* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT file
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Indian Institute of Astrophysics wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Astrophysical X-ray source wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
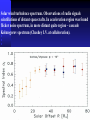
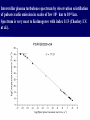
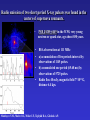
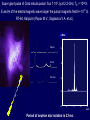
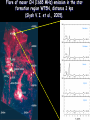
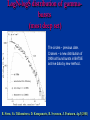
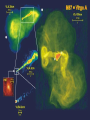
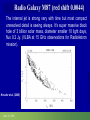
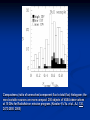
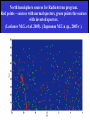
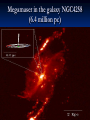
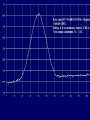
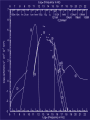
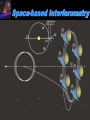
Moscow 2006 Astro Space Center P.N. Lebedev Physical Institute DCR-1000 - cross 1000х1000 m, width 40 m, range 30-120 MHz. BSA – array of 16384 dipoles,187х384 m, 16 separate beams, range 110±1 MHz. RT-64, Kalyazin RT-22, Pushchino Solar wind turbulence spectrum. Observations of radio signals scintillations of distant spacecrafts. In acceleration region was found flicker noise spectrum, in more distant quite region – cascade Kolmogorov spectrum (Chashey I.V. at collaboration). Interstellar plasma turbulence spectrum by observation scintillation of pulsars radio emission in scales of few 103 km to 1013 km. Spectrum is very near to Kolmogorov with index 11/3 (Chashey I.V. at al.). Radio emission of two short period X-ray pulsars was found in the centers of supernova remnants. • PSR J0205+6449 in the 3С58, very young neutron or quark star, age about 850 years. • BSA observations at 111 MHz • a) accumulation of five periods interval by observations of 1145 pulses. • b) accumulated one period (65.68 ms) by observations of 5725 pulses. • Radio flux 40 mJy, magnetic field 7*1012 G, distance 6.4 kps. Malofeyev V.M., Malov O.I., Malov I.F., Teplykh D.A., Glushak A.P. Super giant pulse of Crab nebula pulsar: flux 7·106 Jy at 2.2 GHz, TB = 1040 K. E and H of the electromagnetic wave larger the pulsar magnetic field H~1012 G. RT-64, Kalyazin (Popov M.V., Soglasnov V.A. et al.). 8 МЯн Радио Оптик а Рентген 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 Period of neutron star rotation is 33 ms. 6 8 мкс Flare of maser OH (1665 MHz) emission in the star formation region W75N, distance 2 kps (Slysh V.I. et al., 2005). Калязин Калязин Нансэ VLBA VLBA VLBA VLBA More 25 years of H2O space masers monitoring at 22 GHz in PRAO. It’s the most long set observations. 125 sources are in the modern list for observation once in the month. Here two type sources: super compact (~1au) gaze clouds in star formation regions and envelopes of variable late spectra classes stars. In star formation regions was found periodicity of masers variations (few years periods). This sources have usually three spectral components and probably correspondent to proto planet disks formed around proto star. It was found that variability of masers in stars envelopes strong correlate with IR and optic variation of the star at definite delay. It’s confirm a shock model, which propagates from the star across envelope. Here demonstrated a maser and optics observations in 2000-2004 of variable star в 2000-2004 гг и оптического блеска переменной звезды V391 Cyg. Delay is 100-150 days. (RT-22, LPI and SAI collaboration, Samodurov V.A. et al.). New method of Universe parameters determination by SMB analysis. Project GLESP (Gauss-LEgendre Sky Pixelization) for PLANCK mission (2007). As expected this method will be used for determination of the dark matter and dark energy, neutrino mass, Hubble constant, spectrum of density perturbation, spectrum of primordial gravity waves, parameters of secondary ionization and others with accuracy 1%. A.G. Doroshkevich, P.D. Naselsky, O.V. Verhodanov, D.I. Novikov, V.I. Turchaninov, I.D. Novikov, P.R. Christensen, L.-Y. Chiang, Inter . J. Modern Physics D (2005) Inflation stage Universe parameters determination. New model (Lambda-inflation) permit by observation data on density galactic clusters and CMB anisotropy to find limitations on model parameters and amplitudes of primordial gravitational waves (vertical axis) and spectral index density perturbations (horizontal axis). V.N.Lukash, E.V.Mikheeva, V.Muller, A.M.Malinovsky, MNRAS (2000) V.N.Lukash, E.V.Mikheeva, Inter. J. of Modern Physics A (2000) Е.В.Михеева, В.Н.Лукаш, Астроном. Журнал (2004); В.Н.Лукаш, УФН (2006) LogN-logS distribution of gammabursts (most deep set) The circles – previous date. Crosses – a new distribution of 3906 all found bursts in BATSE archive data by new method.. B. Stern, Ya. Tikhomirova, D. Kompaneets, R. Svensson, J. Poutanen, ApJ (2001) Kalyazin Radio Observatory. RT-64 beamwidths are ~11' at 1.4 GHz and ~7' at 2.3 GHz. The expected events should be near the limb of the Moon, so the pointing was at 14' apart from the center of the Moon (Dagkesamanskiy R.D. et al.). Position of the antenna beams on the Moon ARENA-2005 Detection of Ultrahigh-Energy Cosmic Rays and neutrinos by Radio Method LUNAR ORBITAL RADIO DETECTOR LPI, Lavochkin Association, MSU, IAS, JINR, ISP (Sweden) expected launch 2009 V.Tsarev, e-mail [email protected] Radio Galaxy M87 (red shift 0.0044) The internal jet is strong vary with time but most compact unresolved detail is seeing always. It’s super massive black hole of 3 billion solar mass, diameter smaller 10 light days, flux 0.2 Jy. (VLBA at 15 GHz observations for RadioAstron mission). Kovalev et al. (2005) April June11, 10, 18,2005 2005 2005 April Jansky Symposium, NRAO Blazar Variability Workshop II Arecibo Observatory Library Colloquium Compactness (ratio of unresolved component flux to total flux) histogram: the most variable sources are more compact. 250 objects of VLBA observations at 15 GHz for RadioAstron mission program. (Kovalev Yu.Yu. et al., AJ, 130, 2473-2505 2005) North hemisphere sources for RadioAstron program. Red points – sources with normal specters, green points the sources with inverted specters. (Larionov M.G. et al. 2005). (Ларионов М.Г. и др., 2005 г ). RADIO INTERFEROMETER MUCH LARGER THE EARTH “SPECTR-R” (Mission “RadioAstron”) Main scientific tasks of the mission – syntheses of high-precision images of various Universe objects, its coordinates measurements and search their variability with the time. A fringe width of the system is up to 7 micro arc seconds. Main characteristics of the space radio telescope Spectral band: wavelength (cm) 92; 18; 6.2; 1.19-1.63 frequency (GHz) - 0.327; 1.66; 4.83; 18-26 Main organizations: on scientific complex - Astro Space Center of Lebedev Physical Institute of Russian Academy of Science; of spacecraft - Lavochkin Research Production Association of Russian Space Agency. Planned launch date of the mission is 2007. The orbit of the mission : apogee 310 000 - 370 000 km perigee 10 000 - 70 000 km declination 51.6 ° period variation 7 - 10 days Guarantied time of activity 5 years Scientific payload mass 2100 kg Pointing accuracy of radio telescope - 35" OBJECTS OF EXPLORATION BY RADIOASTRON MISSION 1. GALAKTIC NUKLEI (SYNCHROTRON EMISSION, COSMIC RAYS, MEGAMASERS, BLACK HOLES, WORMHOLES, NEW PHYSICS). 2. COSMOLOGY, DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY, TIME-SPACE METRIC BY OBSERVATIONS OBJECTS AND GRAVITATION LENSES AT DIFFERENT REDSHIFTS. 3. STAR AND PLANETARY SYSTEM FORMATION REGIONS (MASERS). 4. STELLAR MASS BLACK HOLES AND NEUTRON (QUARC?) STARS. 5. INTERSTELLAR AND INTERPLANETARY PLASMA. 6. HIGH ACCURACY COORDINATE SYSTEM AND FUNDAMENTAL ASTROMETRY. 7. HIGH ACCURACY BALLISTIC AND PRECISION EARTH GRAVITY FIELD. The main expectable goals of Radioastron mission Super massive black holes in galactic nuclei: behavior of the matter near the events horizon, the structure and value of magnetic field near internal accretion disc and near black hole poles, mechanism of the relativistic particle acceleration (protons or/and electron/positron pairs, direct detection of cosmic ray acceleration sources, Blanford-Znajek or/and electric field in vacuum acceleration), evolution of this parameters in cosmological time scale and the role of normal and dark matter), super luminal motion and expansion of radio sources at different redshifts, dark matter distribution from the lensing superluminal sources, cosmological proper motions of extragalactic radio sources, black holes and neutron stars in our galaxy (a study of the energy production mechanism, determination of distance and proper motion, Galaxies gravity potential from pulsar proper motion observations, measurements of relativistic binary system orbits), interstellar plasma in Galaxy (scintillation of fringe visibility and refraction phenomena by pulsar observations), young stars and planets (a study of the structure and dynamics of the star-birth regions in galaxies by their megamaser emission, a study of young stars and protostars with protoplanetary rings in our galaxy by their maser emission), 3D Earth gravity field and fundamental astrometry with high accuracy. More than 6000 objects in total are accessible to Radioxplorations with highest angular resolution. Megamaser in the galaxy NGC4258 (6.4 million pc) РТ-70 миллиметрового диапазона на плато Суффа. Миллиметровый РТ-70. MILLIMETRON. 12 m cryogenic mirror. λ = 0,01-20 mm. Bolometric sensitivity 5*10-9 Jy (σ) (λ=0.3 mm, 1 hour int.). Space-ALMA VLBI sensitivity 10-4 Jy (σ) (λ=0.5 mm, 300 s int.), fringe size up to nanoarcseconds. Ground-space Interferometer Millimetron ALMA Suffa (Uzbekistan) Space-based Interferometry