street>120 Northwestern Ave</Street> </Address> </Patient>‘ ; -- Now Insert this Patient Record XML into an XMLType column INSERT INTO prTable (patientRecord) VALUES (XMLTYPE(prXML)); END; Example TO PRINT PATIENT ID of ALL PATIENTS SELECT EXTRACT(p.patientRecord, '/Patient/@id').getStringVal() FROM prTable p; USE XPATH Oracle JDBC JDBC an API used for database connectivity Creates Portable Applications Basic Steps to develop JDBC Application Import JDBC classes (java.sql.*). Load JDBC drivers Connect and Interact with database Disconnect from database Oracle JDBC DriverManager provides basic services to manage set of JDBC drivers Connection object sends queries to database server after a connection is set up JDBC provides following three classes for sending SQL statements to server Statement SQL statements without parameters PreparedStatement SQL statements to be executed multiple times with different parameters CallableStatement Used for stored procedures Oracle JDBC SQL query can be executed using any of the objects. (Statement,PreparedStatement,CallableStatement) Syntax (Statement Object ) Public abstract ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) throws SQLException Syntax (PreparedStatement,CallableStatement Object ) Public abstract ResultSet executeQuery() throws SQLException Method executes SQL statement that returns ResultSet object (ResultSet maintains cursor pointing to its current row of data. ) Oracle JDBC (Example) Import java.sql.*; Import java.io; Class simple{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Connection conn=null; try{ String conStr = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@oracle.cs.purdue.edu:1521:orb"; DriverManager.registerDriver(new oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver()); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(conStr,”username”,”passwd"); Statement cursor = conn.createStatement(); // Connection Est. ResultSet rset = stmt.executeQuery(“Select* from table_name”); while(orset.next()){ System.out.println(“Printing column name ”+orest.getStringVal(1)); } }Catch(ClassNotFoundException e){} cursor.close(); conn.close(); } References [1] Database Management Systems by Ramakrishnan and Gehrke Thank You