* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Planetarium wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
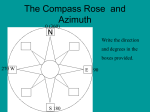
Diurnal Motion Annual Motion o Daily East / West motion of the sky Due to the Earth’s rotation (15°/hour) [360°/24 hours = 15°/hour] [1° in 4 minutes] o Stars fall into two groups Circumpolar - never rise or set Equatorial Circle going through north and south points on the horizon and the zenith Z The sky appear like a dome overhead. Zenith-directly overhead Meridian – imaginary line running north & south through the zenith Horizon – where the sky appears to intersect the ground. Altitude – height of a star above horizon (degrees). Objects on the Meridian are at their highest point in the sky (transit) Astronomical noon is when Sun is on the Meridian. Does not mean the Sun is directly overhead. Midnight is when the Sun is on the Meridian below the horizon. Sky looks like a dome with the star painted on the inside. 88 constellations such as Ursa Major, Orion, etc. Asterisms are not constellations for example the Big Dipper, the Teapot, etc. Stars are not a same distances. So, constellations are not real places. North Celestial Pole (NCP) – extension of Earth’s rotation axis onto the sky. South Celestial Pole - ditto Celestial Equator – extension of Earth’s equator onto the sky. Ecliptic – apparent yearly path of Sun. NCP Celestial Sphere Autumnal Equinox 23.5° Ecliptic Vernal Equinox SCP Celestial Equator The stars, sun, moon and planets all appear to rise in the east and set in the west. Reflection of Earth’s rotation from west to east. We live on the side of the Earth. NCP’s altitude equals your latitude. Circumpolar stars never rise or set but circle the NCP We live on the side of the Earth. Sky appears tilted at an angle equal to our latitude. Stars appear to move in arcs across the sky that are not perpendicular to horizon. The sky appears to rotate around NCP. Altitude of NCP is always equal to your latitude on Earth's surface. A space ship lands on an unknown planet. The occupants notice that the stars never rise or set but appear to move in circles parallel to the horizon. Where on the planet did the space ship land? a) At the equator. b) At 45 degrees latitude. c) At one of the celestial poles. d) Cannot be determine. Atlanta has a latitude of about 33 north degrees. The star Polaris is very close to the Celestial North Pole. What is the altitude of Polaris when viewed from Atlanta? a) 33 degrees b) 45 degrees c) 57 degrees d) 90 degrees This picture is a time exposure of the night sky showing star trails as the stars appear to rotate around the NCP. What is the name of the bright star near the center of the rock arch? Where are the circumpolar stars?