* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Put your title in here…
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Hawking radiation wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
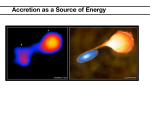
Stellar Disruptions of Super Massive Black Holes Ron Caplan March 7, 2003 Outline Overview of Black Holes The Stellar Disruption Event The Flare The Stellar Wind Core Remnants Observations When a star gets too close to a super massive black hole, it becomes disrupted causing a flare. Detecting these flares is a way to find such holes, as well as learn about them. The study of super massive black holes is important for galaxy evolution studies. Outline Structure Accretion Disruption Flare Wind Remnants Observation End Ron Caplan Black Hole Structure Space-Time Geometry How to Make a BH Event Horizon Singularity Tidal Forces Stellar vs. Super Massive Outline Structure Accretion Disruption Flare Wind Remnants Observation End Ron Caplan Black Hole Accretion Disks Outline Friction and Heat Active Galactic Nuclei Thermal Radiation Gamma-Ray Bursts Structure Accretion Disruption Flare Wind Remnants Observation End Ron Caplan The Stellar Disruption Event Velocity Dispersion – Capture of Star Inevitable Once Every 10,000 Years in an Average Galaxy ~Half of Star is Ejected, ~Half of Star is Accreted Outline Structure Accretion Disruption Flare Wind Remnants Observation End Ron Caplan The Flare Material Left from Star Forms Accretion Disk Disk Radiates Large Energies Mostly in UV – X-Ray Disk Can Last Up to a Few Years Before Being Consumed by the Hole Outline Structure Accretion Disruption Flare Wind Remnants Observation End Ron Caplan The Wind The material that gets blown off, does so at a very high velocity Energy of this stellar wind is equal to the that from a supernovae It can cause shockwaves in the surrounding ISM, as well as create shells Outline Structure Accretion Disruption Flare Wind Remnants Observation End Ron Caplan Stellar Remnants When a large red giant star is disrupted, there is a possibility its core survives, and is ejected very fast away from the galactic center This core star would be a Helium star much like a White Dwarf Outline Structure Accretion Disruption Flare Wind Remnants Observation End Ron Caplan Observations Flare Light Frequency Problem? Wind and Atmosphere to the Rescue How many?? UCSB Lubin Group Core Remnants Live Longer than Flare Harder to See – HST, Keck Very Similar to Standard White Dwarfs Circular Patterns Outline Structure Accretion Disruption Flare Wind Remnants Observation End Ron Caplan The End Any Questions?