* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
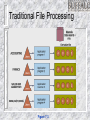
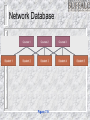
Intro to MIS – MGS351 Databases and Data Warehouses Chapter 3 Chapter Overview Data Hierarchy Traditional File Environment Databases – Relational, Hierarchical, Network Design and Normalization Data Warehousing Data Hierarchy Database Table, File, Relation Records, Rows, Tuples Fields, Columns, Attributes Bytes Bits Data Hierarchy Figure 7-1 Traditional File Environment Issues: Data Redundancy Data Inconsistency Data Isolation Data Integrity Security Application / Data Dependence Traditional File Processing Figure 7-3 Database Approach Minimal data redundancy Data consistency Integration of data Sharing of data Uniform security, privacy and integrity Data independence Database Environment Figure 7-4 DBMS Components • Data definition language: Specifies content and structure of database and defines each data element • Data manipulation language: Manipulates data in a database • Data dictionary: Stores definitions of data elements, and data characteristics Evolution of Databases Relational Database • Represents data as twodimensional tables called relations • Relates data across tables based on common data element • Examples: DB2, Oracle, MS SQL Server Relational Database Figure 7-6 Hierarchical Database • Organizes data in a tree-like structure • Supports one-to-many parent-child relationships • Prevalent in large legacy systems Hierarchical Database Figure 7-8 Network Database Depicts data logically as many-tomany relationships Less flexible compared to RDBMS Lack support for ad-hoc and English language-like queries Network Database Figure 7-9 Database Design Conceptual / Logical Design – Abstract model of database from business perspective. Physical Design – shows how the database is arranged on storage devices. ER Diagram Figure 7-10 Business Intelligence Knowledge about your: – Customers – Competitors – Partners – Competitive environment – Internal operations Business Intelligence Business Intelligence o Online transaction processing (OLTP) - the gathering of input information, processing that information, and updating existing information to reflect the gathered and processed information. o Operational databases - databases that support OLTP. o Online analytical processing (OLAP) - the manipulation of information to support decision making. Data Warehousing Multidimensional Data Models OLAP Data Marts – subset of data warehouse Data Mining – finding hidden patterns and trends in data Data Warehousing Data warehouse - a logical collection of information gathered from many different operational databases (Extract, Transform, Load) used to create business intelligence that supports business analysis activities and decisionmaking tasks. Data Warehouse Multidimensional Data Model Figure 7-15 Data Marts Data mart - a subset of a data warehouse in which only a focused portion of the data warehouse information is kept. Data Mining Tools Distributed Databases Figure 7-13 Databases and the Web Figure 7-18