* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structured Database Running on Appaserver
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
ContactPoint wikipedia , lookup
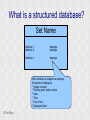
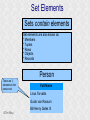
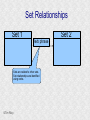
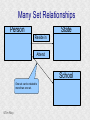
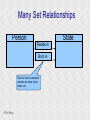
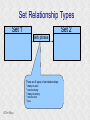
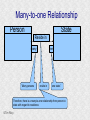
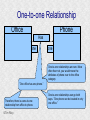
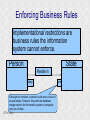
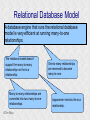
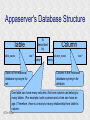
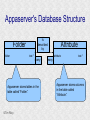
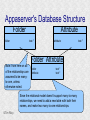
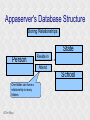
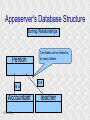
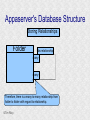
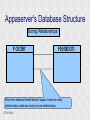
Structured Database Running on Appaserver What is a structured database? What is Appaserver? ©Tim Riley What is a structured database? Unstructured database: Do this better than Google, and you'll become a billionaire. ©Tim Riley An unstructured database is a set of documents available to a software crawler. The crawler traverses each document and makes a searchable index. Database users are presented with a text field to search for key words. Those documents deemed significant are presented to the user. What is a structured database? Unstructured database: Structured database: In a structured database, a specialist categorizes all of the organization's information into sets. ©Tim Riley What is a structured database? Set Name Every set has a name. The name should be either a noun or an event. All of the organization's persons, places, and things should be categorized. Also, all of the organization's events, starting with its transactions, should be categorized. ©Tim Riley What is a structured database? Set Name Database sets are also known as: * categories * tables * folders * collections ©Tim Riley Represent database sets in rectangles, with the set name above the title line. What is a structured database? Set Name Attribute 1 Attribute 2 … Attribute n Describe set characteristics with attributes. Attributes are used to divide a set into many subsets. ©Tim Riley datatype datatype datatype Attributes are also known as: * columns * fields * properties What is a structured database? Set Name Attribute 1 Attribute 2 … Attribute n datatype datatype datatype Each attribute is assigned a datatype. Examples of datatypes: * Integer number * Floating point (real) number * Date * Time * Line of text * Notepad of text ©Tim Riley Example Set Person full_name skin_color religion height_inches weight_pounds birth_date annual_income general_characterists These attributes help describe a person. ©Tim Riley text text text integer integer date float notepad Set Elements Sets contain elements Set elements are also known as: * Members * Tuples * Rows * Objects * Records Person There are 3 elements in the person set. Full Name Linus Torvalds Guido van Rossum Bill Henry Gates III ©Tim Riley Making Subsets Person You can divide all persons into two subsets: those named Bill Henry Gates III, and those who are not. You can divide all persons into two subsets: those making over a billion dollars a year, and those who do not. ©Tim Riley full_name skin_color religion height_inches weight_pounds birth_date annual_income general_characterists text text text integer integer date float notepad Set Relationships Set 1 Set 2 Verb phrase Sets are related to other sets. Set relationships are identified using verbs. ©Tim Riley Set Relationships Person State Reside in Sets are related to other sets. Set relationships are identified using verbs. ©Tim Riley Many Set Relationships Person State Reside in Attend School One set can be related to more than one set. ©Tim Riley Many Set Relationships Person State Reside in Born in One set can be related to another set twice, three times, etc. ©Tim Riley Set Relationship Types Set 1 Set 2 Verb phrase There are 5 types of set relationships: * many-to-one * one-to-many * many-to-many * one-to-one * is-a ©Tim Riley Many-to-one Relationship Person State Reside in many ”Many persons one reside in one state.” Therefore, there is a many-to-one relationship from person to state with regard to residence. ©Tim Riley One-to-many Relationship Person State Has resident many one Reverse the arrow to reverse the relationship. ”One state has as residents many persons.” Therefore, there is a one-to-many relationship from state to person with regard to residence. ©Tim Riley Many-to-many Relationship Person State Visit many many If you have a one-to-many relationship going both ways, then you have a manyto-many relationship. ”One person can visit many states. And one state can have as visitors many persons.” Therefore, there is a many-to-many relationship from person to state with regard to visitation. ©Tim Riley Many-to-many relationships can go both ways. ”Therefore, there is a many-tomany relationship from state to person with regard to visitation.” One-to-one Relationship Office Phone Has one one One-to-one relationships are rare. More often than not, you would move the attributes of phone over to the office category. ”One office has one phone.” Therefore, there is a one-to-one relationship from office to phone. ©Tim Riley One-to-one relationships can go both ways. ”One phone can be located in only one office.” Is-a Relationship Accountant Person Is a one ”An accountant is a person.” Therefore, there is an is-a relationship from accountant to person. ©Tim Riley one An is-a relationship is a special case of a one-to-one relationship. Is-a relationships enable inheritance to take place. An accountant inherits all the attributes of person plus has additional attributes which help to describe accountants. Enforcing Business Rules Two broad categories of business rule enforcement are: * Implementational restrictions (bad) * Integrity constraints (good) ©Tim Riley Enforcing Business Rules Implementational restrictions are business rules the information system cannot enforce. Person State Reside in many Although not common, a person could own a house in several states. However, this particular database design restricts the information system to recognize only one of them. ©Tim Riley one Enforcing Business Rules Integrity constraints are business rules the information system succeeds at enforcing. Two imperative integrity constraints are: * Relational integrity * Element uniqueness ©Tim Riley Enforcing Business Rules Relational integrity is the constraint that an element in each set must exist in order for a relationship to exist between them. Person many A person can exist without residing in a state. ©Tim Riley State Reside in one A state can exist without any persons residing in it. But both the person and the state must exist for that person to reside in that state. In practical terms, the one set must have an existing element first. For example, the state of California must first exist before assigning any persons to California. This prevents the assignment of a person to a state that does not exist, like the state of Caliifornia. Enforcing Business Rules Element uniqueness is the constraint that an element cannot exist more than once in a set. Person full_name text * Only one person named Bill Henry Gates III can belong to the person set. The set of attributes enforcing uniqueness is called the primary key. ©Tim Riley To show that an attribute has been assigned to the set of attributes enforcing uniqueness, append an asterisk. Element Uniqueness Natural primary key: the set of attributes that naturally enforce uniqueness. Person Names are likely to be naturally duplicated. If a set has more than one attribute assigned to its primary key, then it's called a multi-attribute primary key. ©Tim Riley full_name street_address Therefore, assign the street address (a place) as an additional attribute to the primary key. text * text * Element Uniqueness Primary keys naturally occur. To identify the natural primary key, always consider the four dimensions. Uniqueness can always be naturally identified with: 1) Longitude 2) Latitude 3) Elevation 4) Time ©Tim Riley All of the organization's places should be categorized. All events need a date/time stamp. Element Uniqueness Surrogate primary key: a made-up attribute used to store a sequential number to force uniqueness. Historically, the attributes assigned as the primary key must be immutable – they could not change. To accommodate this restriction, a made-up attribute was created to store a sequential number. Consider auditing transactions with customer numbers, sales-representative numbers, store numbers, and transaction codes. Sheesh! ©Tim Riley Surrogate primary keys are bad for many reasons, including: 1) They allow for natural key duplication, violating element uniqueness! 2) They require an additional level of indirection from which to audit. 3) They may inadvertently disclose the organization's volume. Element Uniqueness Mutable primary keys: The value of primary keys can change when using Appaserver. Person full_name street_address text * text * Historically, the attributes assigned as the primary key must be immutable – they could not change. However, Appaserver overcomes this restriction. Therefore, you can change the person's name if she gets married or change the street address if he moves. ©Tim Riley Structured Database Models Three of the many database models are: * Logical * Hierarchial * Relational ©Tim Riley Logical Database Model The logical database model supports all 5 relationships: 1) Many-to-one 2) One-to-many 3) Many-to-many 4) One-to-one 5) Is-a ©Tim Riley Logical Database Model One fact one place. The logical database model has no redundancy. However, no practical database engine has been developed to run the logical model. Therefore, it is used for database conceptualizing only. Once a logical model is finished, then redundancies and implementational restrictions are introduced to convert the logical model to either the hierarchial or relational model. ©Tim Riley Hierarchial Database Model A database engine that runs the hierarchial database model is very efficient at running one-to-many relationships. One-to-many relationships are easy to understand and explain to your client. You need to start with any set that you can identify a one element. Then you logically branch out. For example, a tree has one trunk. One trunk has many branches. One branch has many limbs. One limb has many leaves. One trunk has many roots. One root has many ... ©Tim Riley Relational Database Model A database engine that runs the relational database model is very efficient at running many-to-one relationships. However, many-to-one relationships are difficult to explain to your client. ”Many leaves are contained on one limb. Many limbs are contained on one branch. Many branches are contained on one trunk.” ©Tim Riley Relational Database Model A database engine that runs the relational database model is very efficient at running many-to-one relationships. But the relational model won the database model war. Therefore, Appaserver runs on a database engine that runs the relational model. ©Tim Riley Relational Database Model A database engine that runs the relational database model is very efficient at running many-to-one relationships. The relational model doesn't support the many-to-many relationship nor the is-a relationship. Many-to-many relationships are converted into two many-to-one relationships. ©Tim Riley One-to-many relationships are reversed to become many-to-one. Appaserver mimicks the is-a relationship. Relational Database Model Foreign key: in a many-to-one relationship, the many table needs to have as attributes the primary key of the one table. This adds redundancy; however, it is necessary. Person full_name street_address state text * text * many text state text * one Foreign key is the primary key of the one table. ©Tim Riley State Reside in Primary key of the one table. Foreign Key Multi-attribute Primary Key Person many full_name street_address city state City Reside in text * text * text text one city state text * text * Appaserver requires the foreign key to have the same attribute names as the corresponding primary key. Well, most of the time. ©Tim Riley Foreign Key Multiple Relationships Single-attribute Primary Key State Person Reside in full_name street_address reside_state born_state text * text * text text Born in many state text * one For multiple relationships to the same table, the foreign key can't have the same attribute name as the corresponding primary key. If the one table has a single-attribute primary key, then change each foreign key's name. ©Tim Riley Foreign Key Multiple Relationships Multi-attribute Primary Key Person City Reside in full_name street_address reside_city reside_state born_city born_state text * text * text text text text Born in many city state one If the one table has a multi-attribute primary key, then Appaserver can't handle it. ©Tim Riley text * text * Foreign Key Multiple Relationships Single-attribute Primary Key Person City Reside in full_name street_address reside_city_state born_city_state text * text * text text Born in many city_state state one If the one table has a multi-attribute primary key, then Appaserver requires you to change it to a single-attribute primary key. ©Tim Riley text * text This implemental restriction adds redundancy and the possibility of a contradiction. What is a structured database? A structured database allows you to create an information system. You create sets, attributes, and relationships so that every change in the organization's state is captured. This change in state generates a new instantaneous database. The set of instantaneous databases is an information system. ©Tim Riley What is Appaserver? RDBMS means relational database management system. Currently, Appaserver supports MySQL and Oracle. Although MySQL is much faster. ©Tim Riley What is Appaserver? Appaserver sends an HTML form to a browser, optionally through the secured socket layer. ©Tim Riley What is Appaserver? A user fills out the HTML form requesting to either select, insert, update, or delete data. However, depending upon the user's role, some operations are disallowed. ©Tim Riley What is Appaserver? After the user presses the <Submit> button, the form gets sent to Appaserver via the common gateway interface. ©Tim Riley What is Appaserver? Appaserver takes the request for either select, insert, update, or delete and generates the proper SQL statement. The SQL statement is then sent to the RDBMS. ©Tim Riley What is Appaserver? After the RDBMS executes the SQL statement, it sends Appaserver either the requested rows of data or a results message. ©Tim Riley What is Appaserver? Appaserver then generates the next logical HTML form and sends it to the browser. ©Tim Riley Appaserver is an Application Server Structured databases can grow to hundreds of tables. Each table needs the select, insert, update, and delete operation. Historically, a developer would have to write each operation for each table. On the other hand, Appaserver has a module for each operation. So development is nothing more than adding tables to the Appaserver engine. ©Tim Riley Appaserver is an Application Server Appaserver serves a relational database application to a browser. It knows how to generate the application's screens because the application's tables and columns are stored in a database itself. Appaserver has a database of the database. ©Tim Riley Appaserver's Database Structure Is described by Table table_name text * column_name many Table is the relational database synonym for set. Column many Column is the relational database synonym for attribute. One table can have many columns. And one column can belong to many tables. (For example, both a person and a tree can have an age.) Therefore, there is a many-to-many relationship from table to column. ©Tim Riley text * Appaserver's Database Structure Table Is described by many Column many ”Table” and ”Column” are reserved words. You can't create tables with these names. ©Tim Riley Appaserver's Database Structure Is described by Folder folder text * attribute many Appaserver stores tables in the table called ”Folder.” ©Tim Riley Attribute text * many Appaserver stores columns in the table called ”Attribute.” Appaserver's Database Structure Folder folder Attribute text * attribute Folder_Attribute Note: from here on all of the relationships are assumed to be manyto-one, unless otherwise noted. folder attribute text * text * Since the relational model doesn't support many-to-many relationships, we need to add a new table with both their names, and make two many-to-one relationships. ©Tim Riley text * Appaserver's Database Structure Storing Relationships State Person Reside in Attend School One folder can have a relationship to many folders. ©Tim Riley Appaserver's Database Structure Storing Relationships Person Is a Accountant ©Tim Riley One folder can be related to by many folders. Is a Teacher Appaserver's Database Structure Storing Relationships Folder Has relationship many many Therefore, there is a many-to-many relationship from folder to folder with regard to relationship. ©Tim Riley Appaserver's Database Structure Storing Relationships Folder Relation Since the relational model doesn't support many-to-many relationships, make two many-to-one relationships. ©Tim Riley What is Appaserver? Appaserver is an application server that functions as a liason between a relational database management system and a browser. It allows a database developer to focus on conceptualizing the application, not the screens. The developer uses Appaserver to create the application. The application user uses Appaserver to run the application. Creating the application involves inserting the application's tables, columns, and relations into a database. Appaserver creates screens by selecting from this database. Appaserver is committed to preserving relational integrity and element uniqueness. The critical development activity is categorizing all of the organization's information into sets. ©Tim Riley