* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Relativity
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
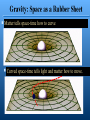
Einstein’s Universe 20th Century Physics and Relativity Late 1800s • “Many wise people believed that there was nothing much left for science to do.” • Newtonian Mechanics was mostly right, but some things turned out to be wrong: – Space and time are constant – Light travels as a wave through the “ether”, a mysterious imaginary medium – Speed of light should seem different depending on how fast you are moving Speed of light is constant • Michelson-Morley Experiment – American physicists, late 19th Century – Perpendicular beams of light bounced off mirrors Ether Time difference between paths is same, whether pointed North, South, East, or West, whether noon or midnight, spring or fall • Speed of light (c) is constant –It’s the same in ANY frame of reference Albert Einstein (1905) • Photoelectric effect – Evidence for photons • Brownian Motion – Evidence for atoms • Special relativity – Explains why speed of light is constant • General relativity (1917) – Gravity and the structure of space Special Relativity: The World of Fast Things • Based upon observation that speed of light is constant in all reference frames • The laws of physics hold true for all frames of reference (does not mean that we will get the same experimental results in differing frames) • Implications – – – – Time is not constant (time dilation) Space is not constant (length contraction) Mass is not constant E = mc2 Speed of light is constant Time is NOT constant Twin Paradox • Twins, Al and Bert, both of whom are 10 years old. • Al goes to summer camp in the Alpha-3 star system (which is 25 light-years away), at 99.99 percent the speed of light. • Bert stays home on Earth. • The trip to the star and back takes 50 years. • What happens when Al returns? • His twin brother is now 60 years old, but Al is only 10 and a half. • Has Al just discovered the fountain of youth? • Not at all. Al's trip into space lasted only a half year for him, but on Earth 50 years passed. • Does this mean that Al can live forever? • Nope. He may have aged by only half a year in the time it took 50 years to pass on Earth, but he also only lived half a year. And since time can slow down but never goes backwards, there's no way he could grow younger. Time is physically different in the two different frames of reference Time actually slows with motion but it only becomes apparent at speeds close to the speed of light. Length is NOT constant Lengths become contracted • When an object (with mass) is in motion, its measured length shrinks in the direction of its motion. • Only a person that is in a different frame of reference from the object would be able to detect the shrinking as far as the object is concerned, in its frame of reference, its size remains the same. Rulers have different lengths!!! Implication for energy • Conservation of Energy and Conservation of Mass are not exactly true, because one can be converted into the other. • E = mc2 • Radioactivity! • Implications for stars, age of earth (Chapter 10), nuclear energy Stars • The energy generated as hydrogen deep within our star continuously fuses to form helium. Earth • Einstein's formula accounts for the heat in our planet's interior, which is kept warm by a steady barrage of E = mc2 conversions occurring within unstable radioactive elements such as uranium and thorium. Nuclear energy • Fission reactors in nuclear power plants generate electricity by unlocking the energy tied up in fissionable materials. Fusion: when two hydrogen atoms fuse to form a helium atom, the mass of the resulting helium is less than the two hydrogens, with the missing mass manifesting itself as fusion energy. • Activity: How much energy is released by 1 gram of hydrogen? (1 J = 1 kg m2/s2 ) c = 3x108 m/s • How does this number compare to the energy released by 1 gallon of gasoline = 100 million J? General relativity (1917) • Gravity is caused by the bending of spacetime caused by objects with mass • A uniform gravitational field (like that near the Earth) is equivalent to a uniform acceleration. Matter tells space-time how to curve Curved space-time tells light and matter how to move. But is it real? • The Sun warps space: QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. – Mercury’s orbit inexplicable without relativity – During eclipse, apparent positions of stars near Sun different • Galaxies warp space: – Gravitational lensing (see picture at left) – bending of starlight by gravity • GPS won’t work without corrections for general relativity J. Rhoads (STScI) et al., WIYN, AURA, NOAO, NSF Einstein’s “Biggest Blunder” • His theory of General Relativity predicted that a static universe would not be stable – Universe should either expand or contract • He did not believe it. He believed in a “steadystate” (like Hutton and the mountains!) • So he put an extra piece into his equations, a “cosmological constant” to keep universe from expanding! An artificial fix! • Slipher and Hubble measured doppler shift • They found the UNIVERSE IS EXPANDING - in agreement with Einstein’s equations before the “fix”. So the fix was a major blunder.