* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download West 11 orientation - Children`s Hospital of Wisconsin
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Harm reduction wikipedia , lookup
Child migration wikipedia , lookup
Transnational child protection wikipedia , lookup
Child protection wikipedia , lookup
Unaccompanied minor wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
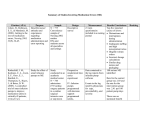
Welcome to West 11 and Medication Administration Summer, 2014 Clinical Practicum MSOE West 11 • 24-bed acute care unit • general medical patients • Specialties: – gastroenterology – endocrine/diabetes – cystic fibrosis – pulmonary – adolescent eating disorders – failure to thrive A little about you: • • • • • • • Name/nickname What is your favorite TV show What are your past times One thing that no one knows about you Why become a nurse What is your experience with kids/families Area of interest; plans after graduation Let’s Talk Pediatrics • What excites you about this clinical rotation? • What frightens you about this clinical rotation? • What have you heard about Children’s Hospital? • What questions do you have? Pediatric Considerations – – – – – – – – Greater percent of total body weight is water Greater insensible loss Greater potential for dehydration Infants have decreased ability to concentrate urine More susceptible to fluid/electrolyte shifts Decreased glycogen storage Higher metabolic rates Drugs metabolize at different rate than adults Tips for Pediatric Assessment – Varies with child – Approach slowly – Non-invasive assessment FIRST and involved system LAST – Allow child to play with equipment – Do procedures on toys or parents first – Save intrusive procedures for last Do as much as possible with the child being held by parent – Give kids toys to play with during history-taking time – Make assessment a game – Get down to child’s level – Ask history questions of child, if old enough – If directions necessary, keep them simple – Use praise – Use distraction Initial Assessment Impression – Facial expression – Posture – Activity level/behavior – Skin assessment – Overall state of health – ‘gut feeling’ Hydration Status – Weight – Mucous membranes – Skin turgor – Tears – Urine output – Fontanel – History: vomiting, diarrhea, etc. Metrics • Pediatric fluids and medication doses are calculated by weight in kilograms • Patient’s weight - kilograms BUT parents often do not know what this means • Need to be able to convert to pounds for the family • Conversion: 2.2 lb = 1 kg Calculations • Child weighs 88 lbs, what is the weight in kg? 88 lbs divided by 2.2 kg = 40 kg • Child weighs 22 kg, what is the weight in pounds? 22 kg times 2.2 lbs – 48.4 lbs • Child weighs 6 lbs what is the weight in kg? 6 lb divided by 2.2 kg = 2.72 kg Fluid Maintenance • Critical: Must know your child’s fluid maintenance • Includes IV and oral/GT/JT intake • Hourly documentation of fluid intake (IV, po, g-tube, j-tube) is required • Fluids used to administer IV medications must be included in the hourly fluid volumes Fluid Maintenance MUST BE DONE on all kids!! Daily Fluid Maintenance < 10 kg 10 – 20 kg 20 kg 100 ml/kg 1000 ml + 50 ml/kg 1500 ml + 20 ml/kg Hourly Fluid Maintenance < 10 kg 10 – 20 kg > 20 kg 4 ml/kg 40 ml + 2 ml/kg 60 ml + 1 ml/kg Let’s work out daily fluid needs Daily Fluid Maintenance 8.2 kg child: 8.2 kg x 100 cc = 820cc/Day 12.6 kg child: 10 kg x 100 cc = 1000cc Plus: 2.6 kg x 50 cc = 130 cc Total: 1130cc/day 28.2kg child: 10 kg x100 cc = 1000cc Plus: 10 kg x 50 cc = 500 cc = 1500 cc Plus: 8.2 kg x 20 = 164 cc = 1164 ml Total: 1664 cc/day (Hourly total: total fluids/24) Let’s work out hourly fluid needs Daily Fluid Maintenance 8.2 kg child: 8.2 kg x 4 ml = 32.8 ml/hour 12.6 kg child: 10 kg x 4 ml = 40 ml Plus: 2.6 kg x 2 ml = 5.2 ml Total: 45.2 ml/hour 28.2kg child: 10 kg x 4ml = 40 ml/hour Plus: 10 kg x 2 ml = 20 ml = 60 ml/hour Plus: 8.2 kg x 1 = 8.2 ml = 68.2 ml/hour Total: (per day-> hourly fluids x 24) Practice Scenario • Marisa is a 10 year old admitted to the unit with pneumonia. She weighs 80 lbs. • What is her weight in kilograms? • What is her hourly fluid maintenance requirements? • What is her daily fluid maintenance requirements? 80 lbs - using daily fluid equation 80 lbs/2.2 kg = 36.4 kg First 10 kg = 1000 ml Second 10 kg = 500 ml Remaining: 16.4 kg x 20 = Fluid maintenance/day = 1000 ml + 500 ml + 360 ml 1860 ml/day Fluid maintenance/hour->1860/24=77.5 ml/hour 80 lbs - using hourly fluid equation 80 lbs/2.2 kg = 36.4 kg First 10 kg = 4 ml 40 ml Second 10 kg = 2 ml x 10 + 20 ml Remaining: 16.4 kg x 1ml + 16.4 ml Fluid maintenance/day = 76.4 ml/hour Fluid maintenance/day ->1834 ml/day Some more practice Calculate the daily and hourly fluid maintenance • 4.8 kg • 222 pounds • 34.5 kg • 18.2 pounds • 16.2 kg What information is unique to pediatrics? • • • • • • Fluid Maintenance Medications: safe dose, safe calculations, IV: dilution, safe range, infusion time Policy and Procedures Growth and Development Teaching strategies Drug dosing in infants and children • Doses based on weight • Accurate drug dose is critical since infants/children do not have the mature physiological responses to compensate for drug errors General guidelines for administration of medications to pediatric patients • Growth and development – Developmental age = functional level of the child. – Strategies consistent with the child's developmental level -> to ensure safe and effective medication administration. – Assessing the child's temperament can led to determining best method of administering a medication. • Honesty, reward, and praise help to gain trust and cooperation • Ask parent or other staff member to assist • Provide rewards for good behavior and for trying Strategies for Medicating Children Infants Toddlers Preschoolers School-age Adolescents Cuddle and comfort Use play, minimize restraint, give praise and stickers as rewards Offer choices Provide choices, explanations, distraction, and support Explain, allow participation in decisions, praise cooperation, provide outlet for frustrations HONESTY, REWARD, & PRAISE ARE KEY! BEFORE giving a med MUST know • • • • • • • Generic & brand name of drug Action of drug Reason child is receiving med Recommended safe dosage Common side effects Nursing implications Teaching implications for family Oral Medications • Infants – may take liquid med out of nipple, oral syringe, or medication dropper. • Toddlers & Preschoolers – may use oral syringe, dropper, or medication cup. • Pre-school & School-age – may use chewable tablet “He spit it up” = notify the physician BEFORE giving another dose! Need to remember the basics. • • • • 1 teaspoon = 5 ml 1 tablespoon = 15 ml 1 ounce = 30 ml 1000 mg = 1 gram Medication Safety • Where do I find medication calculation info: – Safe dose range – Dilution infusion – Time to infuse – Compatibility • LexiComp drug book • Drug Handbook • • • • • • • • • SAFETY Increased opportunities for error -> weight-based dosing for all medications Potential for more serious consequences: limited reserves of smaller children. Most recognized errors>computation of dosage; dosing interval; transcription of drug orders ; drug preparation or conflicts with prescribed dosages Children are at particular risk for these errors -> dosage individualization requiring dosage equations. Dosages calculated on weight ->significantly different from adults. Computation error can result in a significant under or over-dosage. ‘ten-fold’ error (e.g., a misplaced decimal point can mean a ten-fold change in the appropriate dosage of medication) One example: Jose Eric Martinez; ill two-month-old with signs of CHF MD ordered IV Digoxin; a decimal point error in calculating appropriate dosage -> infant given dose that was 10 times safe dose -> cardiac arrest and child died • AS THE NURSE YOU ARE THE LAST PERSON TO ENSURE THE SAFE DOSE BEFORE THE PATIENT RECEIVES THE MEDICATION – • HUGE RESPONSIBILITY NEED TO READ CAREFULLY • Read the medication information carefully – – – – – Some are the dose ranges are for 24 hours Some are the dose ranges are for q 8 hours Some are the dose ranges are for q 12 hours Some safe dose information is per dose range Some safe dose information is per day range Med Calculation Check MD order Calculate parameters of safe dose and safe range Is the patient’s ordered dose within the safe range? – If yes, what do you do? – If no, what do you do? Two year old: weight is 36 lbs Amoxicillin 215 mg, po, tid for pneumonia Convert lbs -> kg 36 lb divided by 2.2 kg = 16.36 kg Recommended safe range: (PO < 40 kg: 6.7 to 13.3 mg/kg q 8 hours) – 16.36 kg x 6.7 mg = 109.6 mg q 8hours – 16.36 kg x 13.3 mg = 217.5 mg q 8 hours – Safe range: 110 mg to 218 mg Q 8 hours Question Is the dose safe? How much to you give? • Amoxicillin suspension is dispensed as 250 mg per 5 ml. How much do you give? – 250 mg / 5 ml = 215 mg / X ml – Give 4.3 cc po every 8 hours Giving Medications: Intravenous Route Fluid Maintenance Key concepts • Pediatric population requires keen awareness of fluid maintenance; Fluid overload must be avoided. • Minimal and maximum dilution is important for medication safe administration • REMEMBER: you are the last person to touch the med before it touches the patient Fluid Maintenance Key concepts • Policies reflect specific pediatric considerations for children who are receiving IV fluids/IV medication • IVF and meds must be placed on an infusion pump or syringe pump, unless in defined emergency situations. • Infusion time is critical information. ALARIS IV pumps All IV infusions must be on an infusion pump, except in critical defined situations Large volume medications With Alaris pumps: * medication volumes greater than 60 ml * secondary infusion * separate Alaris channel used for medication administration and IV fluids Med Flush • The MD will not order to flush the line after medication – institution policy • From IV pump to patient –> 30 ml of IV line • The line must be flushed to ensure all mediation is given to patient • SO, flush is 30 ml after each medication Syringe pump: for infusions less than 60 mls •Used for many medications - both continuous infusion and intermittent medications •Syringe size from 3ml to 60 ml (but preferable to use 5 ml syringe or larger) • Allows for smaller volume for med flushes Tubing med flush volume is 1 ml. Med Flush for syringe pump • The MD will not order to flush the line after medication – institution policy • From syringe pump to patient –> 1 ml of IV line (microtubing) • The line must be flushed to ensure all mediation is given to patient • Flush is typically 2-3 ml after each medication Intravenous calculations • • • • • • • • • • • Medication order Allergies Weight Fluid maintenance – per day/per hour Safe dose PIV or CVL - will effect dilution of medication Dilution Infusion time Infusion rate Syringe pump or mini bag Discuss how you are going to give the medication IV rate calculation • Formula: Amount of fluid x 60 (min) Time in minutes for infusion • OR: 60 minutes: multiple volume in infuse x 1 30 minutes: multiple volume in infuse x 2 20 minutes: multiple volume in infuse x 3 15 minutes: multiple volume in infuse x 4 10 minutes: multiple volume in infuse x 5 •Medication order: Cefuroxime 725 mg IV Q 8 hours • Allergies: No known allergies • Weight: 14.5 kg • Fluid maintenance – per day: 1225 cc/day; Per hour: 51 cc/hour • Safe dose -- 50 mg/kg/dose THUS 50 mg x 14.5 kg = 725 mg/dose •SO DOSE IS SAFE • PIV or CVL - child has PIV • Dilution 20-40mg/ml -> 725 mg/20= 36,2cc -> 725mg/40 = 18.3 cc DILUTION RANGE IS 18.3 cc and 36.2 cc Pharmacy sends up 36.2 cc • Infusion time: 30 minutes • Infusion rate: -> 36.2 cc x 2 = 72 cc/hour Syringe pump or piggy back bag? • medication volume less than 60 ml, sent up in syringe – use syringe pump Practice • Jose: 5 year old, 50 lbs: MD order for 750 mg of Ancef (Cefazolin) Q 8 hours. • Pharmacy sends vial of powdered Ancef. The direction for dilution states: ‘dilute the powder with 10 ml of sterile water to make a concentration of 1 gram per 10 ml’. • How many ml’s will you need to draw up for Jose’s dose? Reconstitution math • 1 gm = 1000mg 1000 mg = 750 mg 10 ml X 1000 x = 7500mg 1000 1000 X = 7.5 ml to be drawn up from vial Medication order: Ancef 750 mg IV, Q 8 hours Peripheral IV • • • • • • • • Allergies – NKDA Weight: 50 lbs - 22.7 kg Fluid maintenance – per day/per hour 1554 ml/day AND 64.75 ml/hour Safe dose: is 33.3 mg/kg/dose = 756 mg/dose - dose is SAFE PIV or CVL: child has a peripheral IV (PIV) Dilution factor: 40 mg/ml: 750 mg/20 = 37.5 ml Infusion time: 30 min so: 37.5 x 2 = 75 ml/hour Infusion rate: 75 ml/hour Syringe pump or mini bag? Syringe since volume is less than 60 ml Medication order: Ancef 750 mg IV, Q 8 hours: Central line • • • • • • • • Allergies – NKDA Weight: 50 lbs - 22.7 kg Fluid maintenance – per day/per hour 1554 ml/day AND 64.75 ml/hour Safe dose: is 33.3 mg/kg/dose = 756 mg/dose - dose is SAFE PIV or CVL: child has a central line (CVL) Dilution factor: 20 mg/ml: 750 mg/40 = 18.74 ml Infusion time: 30 min so: 18.75 x 2 = 37.5 ml/hour Infusion rate: 37.5 ml/hour Syringe pump or mini bag: volume is less than 60 ml so use syringe pump Key points - IV med administration • • • • • • • Weight and fluid maintenance Allergies What is safe dose Does child have PIV or a CVL Any cardiac/renal/fluid restrictions If < 60 ml total use syringe pump If > 60 ml will be dispensed in mini bag PREP TIME • What Baseline Information Do I Need To Get – Admitting diagnosis and previous health history – Weight, height; fluid requirements – Medical and nursing orders – Medications – Policy and Procedures – Medical tests and procedures – Age: developmental and cognitive Again welcome to West 11 • • • • • ? ? ? ? ?