* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MySQL Quick Guide - San Francisco State University
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
MySQL Quick Guide
ISYS 475
Working with MySQL
• MySQL executable is stoted in this folder:
– c:\xampp\mysql\bin
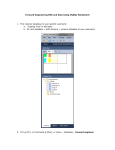
Managing MySQL using phpMyAdmin
• Start XAMPP control panel
• Click MySQL Admin button
• This will open the phpMyAdmin with the
default browser. FireFox works better
than IE.
phpMyAdmin Windows
Create a New MySQL Database: HRDB
• Add a new table: EmployeeTable
– EID
–
–
–
–
Ename
Sex
Salary
HireDate
Char 10 *** Under Index, select
Primary
VARChar 30
Char 1
Decimal and enter 10,2 for value
Date
• Enter data:
– Click the Insert button.
To Create a New Database
• 1. Click the Home button of phpMyAdmin
• 2. Click the Databases button
• 3. Enter a new database name and click Create
Add A New Table in the New Database
• 1. Click the Home button
• 2. Select the database
• 3.Click the Create Table button
Enter Data
• Click the Insert button.
• Enter data
• Click GO button
To View Data
• Click SQL button
• Enter a query
• Click GO
MySQL Command Line
• To get Windows command prompt:
– Start/Enter cmd
• Change directory to:
– C:\xampp\mysql\bin
– C:\Users\David>cd c:\xampp\mysql\bin
• Enter command:
– c:\xampp\mysql\bin>mysql -u root -p
Creating and Use a Database
• CREATE DATABASE mydb;
• USE mydb
Show
• SHOW DATABASES
– Show all databases
• SHOW TABLES
– List all tables in the default database
• SHOW COLUMNS FROM tableName
– List all columns in a given table.
Editing SQL Commands
• MySQL stores the most recent commands.
We can edit the command as follow:
– Use the Up, Down arrow key to select and
correct the command, then press Enter.
Creating Command Files
• Use a text editor to create a file with SQL
commands and save it with extension .txt
• To run the command file:
– SOURCE commandFileName.txt
• Ex: mysql> source c:\MySQLCommand.txt
Note: Use the “/” for Windows
mysql> source c:\teaching\475\ProcShowCustomers.txt;
Outfile disabled.
ERROR:
Unknown command '\4'.
ERROR:
Unknown command '\P'.
ERROR:
Failed to open file 'c:eaching\475\ProcShowCustomers.txt', error: 2
mysql> Source C:/teaching/475/ProcShowCustomers.txt;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Example of a command file
Drop table IF EXISTS customers;
Create table customers (cid char(3), cname varchar(20),city varchar(20), rating
char(1));
Insert into customers values('C1', 'MYERS','CHICAGO','A');
Insert into customers values('C2', 'GOODMAN','SAN FRANCISCO','B');
Insert into customers values('C3', 'LEE','CHICAGO','A');
Insert into customers values('C4', 'GRAUER','LOS ANGELES','C');
User-Defined Variables
• User variables are written as @var_name.
mysql> SET @t1=1, @t2=2, @t3:=4;
mysql> SELECT @t1, @t2, @t3, @t4 := @t1+@t2+@t3;
+------+------+------+--------------------+
| @t1 | @t2 | @t3 | @t4 := @t1+@t2+@t3 |
+------+------+------+--------------------+
| 1| 2| 4|
7|
+------+------+------+--------------------+
Create a New Database from a command file
using PHPMyAdmin
• 1. Click the Home button and click the Databases button; enter a new
database name and click Create.
• 2. Click the Import button and the Browse button to select the command file.
Basic Query Language Operations
•
•
•
•
Selection
Projection
Join
Aggregates: Max, Min, Sum, Avg, Count
– Totals and SubTotals
– GroupBy
• Having
• Calculated fields
Selection
• Selection operation retrieves records that
satisfy user’s criteria.
• Criteria
: >, >=, <, <=, =, <>
: Range:
odate between '2006-01-01' and '2007-01-01‘
Projection
SELECT fields FROM tableName WHERE criteria;
To eliminate duplication:
• SELECT DISTINCT fields FROM tableName WHERE
criteria;
• Field name alias: AS
• Ex: select cid as CustomerID, cname as customerName from
customers;
Natural Join
• SELECT * FROM table1 NATURAL JOIN table2;
– SELECT * FROM customers NATURAL JOIN orders;
• SELECT * FROM table1, table2 WHERE
table1.JoinAttribute = table2.JoinAttribute;
– SELECT * FROM customers, orders
– WHERE customers.cid = orders.cid;
• Table name alias:
– SELECT * FROM customers c, orders o
• WHERE c.cid = o.cid;
• Other forms:
– FROM customers c JOIN orders o ON c.cid=o.cid;
– FROM customers c INNER JOIN orders o ON c.cid=o.cid;
Aggregates
• SELECT AVG(fieldName) FROM tableName;
–
–
–
–
–
COUNT(fieldName), COUNT(*)
COUNT(DISTINCT fieldName)
MAX(fieldName)
MIN(fieldName)
SUM(fieldName)
• More than one aggregate:
• SELECT AVG(fieldName), MAX(fieldName),
MIN(fieldName) FROM tableName;
• With alias:
– SELECT COUNT(cid) AS NumberOfCustomer FROM customers;
GROUP BY
• SELECT groupingFields, function(fieldname) FROM tablename GROUP
BY groupingFields;
– SELECT cIty, count(cid) FROM customers GROUP BY city;
– SELECT city, rating, count(cid) FROM customers GROUP BY city, rating;
• Compute subtotals from a join Compute the number of courses taken by
each student:
– SELECT cid, cname, COUNT(oid)
• FROM customers NATURAL JOIN orders
• GROUP BY cid;
• Note 1: WHERE clause must come before the GROUP BY:
– SELECT major, count(sid) FROM student WHERE GPA > 3.0 GROUP BY
major;
Adding a Criteria for the Sub Totals
with HAVING
• SELECT city, count(cid) FROM customers
– GROUP BY city
– HAVING count(cid) > 5;
• Sometime the aggregates are not required to
display:
– Find majors that have more than 5 students:
– SELECT city FROM customers
• GROUP BY city
• HAVING count(cid) > 5;
Calculated Fields
• Define a calculated field:
– (salary*.15) as Tax
– (Year(Now()) – Year(DOB)) AS Age
– IF function
Calculated Field Examples
• Using functions:
– Select oid, cid, year(odate) as OrderYear from
orders;
• Using expression:
– select pid, pname,sum(qty*price) as
TotalSales from products natural join odetails
group by pid;
• Using IF function:
– SELECT pid, pname, if( price >500, 'Expensive', ‘Not
expensive' ) FROM products;
SQL Insert Command
INSERT INTO tableName VALUES (field values separated
by commas);
INSERT INTO tableName (Column names separated by
commas)VALUES (field values separated by commas);
Ex 1. Customer table with CID, CNAME, CITY, RATING.
a. INSERT INTO CUSTOMER VALUES (‘C1’, ‘SMITH’, ‘SF’, ‘A’);
b. INSERT INTO CUSTOMER (CID, CNAME,RATING) VALUES
(‘C1’, ‘SMITH’, ‘A’);
SQL Delete Command
DELETE FROM tableName [WHERE criteria];
Ex 1. Delete a record from the Customer table.
DELETE FROM CUSTOMER WHERE CID = ‘C1’;
SQL Update Command
UPDATE tableName SET field = new value [WHERE criteria];
Ex 1.
UPDATE CUSTOMER SET RATING = ‘A’ WHERE CID=‘C1’;
Ex 2.
UPDATE CUSTOMER SET CITY = ‘SF’, RATING = ‘A’ WHERE CID=‘C1’;
Practice: University Database ERD
SID
Sname
GPA
Major
1
Student
M
M
Advise
Has
Enroll
SID
1
Balance
Account
M
Grade
1
Faculty
FID
Fname
Course
Phone
CID
Units
Cname
Use SQL Statements to Answer
• Q1: Display students’ ID, name and account
balance who owe university more than
$2000.
• Q2: Display student’s ID, name and total
units.
• Q3: Find students taking at least 9 units and
display their ID, Name and total units.
• Q4: Display CID, Cname, SID, Sname
• Q5: Display CID, Cname, number of
students in each course.
• Q6: Display faculty’s name and phone if the
faculty advises at least three students.