* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Skin Conditions in Sports
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
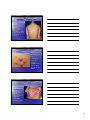
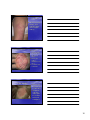
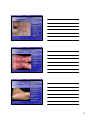
Skin Conditions in Sports Identification WIAA definition for not contagious Kenneth H. Katz, M.D. President, Dermatology Associates of Wisconsin Assistant Clinical Professor, UW Fox Valley Family Medicine Residency Program • Many skin conditions are contagious and may • • • look similar to other nonnon-contagious skin conditions Contagious skin diseases can be transmitted through sporting contact, especially wrestling Contagious skin diseases can disqualify wrestlers If a contagious skin disease is identified by a trainer, therapist, or physician it can be promptly treated to prevent spread to other athletes • Bacterial Infections • Viral Infections • Fungal Infections • Parasitic Infestations • Inflammatory Mimickers 1 Bacterial Infections Impetigo • Honey Colored Crust • Erythema • May have Bullae • Staph >>> Strep Eczema • Dry red scaly • No weeping • Often poorly defined • Chronic • Itching 2 Impetigo • Dicloxacillin • Oral • Antibiotic for minimum 3 days and no new lesions in 24 hours If MRSA then oral antibiotic for minimum of 10 days • Eczema with secondary impetigo – note the “honey colored” colored” crust covering the patches • Very common for eczema patients Folliculitis • Papules and pustules with minimal erythema • Looks like pimples • Not contagious 3 Staph Aureus Folliculitis • Pustles with a • • bright erythema extending well beyond the lesion Contagious Same guidelines as impetigo Furuncles (Boils) • Staph Aureus or MRSA • Tender, fluctuant nodule usually draining purulent material • I&D plus same guidelines as impetigo • Herpetic Infections – Varicella (Chicken Pox) – Varicella Zoster (Shingles) – Herpes Simplex 1 (Cold Sores) – Herpes Simplex 2 (Genital Herpes) • Not Discussed • Molluscum Contagiousum 4 • 85% of US population • • • HSV 1 infected – lives in nerve cell bodies in the cranial or paraspinal ganglions 10% have recurrent outbreaks Numb or tingling prodrome Painful or tender grouped vesicles on a red base HSV 1 • NonNon-contagious • when all lesions scabbed over in the preceding 48 hours Antiviral treatment if given early will shorten duration to nonnoncontagious HSV with Secondary Impetigo • Very common • Treat both conditions • Athletes with frequent recurrence of HSV may take prophylactic therapy during season – especially wrestlers 5 Varicella - Chicken Pox • Less common since • • • vaccination at age one Milder outbreak can occur in vaccinated individuals Prodrome is a URI typically with fever Very itchy >> painful Varicella - Chicken Pox • Dew drop on a rose petal • NonNoncontagious when all lesions scabbed over and no new lesions for 48 hours Varicella Zoster - Shingles • Reactivation of • • Varicella Virus along a dermatome from the neuron cell bodies in the ganglion More common in kids since vaccination Painful >> itchy 6 • NonNon-contagious • • when all lesions scabbed over and no new lesions in 24 hours Looks very similar to HSV 1 – grouped pustules and vesicles on a red base If athlete has “recurrent shingles” shingles” it is HSV 1 on the body Varicella Zoster - Shingles Varicella Zoster - Shingles • Early treatment with antivirals speeds time to nonnon-contagious and can decrease risk of post herpetic neuralgia Molluscum Contagiosum • Umbilicated papule occasionally some erythema • Typically on body • Most adults have been infected as a child 7 Molluscum Contagiosum • Many treatments • Quickest path to nonnoncontagious is currettage (may scar) • No new lesions and all lesions crusted and scabbed for 24 hours Molluscum Contagiosum • Sometimes can be subtle • In the genital area it can be a sexually transmitted disease Tinea - Ringworm • Ringworm is actually a fungal infection with a dermatophyte, usually Tinea Rubrum • It can come from other people, animals, or the soil • It has many manifestations from hair loss to athletes foot to itchy scaly hands to red patches on the body 8 Tinea Corporis • Raised periperhal scaly border with central clearing • Itchy Psoriasis – thick white scale throughout no central clearing Tinea Corporis • Raised peripheral scaly border • Some central clearing 9 Eczema • Uniform dry scaly patches, with indistinct edges and no central clearing Tinea Corporis • May have • • Tinea capitis central pustules if involved in hair bearing areas Oral or OTC Topical treatment for 72 hours If pustules oral tx required • Scaling with hair loss and broken hairs • Treatment with oral antifungals for 14 days before not contagious 10 • Alopecia Areata • No erythema • No scaling • No symptoms • No broken hairs Tinea Capitis • Clearly see areas of scale and rings with hair loss – broken hairs on close inspection Psoriasis of the Scalp •No hair loss •No raised peripheral border •No central clearing 11 Tinea with secondary impetigo •Hair loss present tells you that it is tinea and not just impetigo •Central clearing still evident •Honey colored crusting present especially at periphery •Treat both disorders to be non-contagious Tinea Pedis • Peripheral scale • Extends between toes • In this example involves the great toe nail • Areas of central clearing Eczema • No raised border of peripheral scale • Dry scale and erythema confluent • May or may not extend between the toes – usually does not 12 Tinea Pedis • OTC Topical (or Rx • • • • Oral) treatment for 72 hours to be nonnoncontagious WIAA rules state that “covering” covering” a contagious disease is not adequate WIAA release only lists ringworm of the scalp and skin as disqualifiers I interpret as tinea pedis is not a disqualifier but have athletes treat anyway Same with tinea cruris (jock itch) unless extending widely to be classified as tinea corporis Atopic Dermatitis • No central clearing • Lichenification • Does not involve interdigital toe space Tinea Pedis • Moccassin tinea pedis • Peripheral scale more intense than central • Often tiny vesicles • Usually very itchy • OTC topical treatment 13 Pustular Psoriasis of the foot • Confluent • • pustules but no vesicles, no peripheral scale on palms or soles (no hair follicles) Often painful +/+/- other psoriasis Parasitic Infestations • Scabies • Head Lice Scabies • Itching wrists, between fingers, and frequently genitals • Very, very itchy much out of proportion to the degree of skin findings 14 Scabies Scabies – itchy eroded papules in finger web spaces 15 Scabies • Linear burrows in the wrist area • NonNon-contagious 24 hours after topical treatment • Always treat entire family Head Lice • Intense itching • Head Lice especially on occipital scalp Nits within ½ inch of scalp indicate potential active infection • OTC topical treatment effective • NonNon-contagious 24 • • • hours after first treatment Nits do not need to be removed to be considered nonnoncontagious Treat entire family Nits greater than ½ inch from scalp are “old” old” 16