* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
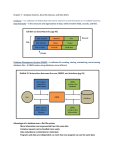
Chapter 5 Organisasi Data dan Informasi Data Data Dibutuhkan oleh seluruh perusahaan untuk menjalankan bisnis. Terdiri dari data raw, bila ditransformasi dapat menjadi informasi . Database Sekumpulan data yang diorganisir untuk memenuhi kebutuhan pengguna. Database management system (DBMS) Sekumpulan program untuk memanipulasi data data dan menyiapkan penghubung antara data base dan pengguna dengan aplikasi lainnya. DBMS ‘Discussion’ (1) Sekumpulan program yang memampukan anda menyipan, memodifikasi, dan menyaring data. Ada sejumlah bentuk, berbagai bentuk yang umum adalah sebagai berikut. computerized library systems automated teller machines flight reservation systems computerized parts inventory systems From a technical standpoint, DBMSs can differ widely. The terms DBMS ‘Discussion’ (2) relational, network, flat, and hierarchical all refer to the way a DBMS organizes information internally. The internal organization can affect how quickly and flexibly you can extract information. Requests for information from a database are made in the form of a query, which is a stylized question. For example, the query SELECT ALL WHERE NAME = "SMITH" AND AGE > 35 requests all records in which the NAME field is SMITH and the AGE DBMS ‘Discussion’ (3) field is greater than 35. The set of rules for constructing queries is known as a query language. Different DBMSs support different query languages, although there is a semi-standardized query language called SQL (structured query language). Sophisticated languages for managing database systems are called fourth-generation languages, or 4GLs for short. The information from a database can be presented in a variety of formats. Most DBMSs include a report writer program that enables you to output data in the form of a report. Many DBMSs also include DBMS ‘Discussion’ (4) a graphics component that enables you to output information in the form of graphs and charts. Hierarchy of Data Schematic Hierarchy of data Example Personel file Database Department file (Project database) Payroll file Files 005-10-6321 Johns Francine 10-7-65 549-77-1001 Buckley Bill 2-17-79 098-40-1370 Fiske Steven 1-5-85 Records 098-40-1370 Fiske Steven 1-5-85 598 Fields Fiske Characters (bytes) 1000100 (Last name field) (Letter ‘F’ in ASCII) (Personnel file) (Record containing SSN, last name, first name, date of hire) Terminology Database • Sekumpulan fifle yang terintegrasi. File • Sekumpulan catatan yang berkaitan Record • Sekumpulan bidang yang berkaitan Field • Sekumpulan karakter Character • Informasi yang terbatas dinyatakan dalam bait. Data Entities, Attributes, and Keys Entity chika • A generalized class of people, places, or things (objects) for which data are collected, stored, and maintained • E.g., Customer, Employee Attribute • A characteristic of an entity; something the entity is identified by • E.g., Customer name, Employee name Keys • A field or set of fields in a record that is used to identify the record • E.g, A field or set of fields that uniquely identifies the record Keys and Attributes Employee # Last name First name Hire date Dept. # 005-10-6321 Johns Francine 10-7-65 257 549-77-1001 Buckley Bill 2-17-79 650 098-40-1370 Fiske Steven 1-5-85 598 Key field Attributes (fields) Entities (records) The Traditional Approach The traditional approach… Separate files are created and stored for each application program Schematic Data Files Application programs Users Payroll Payroll programs Reports Invoicing Invoicing programs Reports Inventory control Inventory control programs Reports Management inquiries Management inquiries programs Reports Drawbacks Data redundancy Duplication of data in separate files Lack of data integrity The degree to which the data in any one file is accurate Program-data dependence A situation in which program and data organized for one application are incompatible with programs and data organized differently for another application Database Approach The database approach… A pool of related data is shared by multiple application programs Rather than having separate data files, each application uses a collection of data that is either joined or related in the database Schematic Payroll program Reports Inventory program Reports Invoicing program Reports Payroll data Inventory data Invoicing Data Database management system Other data Database Interface Other programs Reports Applications programs Users Advantages Improved strategic use of corporate data Reduced data redundancy Improved data integrity Easier modification and updating Data and program independence Better access to data and information Standardization of data access A framework for program development Better overall protection of the data Shared data and information resources Disadvantages Relatively high cost of purchasing and operating a DBMS in a mainframe operating environment Increased cost of specialized staff Increased vulnerability Data Modeling and Database Models (1) Planned data redundancy A way of organizing data in which the logical database design is altered so that certain data entities are combined Summary totals are carried in the data records rather than calculated from elemental data Some data attributes are repeated in more than one data entity to improve database performance Data Modeling and Database Models (2) Data model A map or diagram of entities and their relationships Enterprise data modeling Data modeling done at the level of the entire organization Entity-relationship (ER) diagrams A data model that uses basic graphical symbols to show the organization of and relationships between data Example: Entity Relationship (ER) Diagram for a Customer Ordering Database Schematic Attributes Last name Colour Entities First name Customer 1 Order N Product 1:N one-to-many relationship Identification number Identification number Name Hierarchical Database Model Hierarchical database model A data model in which data are organized in a top-down, or inverted tree structure Schematic Project 1 Department A Employee 1 Employee 2 Department B Employee 3 Employee 4 Department C Employee 5 Employee 6 Network Data Model Network data model • An expansion of the hierarchical database model with an owner-member relationship in which a member may have many owners Project 1 Department A Project 2 Department B Department C Relational Data Model Relational data model All data elements are placed in twodimensional tables, called relations, that are the logical equivalent of files Schematic Data Table 2: Department Table Data Table 1: Project Table Project Number Description Dept. Number Dept. Number Dept. Name Manager SSN 155 Payroll 257 257 Accounting 421-55-99993 498 Widgets 632 632 Manufacturing 765-00-3192 226 Sales manager 598 598 Marketing 098-40-1370 Data Table 3: Manager Table SSN Last Name First Name Hire Date Dept. Number 005-10-6321 Johns Francine 10-7-65 257 549-77-1001 Buckley Bill 2-17-79 650 098-40-1370 Fiske Steven 1-5-85 598 Relational Database Terminology Selecting Data manipulation that eliminates rows according to certain criteria Projecting Data manipulation that eliminates columns in a table Joining Data manipulation that combines two or more tables Linked Relating tables in a relational database together Linking Data Tables to Answer an Inquiry Schematic Project Number Description Dept. Number 155 Payroll 257 498 Widgets 632 226 Sales manager 598 Dept. Number Dept. Name Manager SSN 257 Accounting 421-55-99993 632 Manufacturing 765-00-3192 598 Marketing 098-40-1370 SSN Last Name First Name Hire Date Dept. Number 005-10-6321 Johns Francine 10-7-65 257 549-77-1001 Buckley Bill 2-17-79 650 098-40-1370 Fiske Steven 1-5-85 598 Building and Modifying a Relational Database Using Microsoft Access Screen snap Schemas and Subschemas Schema A description of the entire database Subschema A file that contains a description of a subset of the database and identifies which users can perform modifications on the data items in that subset Schematic DBMS Schema Subschema A User 1 Subschema B User 2 User 3 Subschema C User 4 User 5 Schema ‘Discussion’ Pronounced skee-ma, the structure of a database system, described in a formal language supported by the database management system (DBMS). In a relational database, the schema defines the tables, the fields in each table, and the relationships between fields and tables. Schemas are generally stored in a data dictionary. Although a schema is defined in text database language, the term is often used to refer to a graphical depiction of the database structure. Data Definition Language Data Definition Language (DDL) A collection of instructions and commands used to define and describe data and data relationships in a specific database Schematic SCHEMA DESCRIPTION SCHEMA NAME IS XXXX AUTHOR XXXX DATE XXXX FILE DESCRIPTION FILE NAME IS XXXX ASSIGN XXXX FILE NAME IS XXXX ASSIGN XXXX AREA DESCRIPTION AREA NAME IS XXXX RECORD DESCRIPTION RECORD NAME ISXXXX RECORD ID IS XXXX LOCATION MODE ISXXXX WITHIN XXX AREA FROM XXXX THRU XXXX SET DESCRIPTION SET NAME IS XXXX ORDER IS XXXX MODE IS XXXX MEMBER IS XXXX . . . Data Dictionary Data Dictionary A detailed description of all data used in the database Schematic NORTHWESTERN MANUFACTURING PREPARED BY: DATE: APPROVED BY: VERSION: PAGE: D. BORDWELL 04 AUGUST J. EDWARDS 3.1 1 OF 1 DATA ELEMENT NAME: DESCRIPTION: OTHER NAMES: VALUE RANGE: DATA TYPE: POSITIONS: PARTNO INVENTORY PART NUMER PTNO 100 TO 5000 NUMERIC 4 POSITIONS OR COLUMNS DATE: 13 OCTOBER Data Dictionary Features Provide a standard definition of terms and data elements Assist programmers in designing and writing programs Simplify database modification Reduce data redundancy Increase data reliability Faster program development Easier modification of data and information Logical and Physical Access Paths Logical access path (LAP) Application requires information from the DBMS Physical access path (PAP) DBMS accesses a storage device to retrieve data Schematic Data on storage devices Physical access path (PAP) DBMS Logical access path (LAP) Management inquiries Other software Application programs Manipulating Data Concurrency control A method of dealing with a situation in which two or more people need to access the same record in a database at the same time Data manipulation language (DML) The commands that are used to manipulate the data in a database Structured query language (SQL) A standardized data manipulation language Structured Query Language (SQL) “Invented” at IBM’s Almaden Research Centre (San Jose, CA) in the 1970s E.g., SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE JOB_CLASSIFICATION = “C2” Select all (“*”) columns from the EMPLOYEE table in which the JOB_CLASSIFICATION field is equal to “C2” SQL ‘Discussion’ (1) Abbreviation of structured query language, and pronounced either see-kwell or as separate letters. SQL is a standardized query language for requesting information from a database. The original version called SEQUEL (structured English query language) was designed by an IBM research center in 1974 and 1975. SQL was first introduced as a commercial database system in 1979 by Oracle Corporation. Historically, SQL has been the favorite query language for database management systems running on minicomputers and mainframes. SQL ‘Discussion’ (2) Increasingly, however, SQL is being supported by PC database systems because it supports distributed databases (databases that are spread out over several computer systems). This enables several users on a local-area network to access the same database simultaneously. Although there are different dialects of SQL, it is nevertheless the closest thing to a standard query language that currently exists. In 1986, ANSI approved a rudimentary version of SQL as the official standard, but most versions of SQL since then have included many SQL ‘Discussion’ (3) extensions to the ANSI standard. In 1991, ANSI updated the standard. The new standard is known as SAG SQL. Database Output Screen snap Popular Database Management Systems for End Users Microsoft Access 98 Lotus Approach 98 Inprise (formerly Borland) dBASE DBMS Selection Criteria • • • • • • • Database size Number of concurrent users Performance Integration Features The vendor Cost Distributed Databases Distributed database… A database in which the actual data may be spread across several smaller databases connected via telecommunications devices ‘Pretty’ picture Data Warehouse Data warehouse A relational database management system designed specifically to support management decision making Current evolution of Decision Support Systems (DSSs) Data mart A subset of a data warehouse for small and mediumsize businesses or departments within larger companies Schematic Relational databases Data extraction process Hierarchical databases Network databases Data cleanup process Flat files Spreadsheets End user access Data wharehouse Query and analysis tools Designing a Customer Data Warehouse Sharply define your goals and objectives before you build the warehouse Choose the software that best fits your goals Determine who/what should be in the database Develop a plan Measure results Data Mining Applications Data mining The automated discovery of patterns and relationships in a data warehouse Data mining applications • • • • • • Market segmentation Customer queries Fraud detection Direct marketing Market basket analysis Trend analysis On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) On-line analytic processing (OLAP) • Access to multidimensional databases providing • managerially useful display techniques Now used to store and deliver data warehouse information Data warehouse and OLAP • Provides top-down, query-driven analysis Data mining • Provides bottom-up, discovery-driven analysis Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) Open database connectivity (ODBC) • A set of standards that ensures software written to comply with these standards can be used with any ODBC-compliant database Schematic dBASE ODBC Import ACCESS database ODBC Link Lotus 1-2-3 spreadsheet ODBC Export Paradox database Object-Relational Database Management Systems (ORDBMS) Object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) • A DBMS capable of manipulating audio, video, and graphical data. Hypertext • Users can search and manipulate alphanumeric data in an unstructured way Hypermedia • Allows businesses to search and manipulate multimedia forms of data Spatial data technology • Use of an object-relational database to store and access data according to the location it describes and to permit spatial queries and analysis End of Chapter 5 Chapter 6