* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Software Engineering Syllabus
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
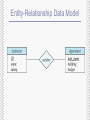
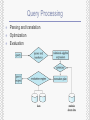
Chapter 1 Introduction Yonsei University 1st Semester, 2011 Sanghyun Park Database Management System (DBMS) Collection of interrelated data Set of programs to access the data DBMS contains information about a particular enterprise DBMS provides an environment that is both convenient and efficient to use Databases touch all aspects of our lives Purpose of Database System In the early days, database applications were built on top of file systems Drawbacks of using file systems to store data: Data redundancy and inconsistency Difficulty in accessing data Integrity problems Atomicity of updates Concurrent access by multiple users Security problems DBMS offers solutions to all the above problems View of Data An architecture for a database system Data Models A collection of tools for describing Data Data relationships Data semantics Data constraints Entity-Relationship model Relational model Other models: Object-oriented model, semi-structured data models Older models: network model and hierarchical model Entity-Relationship Data Model Relational Model Data Definition Language (DDL) Language for defining the database structure create table instructor ( ID char(5), name varchar(20), dept_name varchar(20), salary numeric(8,2) ) Execution of the above DDL statement creates the instructor table In addition, it updates a special set of tables called the data dictionary Data Manipulation Language (DML) Language for accessing and manipulating the data organized by the appropriate data model Procedural DMLs require a user to specify what data are needed and how to get those data Declarative (or Nonprocedural) DMLs require a user to specify what data are needed without specifying how to get those data It is common to use the terms query language and data manipulation language synonymously SQL is the most widely used query language Database Access From Applications Application programs are programs that are used to interact with the database Application programs are usually written in a host language, such as Cobol, C, C++, or Java Application programs generally access databases through one of: Language extensions to allow embedded SQL Application program interface (e.g., ODBC/JDBC) which allow SQL queries to be sent to a database Application Architecture Two-tier architecture: E.g. client programs using ODBC/JDBC to communicate with a database Three-tier architecture: E.g. web-based applications Overall Database System Structure Storage Management Storage manager is a program module that provides the interface between the low-level data stored in the database and the application programs and queries submitted to the system Issues Storage access File organization Indexing and hashing Query Processing Parsing and translation Optimization Evaluation Transaction Management What if the system fails? What if more than one user is concurrently updating the same data? A transaction is a collection of operations that performs a single logical function in a database application Transaction-management component ensures that the database remains in a consistent (correct) state despite system failures and transaction failures Concurrency-control manager controls the interaction among the concurrent transactions, to ensure the consistency of the database History of Database Systems (1/2) Late 1960s and 1970s Network and hierarchical data models in widespread use Ted Codd defines the relational data model (Win the ACM Turing Award for this work) (IBM Research begins System R prototype) (UC Berkeley begins Ingres prototype) 1980s Research relational prototypes evolve into commercial systems (SQL becomes industrial standard) Parallel and distributed database systems Object-oriented database systems History of Database Systems (2/2) 1990s Large decision support and data-mining applications Large multi-terabyte data warehouses Emergence of Web commerce 2000s XML and XQuery standards Automated database administration