* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is light?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
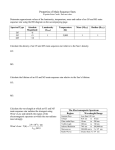
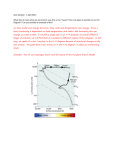
The Origin and Nature of Lecture 9 (Part I: Light and Luminosity) •What is LIGHT? •How is the Luminosity of a star related to it’s Temperature & Size [Stephan –Boltzman Law] What is light? • In the 17th Century, Isaac Newton argued that light was composed of little particles while Christian Huygens suggested that light travels in the form of waves. • In the 19th and 20th Century Maxwell, Young, Einstein and others were able to show that light behaves both like a wave and a particle depending on how you observe it. Thomas Young’s interference experiment (1801) Confirmed the wave nature of light. Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell showed mathematically in the 1860s that light must be a combination of electric and magnetic fields. In 1905 Einstein calculated the energy of a particle of light (a photon) and proposed the photoelectric effect. (Confirmed the particle nature of light.) Ephoton = hc/l or Ephoton = hf Which light is higher energy: A) Radio waves photon e- B) Ultraviolet radiation C) Yellow light D) X-rays But, where does light actually come from? Light comes from the acceleration of charged particles (such as electrons and protons) But, where does light actually come from? electron Accelerating charges produce light – electromagnetic radiation! What if all colors are combined? Speed of light = wavelength x frequency c=lf Speed of light is CONSTANT in a vacuum (space has Luminosity is the total energy (light) emitted by an object in each second. Like Watts of a light bulb. Stefan-Boltzmann law Luminosity depends on a surface area (A), and its temperature (T4) Luminosity = 5.67x10-8(A)T4 Big and ? objects have greater luminosity than __?__ Cool objects Think hot plates or burners on an electric stove! Luminosity = 5.67x10-8(A)T4 The stars Antares and Mimosa each have the same luminosity. Antares is cooler than Mimosa. Which star is larger? a) Antares b) Mimosa c) the same size d) not enough information Luminosity = 5.67x10-8(A)T4 Rigel is much more luminous than Sirius B. Rigel and Sirius B have the same temperature. Which star has the greater surface area? a) Rigel b) Sirius B c) the same 2) You observe two stars with the same luminosity and determine that one is larger than the other. Which star has the greater temperature? a) the smaller star b) the larger star c) The temperatures are the same. You observe a very large and very hot star in the constellation Orion. On the same night, you observe another star in Orion that is much smaller but has the same temperature. Which star is more luminous? a) the larger star b) the smaller star c) They have the same temperature. d) There is insufficient information to determine this. Which star is Hot and Dim? Below we are building a “Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram”… 10,000 A D 1,000 100 10 C 1 .1 .01 B E .001 .0001 20,000 10,000 Temperature (K) 5,000 Which star is Cool and Dim? 10,000 A D 1,000 100 10 C 1 .1 .01 B E .001 Temperature (K) .0001 20,000 10,000 Temperature (K) 5,000 Which star is Largest? 10,000 A D 1,000 100 10 C 1 .1 .01 B E .001 Temperature (K) .0001 20,000 10,000 Temperature (K) 5,000 Which star is smallest? 10,000 A D 1,000 100 10 C 1 .1 .01 B E .001 Temperature (K) .0001 20,000 10,000 Temperature (K) 5,000