* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Orbits
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy satellite wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
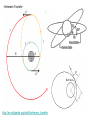
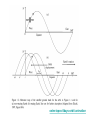
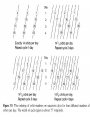
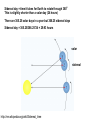
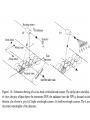
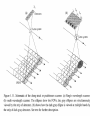
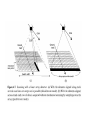
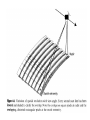
Remote Sensing of the Ocean and Atmosphere: John Wilkin [email protected] IMCS Building Room 214C 732-932-6555 ext 251 609-933-7753 (cell/txt) Orbits and Measurement Geometry (1) Johannes Kepler (1571 – 1630) German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer 1. Planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun as one focus 2. the radius vector from the sun to the planet sweeps out equals areas in equal times 3. T2 : R3 ratio is constant for all planets, where T is orbital period and R is semimajor axis of the orbit Isaac Newton (1643 - 1727) English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, theologian) 1. Newton discovered the laws of gravitation and explained planetary and satellite orbits in terms of the balance of forces: 2. Centripetal acceleration F ma m 3. Gravity Fgravity dv dt GMm r2 Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642) Italian physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher Galileo's pupil Vincenzo Viviani stated that Galileo had dropped balls of the same material, but different masses, from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to demonstrate that their time of descent was independent of their mass. This was contrary to what Aristotle had taught: that heavy objects fall faster than lighter ones, in direct proportion to weight. There is no account by Galileo himself of such an experiment, and it is generally accepted that it was at most a thought experiment which did not actually take place. Epoch (UTC): 10:07:53 AM, Monday, January 28, 2008 Eccentricity: 0.0005362 Inclination: 51.6418° Perigee Height: 334 km Apogee Height: 341 km Right Ascension of Ascending Node: 22.2238° Orbit Number at Epoch: 52631 Revolutions per Day: 15.77540422 Nov 5, 2007 view from Space Shuttle Remote Sensing of the Ocean and Atmosphere: John Wilkin [email protected] IMCS Building Room 214C 732-932-6555 ext 251 or 609-933-7753 (cell) Orbits and Measurement Geometry (2) Stewart, R. H., 1985, Methods of Satellite Oceanography, University of California Press, 360 pp. Right ascension - declination coordinate system First Point of Aries: One of the two points on the Celestial Sphere where the Ecliptic and the Celestial Equator cross one another. Ecliptic: An imaginary line that approximates the plane in which the planets (other than Pluto) orbit the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the planets and the Sun will always remain close to this line. When the Sun reaches the First Point of Aries, as it does once each year, an equinox occurs. (Northern hemisphere Vernal Equinox) The First Point of Aries, which is actually in Pisces, defines the zero-point for Right Ascension. Right ascension: the celestial equivalent of longitude (starting at the First Point of Aries) Declination: the celestial equivalent of latitude The celestial north pole is at declination +90 http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/realdata/elements See graphics of orbital elements and data for ISS Jason-1 launch from Vandenburg Air Force Base, California Orbit: http://www.aviso.oceanobs.com/en/missions/current-missions/jason-1/orbit/index.html Launch: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z4WHOSF2Ktg Other launches: Delta-II (Themis): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p_pAhPecto0 Ariane launch failure: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kYUrqdUyEpI Jason-2 OSTM http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cf0loVEs_lo Topex/Poseidon launched with Ariane rocket http://sealevel.jpl.nasa.gov/gallery/tiffs/videos/launch.mov Pegasus vehicle aircraft launch http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QRHiTvRHHd8 OSTM / Jason-2 Boost Profile Space craft separation: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1aBpcCVljt4 Hohmann Transfer Maneuver to different inclination http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hohmann_transfer http://www.nytimes.com/2007/02/06/science/space/06orbi.html?emc=eta1 On Jan 11, 2007, China tested an antisatellite rocket. The initial collision added 800 to 1000 pieces of space junk to the current total of detectable objects. How many detectable objects (> 4 inches) are in orbit? Collisions between existing debris generate additional pieces of debris. There is concern that eventually a chain reaction will ensue (the Kessler syndrome) littering the low earth orbit (LEO) with debris making it almost impenetrable to new satellite launches for fear of collision. http://www.nytimes.com/2007/02/06/science/20070206_ORBIT_GRAPHIC.html Kessler, D. J., and Burton G. Cour-Palais. "Collision frequency of artificial satellites – The creation of a debris belt." Journal of Geophysical Research Vol. 83 (June 1978): 2637-2646. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/realdata/elements See graphics of orbital elements and data for ISS ostm-topex-5days-orbit animation SeaWiFS daily coverage seawifs_daily_coverage animation Is this orbit prograde or retrograde? Terra satellite, MODIS instrument, coverage of all instrument swaths during a single day ( 01/28/2006 ) Jason altimeter satellite ENVISAT 35-day repeat Equatorial separation of Jason groundtracks is 315 km Sidereal day = time it takes for Earth to rotate through 360o This is slightly shorter than a solar day (24 hours) There are 365.25 solar days in a year but 366.25 sidereal days Sidereal day = 365.25/366.25*24 = 29.93 hours solar sidereal http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sidereal_time Scan geometry • zenith angle w.r.t. satellite nadir • look angle and solar zenith angle w.r.t local vertical • Fixed solid angle Field of View (FOV) such as for an optical lens, gives elliptical footprint off-nadir and varying spatial resolution in the scan View satellite orbits and ground tracks at: http://science.nasa.gov/realtime/jtrack/Spacecraft.html Internet resources on orbits and satellites • http://science.nasa.gov/realtime/jtrack/Spacecraft.html Shows ground tracks and 3-D orbits for all satellites – Notice the clusters of satellites in the major categories or orbits • • • • Geostationary Polar orbiting (NOAA, Topex, ERS, Envisat) Low Earth orbit (Iridium, HST, ISS) GPS – Unusual orbits (especially ground track) • Chandra • IMAGE • CRRES (in a geosynchronous transfer orbit) • http://heavens-above.com Shows predicted orbits and visibility magnitudes and star charts of pass trajectories for all satellites – See Homework 1 • http://tinyurl.com/11-670-451-homework-1 http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/realdata/elements – See graphics of orbital elements and data for ISS • Real-time satellite tracking at http://www.n2yo.com