* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
ContactPoint wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
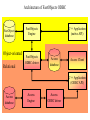
The Clash of the (database) Cultures Relational Objectoriented Two strategies in order to combine the „cultures“: (1) Relational – object-oriented Example: Fastobjects‘ ODBC interface (2) Object – relational Example: SQL 3 or SQL:2003 Object-relational databases based on SQL-3 are Complex objects partwise according to Objekt identity the Manifesto: Encapsulation P P No Types (and Classes) P Class or Type Hierarchies P Overriding, overloading and late binding No Computational completeness P Extensibility P Persistence P Secondary storage management P Concurrency P Recovery P Ad Hoc Query Facility P Examples Structures table type CREATE TYPE PersonType AS (Name VARCHAR (30), Address VARCHAR (50)) NOT FINAL; CREATE TYPE StaffMemberType UNDER PersonType AS (Salary DECIMAL (6)) NOT FINAL; Inherited type CREATE TABLE StaffMember OF StaffMemberType (REF IS oid SYSTEM GENERATED); For more details see: http://www.objs.com/x3h7/sql3.htm Table definition based on a type; insertion of an OID (2) Object-oriented database systems offer relational interfaces Example: Fastobjects‘ ODBC interface Architecture of FastObjects ODBC FastObjects database Object-oriented Relational FastObjects Engine FastObjects ODBC driver C++ Application (native API) Access database Access Client C++ Application (ODBC API) Access database Access Engine Access ODBC driver