* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download data terminology/hierarchy -- character, field, record, file
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
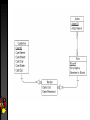
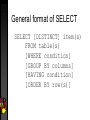
Data at the Core of the Enterprise Objectives Define of database systems Introduce data modeling and SQL Discuss emerging requirements of database systems DATA ? INFORMATION Attributes of data Sharable Moveable Secure Accurate Timely Relevant Data hierarchy Bits Characters Fields (columns) Records (rows) Files (table) Database Why build a database? Handle large amounts of data Satisfy multiple users Make information retrieval faster Make data input faster Provide greater accuracy Database versus Database Management System (DBMS) Database is a self-describing collection of integrated files A DBMS is a complex computer program that acts as a data librarian, supervising the transfer of data between the end user and the database Advantages of DBMS More info from the same data Reduction of data duplication Improved data integrity Programs are independent of the data format Sharing of data resources …and disadvantages Added expense More hardware may be needed If it crashes…. Sophisticated design and programming required Additional training Security is critical Relational model Relation? Attribute? Tuple? Keys Primary and foreign Referential integrity Relational algebra Relational DB rules Every row must have exactly the same number of columns (fields or attributes) Each row can have only one value stored in each column (fields or attributes) A column must contain the same kind of value in every row of that column No two rows can be exactly the same The order of the rows or of the columns can’t be used to provide information Terminology Data Processing Informal Relational DB Formal Relational DB File Table Relation Record Row Tuple Field Column Attribute Data modeling Purpose: control and visualization Process: gathering requirements Results: forms and diagrams Normalization Purpose: Avoid anomalies Reduce redundancy Process: Successive application of rules Bottom-up (data drives process) Move from first through fifth normal form Does it make more or less tables? Entity relationship modeling List the entities or objects in the environment People, things, transactions Describe the relationship between them A single row in table A can be related to how many rows in table B (one or many) A single row in table B can be related to how many rows in table A (one or many) ERD questions What are the subjects/objects of the business? data entities What unique characteristic(s) distinguishes each object from others of same type? primary key What characteristics describe each object? attributes How do you use this data? controls & meaning ERD questions Over what period of time are you interested in this data? cardinality & time dimensions Are all instances of each object the same? supertypes, subtypes, aggregations What events occur that imply associations between objects? relationships (cardinality & degree) Is each activity or event always handled the same way or are there special circumstances? integrity rules, cardinality, time SQL Definition (DDL) CREATE, ALTER, DROP Manipulation (DML) SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE What’s the most used sql command? General format of SELECT SELECT [DISTINCT] item(s) FROM table(s) [WHERE condition] [GROUP BY columns] [HAVING condition] [ORDER BY row(s)] Emerging data requirements Complex Video Streams Graphics Video Audio HTML/ SGML Spatial Data Time Series Unstructured Images Text Structured Audio Streams Current RDBMS Simple Summary Defined of database systems Introduced data modeling and SQL Discussed emerging requirements of database systems