* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Day 14:MICROSOFT access – CHAPTER 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
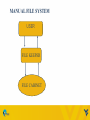
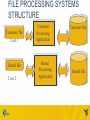
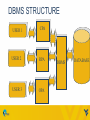
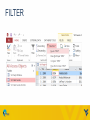
DAY 14: MICROSOFT ACCESS – CHAPTER 1 Madhuri Siddula [email protected] February 25, 2015 TOPICS • File processing system • Database fundamentals • Microsoft access MANUAL FILE SYSTEM USER FILE KEEPER FILE CABINET FILE PROCESSING SYSTEM Information stored as group of records in separate files File systems consisted of a few data files and many application programs Each file called a soft file Flat file contained the processed information for one specific function Use of programming languages to write applications FILE PROCESSING SYSTEMS STRUCTURE Customer file User 1 Rental file User 2 Customer Processing Application Rental Processing Application Customer file Rental file LIMITATION OF FILE PROCESSING SYSTEM i. Separate and isolated data ii. Data redundancy iii. Data independence for file formats and access techniques iv. Difficult in representing data from user’s view v. Data inflexibility Due to this limitations, the concept of Data base management system (DBMS) was born • A database management system (DBMS) is a software system that provides the tools to create, maintain and use a database. • Some of the databases: – MS Access – Oracle – SQL SERVER – MY SQL DBMS STRUCTURE USER 1 CPA USER 2 RPA USER 3 OPA DBMS DATABASE DATABASE FUNDAMENTALS • Database is a collection of data, organized as meaningful information. • It can be accessed, managed, stored, queried, sorted and reported. • Examples – Amazon – Telephone directory – ebay – Cs101 student files DATABASE TERMINOLOGIES Data This is the fact, or about specific entity(person,place or thing) Information Is the data that have been processed and is useful to the user Field Is a single item of information or data in entity e.g. employee name Record Is a group of fields about an entity,example Employee’s particulars FIELD • The smallest data element contained in a table • Field types: – Text – Numeric – Date • Field examples: – – – – Birthdates Last Name Age Social Security # 11 RECORD • Record – a complete set of all of the data elements (fields) about one person, place, event, or concept • Example record in a employee DB: – Name, Number, E-mail, Class, Section 12 TABLE • The foundation of every database • Contains a primary key (unique field) • Is a collection of related records – Example Table: • All Student records in my CS 101 sections would be added to my Section Roster Table during registration 13 KEY • A field that contains a unique identifier • Foreign key – A field in one table, that is a primary key in another 14 MICROSOFT ACCESS ACCESS OBJECTS • Tables, Forms, Queries, Reports, Macros Modules THINGS TO DO • Open an access file and work with content security. • Examining the access interface, views and organize information THINGS TO DO • Edit and Delete a record • Save as, compact and repair and backup the database. SORT TABLE FILTER OTHER OPTIONS • • • • Toggle filter Filter by form Load from query Save as query