* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Renal artery
Intersex medical interventions wikipedia , lookup
Human penis wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Kidney stone disease wikipedia , lookup
Kidney transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Interstitial cystitis wikipedia , lookup
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
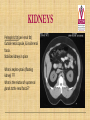
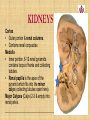
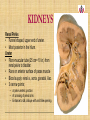
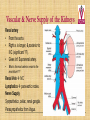
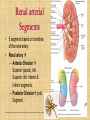
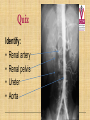
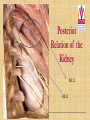
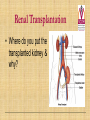
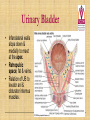
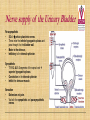
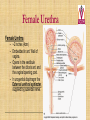
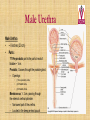
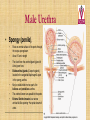
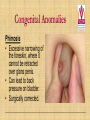
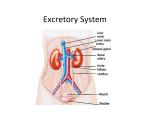
Kidneys, Ureters and Bladder Ahmed Abdellatif, MD, PhD. Objectives Describe/demonstrate the anatomy of: • Kidney, Ureters, & Bladder. • Urethra (male & female). • Clinical correlation. KIDNEYS & SUPRARENALS Anatomy of the Kidneys - Retroperitoneal. - Obliquely situated, long axis parallel to lateral boarder of psaos major. - Hilum faces forward & Medial & is posterior to; on right side 2nd part of duodenum, & on left tail of pancreas. - Kidney measures 12X6X3 cm. - Right kidney lower, why? - Fibrous capsule gives shiny appearance to the kidney. - Perinephric fat (peri-renal fat) - Renal fascia, surrounds the perinephric fat, separates kidney from suprarenal glands. KIDNEYS Perinephric fat (peri-renal fat) Outside renal capsule, & inside renal fascia. Stabilizes kidneys in place What is nephro-ptosis (floating kidney) ??? What is the relation of suprarenal glands to the renal fascia?? KIDNEYS Cortex • Outer portion & renal columns. • Contains renal corpuscles Medulla • Inner portion, 8-12 renal pyramids contains loops of henle and collecting tubules. • Renal papilla is the apex of the pyramid which fits into the minor calyx (collecting tubules open here). Major Calyces (Calyx) 2-3 & empty into renal pelvis. KIDNEYS Renal Pelvis • Funnel shaped, upper end of ureter. • Most posterior in the hilum. Ureter • Fibro-muscular tube (25 cm= 10 in.) from renal pelvis to bladder. • Runs on anterior surface of psoas muscle • Blood supply: renal a., aorta, gonadal, iliac. • 3 narrow points; – at pelvi-ureteric junction – At crossing of pelvic brim. – Entrance to UB, oblique with a slit like opening. Ureter • • • • • Enter the pelvis over the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. Left: runs posterior to sigmoid colon. Right may run next to appendix. At level of ischial spine, turns anteriorly. Male; ductus differens crosses the ureter (Water goes under the bridge). Female ureter; – – – – – Runs in base of broad lig., Crossed by the uterine artery, Close to lateral cervical ligament Ureter crosses lateral fornix. AT RISK during hysterectomy ????? Cases • Mrs. Smith goes into postpartum hemorrhage that requires hysterectomy to control the bleeding, after returning home a couple of days later she starts to notice clear fluid soiling here pads. Her doctor explained to her that she may need another surgery to correct a fistula between her vagina and one of the ureters. • Following a hysterectomy to remove a tumor of the uterus, the nurse alerts the doctor that Mrs. Smith’s urine bag is empty, she tells the doctor there is no urine coming out !!! Vascular & Nerve Supply of the Kidneys Renal artery • From the aorta • Right a. is longer, & posterior to IVC (significant ??). • Gives Inf. Suprarenal artery. • What is the most anterior vessel in the renal hilum??? Renal Vein IVC Lymphatics para-aortic nodes. Nerve Supply Sympathetics, celiac, renal ganglia. Parasympathetics from Vagus. Renal arterial Segments • 5 segments based on branches of the renal artery. • Renal artery – Anterior Division Superior (apical), Ant. Superior, Ant. Inferior & Inferior segments. – Posterior Division post. Segment. Quiz Identify: • Renal artery • Renal pelvis • Ureter • Aorta Quiz 1.________ 2.________ 3.________ 4.________ 5.________ 6.________ 7.________ 8.________ Case • Following Surgery to remove a huge kidney stone, Mr. Smith suffered from severe shortness of breath, clinical examination and radiology revealed a diagnosis of pneumo-thorax. Why????? Posterior Relation of the Kidney Rib 11 Rib 12 Renal Transplantation • Where do you put the transplanted kidney & why? Urinary Bladder • • • • Pyramidal (3 sided) shape (ovoid when distended). Superior surface is covered with peritoneum. Full bladder peels the peritoneum off the posterior rectus sheath. Apex points anterior above symphysis pubis. Median Umbilical ligaments (Urachus) attaches to apex. Base, triangular, posterior, – – • • No peritoneal covering (except top part in male), anterior to rectum. In females anterior to cervix and anterior vaginal wall. Lowest part of base is trigone. 2 Infero-lateral walls. Neck, inferior, urethra opens here. Urinary Bladder • • Inferolateral walls slope down & medially to meet at the apex. Retropubic space; fat & veins – – • • Female; Pubovesical ligament. Male; Puboprostatic & pubovescical ligaments Median umbilical ligament, from apex the umbilicus (urachus). Lateral umbilical ligaments, superior surface umbilicus (obliterated umbilical arteries). Case Umbilical Ligaments • Median umbilical lig. • Medial umbilical lig. • Lateral umbilical folds Which one of these ligaments/fold is responsible for urine coming out of the “belly button” in the previous case? Urinary Bladder • Inferolateral walls slope down & medially to meet at the apex. • Retropubic space; fat & veins. • Relation of UB to levator ani & obturator internus muscles. Trigone • • • • • • Triangular area at base of UB Smooth wall; Structure & embryology different from UB. Least mobile part of the UB, Fixed with fibrous tissue to pelvic fascia. The two ureteric opening are connected at top of trigone by the inter-ureteric ridge. Ureteric openings are slit like, ureters enter UB oblique. Internal urethral sphincter; – – Male, circular muscle fibers at the internal urethral opening Female, longitudinal muscle fibers NO internal sphincter. Why?????? Posterior relation of bladder in Male • Seminal vesciles • Ductus deferens & ampulla • Ejaculatory ducts – Embedded in the prostatic tissue – These are the junction and union of the ampulla of the ductus deferens on one side and the tube of the seminal vesicles on the other side • Prostate – Sits underneath bladder Nerve supply of the Urinary Bladder Parasympathetic • S 2-4 pelvic splanchnic nerves. • These enter the inferior hypogastric plexus and pass through it to the bladder wall. • Motor to the detrusor, • Inhibitory to the internal sphincter. Sympathetic • T 11-12 & L1-2 segments of the spinal cord superior hypogastric plexus. • Constriction in the internal sphincter • Inhibit the detrusor muscle. Sensation • Distension and pain. • Via both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. Control of Micturition • Parasympathetic Pee • Sympathetic STOP no pee Female Urethra Female Urethra – ~2 inches (4cm) – Embedded in ant. Wall of vagina. – Opens in the vestibule between the clitoris ant. and the vaginal opening post. – In urogenital diaphragm the External urethral sphincter, supplied by pudendal nerve. Male Urethra Male Urethra • ~ 8 inches (20 cm) • Parts: ?? Pre-prostatic part is the part at neck of bladder ~ 1cm. Prostatic; Crosses through the prostate gland. – Openings: • • • (1) the ejaculatory ducts, (2) Prostatic ducts, (3) Prostatic utricle. Membranous, 1- 2 cm, passing through the external urethral sphincter. – Narrowest part of the urethra. – Located in the deep perineal pouch. Male Urethra • Spongy (penile), • • • • • • • Runs on ventral surface of the penis through the corpus spongiosum. About 15 cm in length The ducts from the urethral gland (gland of Littre) open here. Bulbourethral glands (Cowper's gland) located in the urogenital diaphragm & open in the spongy urethra. May be subdivided into two parts, the bulbous and pendulous urethra. The urethral lumen runs parallel to the penis External Urethral meatus is a narrow vertical slit-like opening a spiral stream of urine. Congenital Anomalies Hypospadius • External urethral opening is abnormally located on the underside (ventral) of the penis, even in the scrotum, or sometimes perineum. Epispadius • Opening is located on the upper side of penis. Stricture/stenosis (narrowing) of the external urethral meatus. Congenital Anomalies Phimosis • Excessive narrowing of the foreskin, where it cannot be retracted over glans penis. • Can lead to back pressure on bladder. • Surgically corrected.