* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Report
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Expression Evaluating
Calculator
Jagadish Rath(2003cs10164)
Dhanshree Nimje(2003cs10160)
Group 4
Instructor: Prof. M.Balakrishnan
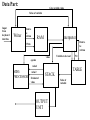
Specifications:
KeyBoard
Interface
Input data
sequence
Restart
evaluation
Digital
Output Data
corresponding to the
input expression and
evaluated value
Calculator
LCD
Display
Reset
Block Diagram of the model
The Digital Calculator takes as input an expression containing
constants(Integer and boolean) ,variables and operators,and evaluates the
expression.While evaluating the expression if it finds a variable which is not
assigned a value, it asks for the value and then gives as output the evaluated
value of the expression.
User Interface:
The user can give the input expression as a sequence of pre-decided
characters from the FPGA keyboard and can see the input expression,the
variable assignment prompt and the evaluated value of the expression on the
LCD Display in FPGA board.
The concrete syntax for the language is given in the next page.
All the expressions involving operators has to be given in postfix notation with
the operands represented as tuples followed by the operator
e.g.
The concrete syntax for 123+ 45 is (123,45)+;
And input sequence is
#*0*1*2*3#*2*4*5#*1#*#0#*3
There will be two inputs from the pushbutton
1.evaluate or re-evaluate an already input expression
2.reset the whole calculator
Syntax
Meaning
Displayformat
*a*b*c*d
number abcd (0<= a,b,c,d <= 9)
abcd
#N
variable numberd N(maximum 10
variables are allowed
the nth in the set {a to j}
#*#N
an operator depending on
N=
*#N
#*N
0 integer addition
+
1 Integersubtraction
-
2 integer multiplication
*
3mod
%
4 integer division
/
5 greaterthan
>
6 boolean and
^
7 boolean not
!
8 boolean or
V
9 equality
=
Boolean value
N= 0 false
N=1 true
F
T
N=0 open parentheses
N=1 closedparentheses
N=2 comma
N=3 end of expression
(
)
,
;
Main-Macros of the Digital Calculator:
1.Keyboard Interface
2.Writer: State Machine which writes into a RAM
3.RAM : It stores the data of the expression
4.Interpreter: State Machine which reads the RAM and generates
corresponding opcodes (for operators),binary number (for integers which are
stored in BCD format in RAM),binary digit(1,0 for boolean constants true,false
respectively).While reading the RAM if it finds a variable it looks for its value
in the TABLE. If it does not find a value for the variable,then it asks for it(which
is displayed on the LCD screen) and then takes the input through Writer and
updates the TABLE.If it finds a value then it generates the binary of the value.
5.TABLE:it is a RAM which stores the value corresponding to the
variable(numbered n) in the nth row.
6.STACK: It is a RAM which has the values corresponding to the expression
evaluated till now.
What ever value is generated by the Interpreter is stored in the stack.When an
opcode is produced by the Interpreter,according to the arity of the operator
corresponding to the opcode those many values are taken from the STACK and
passed on to the MINI-PROCESSOR .
7.MINI-PROCESSOR:It evaluates the values and operator given to it and returns
back the result to the STACK which is then pushed into the STACK.
8.OUTPUT UNIT: uptill the evaluation continues it outputs the data
corresponding to the Input expression to the LCD Display.After completion of
evaluation the result from top of STACK is output to the LCD display.
Data Part:
Give variable value
Value of variable
Input
from
keyboard
interface
Writer
Data to
be
written
RAM
Interpreter
Data to
be
written
Write
opcode
value
Variable to be read
value1
MINIPROCESSOR
value2
Evaluated
value
Wr
TABLE
STACK
OUTPUT
UNIT
Value of
variable
Writer: state diagram
Inputs:star,hash,clk,clear outputs:clstar,clhash,write,ds(6)
States:s0(intial),s1,s2,s3,s4,s5 DefaultOutputs:clstar=1,ds=000001,clhash=0,write=0
s0
*All the transitions
are at rising clk
edge
star
hash
clear
S1
ds=000010,
clstar, write
clear
clear
S3
clear
ds=001000,
clhash, write
clear
star
hash
S5
S2
ds=000100,
clhash, write
ds=100000,
clstar, write
S4
ds=010000,
clhash, write
hash
Simulation Results:
RAM:
The RAM has a word length of 6 and depth 256.Hence the maximum
number of characters that can be stored or evaluated is 256.
Format of storing data:
The 1st two columns say either the data stored is a digit,boolean ,
operator,variable,or special characters
Nature of data
R5 R4 R(3-0)
Digit
0 0
Variable
0 1
value of digit
no of the variable
Operators
10
value of the input key
(
10
1010
)
10
1011
,
10
1100
;
10
1101
Boolean
11
value of the input key
Interpreter:
MINI-PROCESSOR:
The opcodes of any operator is same as the value stored in the
RAM at locations R(3-0) .any other value of the operator is
considered as a nop. When the opcode corresponds to
multiplication or division or mod the complete signal becomes 1
after the operation is complete. Else the complete is always 1.
Components of the MINI PROCESSOR:
1.
DECODER decodes the opcodes
---loader-loads the argument values into the input regesters of
Multiplier and divider
1.
ADDER/SUBTRACTOR does the addition and subtraction
2.
MULTIPLIER does the multiplication
3.
DIVIDER/MOD does the division and mod operation
4.
COMPARATER does the equality and greaterthan check
5.
AND ,OR,NOT
6.
Output multiplexer:outputs the output of appropriate block to output depending
on the opcode
7.
Complete generator : generates the complete signal
Components in the MINI-PROCESSOR:
Add/sub
decoder
multiplier
Divider/mod
loader
comparator
completegenerator
Output multiplexer
Select signal for output mux
possible extensions:
Possible extension:
1.The model can be extended to operate for sequencing of
expressions.
2.The current model is for fixed no of variables it can be
extended for any number of variables.
3. conditional operations like ifthenelse,while,case
operations like exponentiaton,logarithm,trigonometric
functions,real number operations can be included in the
language.
4.The model can be made more user friendly by taking input
from the keyboard of PC.