* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 발표자료
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
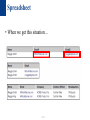
Querying the Semantic Web-SPARQL A TEAM 오혜성, 조형헌, 권윤, 신동준, 이인용 contents What is SPARQL Tell and Ask system. Development of Relational DB RDF and SPARQL Use of SPARQL 2/37 What is SPARQL SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language 3/37 What is SPARQL 1. W3C에 의해 2008년에 개발된 2. RDF 형식으로 정보가 저장된 DB에 대해 3. SPARQL endpoint를 통해 4. 검색, 조작 등의 명령을 내릴 수 있는 5. Query Language 4/37 Advantages of SPARQL 1. subject-predicate-object 의 쿼리 뿐만 아니라 key-value형식 쿼리도 가능하다. 2.쿼리만이 아니라 새로운 RDF를 구성할 수도 있다. 3.그래프패턴의 질의가 가능하다. 5/37 Tell and Ask system • TELL operation :어떠한 fact에 대해 말해준다. (Axioms, TBox, ABox, the ontology) • Ask operation :그로부터 infer 할 수 있는 것을 요청한다. (Answer = boolean or Non-boolean) 6/37 Spreadsheet • 가장 기본적 Tell-Ask 인프라 구조 7/37 Spreadsheet • When we get this situation… 8/37 Spreadsheet • When we get this situation… 9/37 Spreadsheet • How About this? 10/37 Spreadsheet • How About this? This is workable, but begins to degrade the main advantages of spreadsheet We can no longer use visualization to answer questions Relies of cross-references that are not readily visible by examining the spreadsheet 11/37 We need new system! • Advanced tell-and-ask infrastructure It should be more Structured form!! 12/37 The answer is Relational DB It provides a systematic way to link tables together!! 13/37 Relational Database • What change in it? →Represent highly structured data. →Respond to very detailed, structured questions So asking a question becomes a very detailed process 14/37 RDF as a Tell-and-Ask System • Also like a relational database, RDF requires a precise query language to specify questions 15/37 RDF as a Tell-and-Ask System • All of these questions can be asked in SPARQL 16/37 RDF as a Tell-and-Ask System • All of these questions can be asked in SPARQL 17/37 Make it Query Language • It looks like some structure… 18/37 It can be done with “SELECT” • SELECT lists of the question words we are interested in • WHERE indicates the selection pattern, written in braces 19/37 WHERE • WHERE clause can be seen as a graph pattern • Query engine finds all matches for the pattern in the data, and returns all the values that the question word matched • Query can specify a graph pattern with more than one triples • Since the variable ?what appears in both triples, the graph pattern is joined 20/37 21/37 Naming question words • English Question word ->who what where when whom etc • In SPARQL… -> Anything you want! Just Put [?] 22/37 In easy way • We can make the table by selecting descriptive question words 23/37 Query structure vs data structure 24/37 Ordering of triples in SPARQL queries • The order makes no difference to an RDF data graph • However, execution time could be affected by the order • Tip! : Order triples in a query so that the fewest number of new variables are introduced in each new triple 25/37 Other querying 26/37 Other querying 27/37 Other querying 28/37 Other querying (1.1ver) • Negation could be useful • [UNSAID] : Introduces a subgraph; the overall graph pattern will match just if the UNSAID pattern does not match 29/37 Other querying • ASK 쿼리의 TRUE/FALSE 만을 return • CONSTRUCT DB에서 뽑은 정보를 정규RDF형식에 맞춤 • DESCRIBE 결과를 RDF 그래프로 출력 30/37 Advanced Features of SPARQL • ORDER BY : 정렬순서를 속성순으로 • LIMIT : 개수 제한 • 그외 여러가지 기능 (COUNT, MIN, MAX, AVG, and SUM ) 31/37 Advanced Features of SPARQL • GROUP BY: 위의 명령어와 조합하여 그룹 별 개수, 최소 ,최대등을 구할수있다. 32/37 Advanced Features of SPARQL • HAVING: 특정 조건을 만족하는 결과만 보여준다. 33/37 Advanced Features of SPARQL • UNION: OR와 같다고 볼 수 있다. 각 조건을 만족 하는 결과들을 함께 return 한다. 34/37 Federating SPARQL Queries • We assumed that all the data triples were available in a single graph = real? • SPARQL can federate a query across more than one data source • Data sources on the Web can participate in federated query through SPARQL endpoints 35/37 Example of Federating 36/37 Summary 37/37