* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Trivia Question of the Day
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
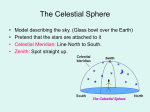
Trivia Question of the Day Astronomy Picture of the Day Lesson 6: Celestial Motions Celestial Motions: The Celestial Sphere ► Imagine all of the stars moved down onto a big glass sphere around the Earth ► Celestial sphere does NOT move ► Earth rotates counterclockwise (as viewed from above the North Pole) Celestial Motions: The Celestial Sphere ► Effect 1: Stars appear to rise in the East, move westward, and set in the West *Zenith*: The highest point in the sky that a star reaches Challenge Question Celestial Motions: The Celestial Sphere ► Effect 2: When we look up, we see the stars “fixed” on the celestial sphere AND rotating counter-clockwise Celestial Motions: The Earth’s Rotation Earth is constanty rotating, or spinning, counter-clockwise around its axis Axis: imaginary line between the North and South Poles Axis is tilted 23.5° Axis is pointed towards Polaris (North Star) Rotates 360° in 24 hours ***Challenge Question*** How many degrees is that per hour??? 15° per hour Earth’s Rotation Celestial Motions: The Earth’s Rotation *Evidence* ► 1. Foucault Pendulum When swings freely, path APPEARS to change in a predictable way Recall: Time-lapsed Motion of a Foucault Pendulum What causes this apparent change in motion? ►Pendulum swings in a fixed direction but Earth rotates under the pendulum No force is making the pendulum rotate – so it must be the Earth that is rotating!!! Celestial Motions: The Earth’s Rotation *Evidence* ►2. Coriolis Effect The deflection, or curving, of all moving objects (air, water, planes, rockets) at the Earth’s surface Caused by Earth’s surface rotating with respect to the objects ►Northern Hemisphere: Deflection to the Right ►Southern Hemisphere: Deflection to the Left In the Northern Hemisphere… In the Southern Hemisphere… Challenge Question FYI… Earth’s Rotation and Time Zones ► Time Zones Created so that each region in the world could have a standard time 24 separate time zones in 15°-wide bans exist ***Challenge Question*** Why 15°-wide bans? Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, so each 15°-wide ban has a time difference of one hour Earth’s Rotation and Time Zones Celestial Motions: The Earth’s Revolution Earth is constanty revolving, or orbiting, counterclockwise around the Sun Earth’s orbit is an ellipse ***Challenge Question 1*** What is Earth’s period of revolution? 365.25 days ***Challenge Question 2*** What does the extra .25 days result in? Leap years Earth’s Revolution Challenge Question Celestial Motions: The Earth’s Revolution *Evidence* ► 1. Seasons Caused by Earth’s tilt and Earth’s revolution around the Sun If Earth did not revolve around the Sun, the same part of Earth would tilt toward the Sun all the time Important Dates in the Northern (Southern) Hemisphere Name Dates Characteristic Summer (Winter) Solstice June 20, 21 - Most (least) hours of daylight - Sun directly over Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N) Fall/Autumnal (Spring/Vernal) Equinox Winter (Summer) Solstice Spring/Vernal (Fall/Autumnal) Equinox September 22, 23 - Equal (12) hours of day and night - Sun directly over Equator (0°) December 21, 22 - March 20, 21 - Least (most) hours of daylight - Sun directly over Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S) Equal (12) hours of day and night - Sun directly over Equator (0°) Picture Challenge Question Celestial Motions: The Earth’s Revolution *Evidence* ►2. Changing Constellations Constellations: ►A group of stars that form a pattern in the sky ►Are used to help people locate celestial objects Different constellations can be seen during each of the four seasons Celestial Motions: The Earth’s Revolution *Evidence* ► 3. Sun’s Changing Apparent Diameter As the Earth revolves around the Sun, its changing distance causes the sun’s size to APPEAR to change Sun appears largest when Earth is closest… When is That? ►January 3 Sun appears smallest when Earth is farthest away… When is That? ►July 4 Celestial Motions: The Earth’s Revolution *Evidence* ► 4. Doppler Effect of Stars As the Earth revolves around the Sun, it travels ►TOWARDS certain stars for half the year ►AWAY from those stars for the other half of the year Results in small yearly cyclic (happening on a cycle) changes in the blue- and red-shifts of starlight Celestial Motions: The Earth Challenge Questions Celestial Motions: The Earth Challenge Questions What would happen if Earth revolved around the Sun but was NOT tilted? What would happen if Earth did NOT revolve around the Sun but was tilted?