* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Day-9
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
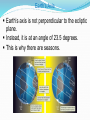
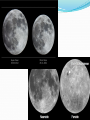
Astronomy 1010-H Planetary Astronomy Fall_2015 Day-9 Course Announcements • • • • • • SW chapter 2 – due Monday 9/21; 2pm How is the lunar observing going? How is the sunset/sunrise observing going? 1st Quarter night – Mon. 9/21 -7:30pm – on campus Exam 1: Mon. Sept. 21 This Week: APSU-OUR: Research & Creative Activity Week. Events in the library 2:30-3:30 every day. Spacecraft Reports • • • • • • • • • • • Chantal H. – New Horizons Ashley G. – Dawn Mahalia S. – NuStar Tristan C. – Mangalyaan Spencer B. – Voyager Arielle P. – Curiosity Rover Lars A. – Cassini Sarah E. – Rosetta John M. – Mars Phoenix Jordan T. – Galileo Rashun B. – Apollo Missions That Picture Question • • • • • • • • 37: <= 12hrs 14: 24 hrs 5: 10 hrs 4: 6 hrs 3: 14-16 hrs 2: “A night” 2: Answer had nothing to do with question 1: 5hr, 9.5hr, 8hr, 72 hrs,6 min, “Couple of days”, No Answer Stuff in Chapter 2 • • • • • • • • • Coordinates Position Daily Motion (spin of Earth on its axis) Visibility of the sky Year Motion (Earth orbits the Sun) Seasons (tilt of the Earth’s axis) Precession of the equinoxes Motion and phases of the Moon Eclipses Earth’s Axis Earth’s axis is not perpendicular to the ecliptic plane. Instead, it is at an angle of 23.5 degrees. This is why there are seasons. Earth’s Axis The angle of sunlight is closer to perpendicular in summer. Energy is more concentrated. The southern hemisphere is opposite the northern hemisphere. Special Days of the Year Summer solstice: Sun farthest north. Autumnal equinox: Sun on the equator, moving southward. Winter solstice: Sun farthest south. Vernal equinox: Sun on the equator, moving northward. Lecture – Tutorial Path of the Sun: pg 89 Work with a partner! Read the instructions and questions carefully. Discuss the concepts and your answers with each other. Come to a consensus answer you both agree on. If you get stuck or are not sure of your answer, ask another group. If you get really stuck or don’t understand what the Lecture Tutorial is asking, ask one of us for help. I Realize this is Like Trying to Drink from a Fire Hose Lecture – Tutorial Seasons: pg. 93 Work with a partner! Yada Yada Yada … This one is homework Stuff in Chapter 2 • • • • • • • • • Coordinates Position Daily Motion (spin of Earth on its axis) Visibility of the sky Year Motion (Earth orbits the Sun) Seasons (tilt of the Earth’s axis) Precession of the equinoxes Motion and phases of the Moon Eclipses Precession Currently, the north celestial pole is near the bright star Polaris. Earth’s axis wobbles with a period of 26,000 years. Location of the poles slowly shifts. Earth wobbles like a top, slowly. Since the axis shifts, the equator shifts. Positions of the equinoxes precess as well. Stuff in Chapter 2 • • • • • • • • • Coordinates Position Daily Motion (spin of Earth on its axis) Visibility of the sky Year Motion (Earth orbits the Sun) Seasons (tilt of the Earth’s axis) Precession of the equinoxes Motion and phases of the Moon Eclipses The Moon’s Motions Because the orbit is elliptical and not circular, the rotation speed doesn’t always match the orbital speed. The Month? Full Moon to Full Moon takes 29.53 days The Cycle of Lunar Phases