* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Peritonitis
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
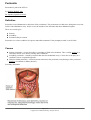
Peritonitis Pronounced: peh-rit-oh-NYE-tis by Michelle Badash, MS En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Peritonitis is an inflammation or infection of the peritoneum. The peritoneum is a thin tissue lining that covers the inside of the abdominal cavity. It also covers the outside of the intestines and other abdominal organs. There are several types: Primary Secondary Peritoneal dialysis related Peritonitis is a serious condition. It requires immediate treatment. If not promptly treated, it can be fatal. Causes Primary peritonitis—occurs when there is a buildup of fluid in the abdomen. This is called ascites. It is caused by chronic liver disease, among other conditions. Secondary peritonitis—caused by bacteria that enter the abdominal cavity. Can be due to an injury or a condition, such as a ruptured appendix. Dialysis-related peritonitis—caused by bacteria that enter the peritoneal cavity during or after peritoneal dialysis (a treatment for kidney disease). Secondary Peritonitis Page 1 of 3 Copyright © 2011 EBSCO Publishing. All rights reserved. © 2011 Nucleus Medical Media, Inc. Risk Factors A risk factor is something that increases your chance of getting a disease or condition. Risk factors for peritonitis include: Abdominal penetration or trauma Immune compromise Blood in the abdomen Ruptured appendix Peptic ulcer Colitis Diverticulitis Gangrene of the bowel Pancreatitis Pelvic inflammatory disease Inflamed gallbladder Recent surgery Tubes or shunts in the abdomen Cortisone drugs Symptoms Symptoms may include: Severe pain or tenderness in the abdomen Pain in the abdomen that is worse with motion Bloating of the abdomen Constipation Fever Nausea and vomiting Weakness or dizziness Shortness of breath Rapid pulse or breathing rate Dehydration —signs include dry skin and lips, decreased urine production Diagnosis The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical exam. Tests may include: Blood tests Analysis of fluids from the peritoneum Abdominal x-rays —to look for signs of inflammation Laparotomy —surgery to open and examine the abdomen Treatment Page 2 of 3 Copyright © 2011 EBSCO Publishing. All rights reserved. Treatment depends on the cause. It may include: Surgery to repair openings in the skin surface or to remove damaged tissue Antibiotics to treat infection Replacement of fluids If you are diagnosed with peritonitis, follow your doctor's instructions. Prevention There are no guidelines for preventing peritonitis. RESOURCES: American Gastroenterological Association http://www.gastro.org/ The American College of Gastroenterology http://www.acg.gi.org/ CANADIAN RESOURCES: Canadian Association of Gastroenterology http://www.cag-acg.org/default.aspx/ Health Canada http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/index-eng.php REFERENCES: Feldman M, et al.Sleisenger & Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 8th ed. St. Louis: Mosby, 2005. Olendorf D, Jeryan C, Boyden K. Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine . Detroit, MI: Gale Group Research Company; 2000. Peritonitis. Mayo Clinic website. Available at: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/peritonitis/ds00990 . Updated July 2009. Accessed July 24, 2009. Townsend CM, et al. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 17th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2004. Yamada T, Alpers DH, et al. Textbook of Gastroenterology . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003. Last reviewed September 2011 by Marcin Chwistek, MD Last Updated: 9/1/2011 Page 3 of 3 Copyright © 2011 EBSCO Publishing. All rights reserved.