* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PERITONITIS
Acute pancreatitis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Appendicitis wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
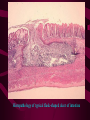
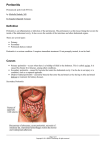
PERITONITIS Tammy McDaniel & Emily Stevens Evaluation of Athletic Injuries I AH 322 September 29, 2003 Peritonitis (pear-ih-tuh-NYE-tis) Infection, or rarely some other type of inflammation, of the peritoneum. Peritoneum is a membrane that covers the surface of both the organs that lie in the abdominal cavity and the inner surface of the abdominal cavity itself. Intra-abdominal infections result in 2 major clinical manifestations • Early or diffuse infection results in localized or generalized peritonitis. • Late and localized infections produces an intraabdominal abscess. 2 Major Types • Primary: Caused by the spread of an infection from the blood & lymph nodes to the peritoneum. Very rare < 1% • Usually occurs in people who have an accumulation of fluid in their abdomens (ascites). • The fluid that accumulates creates a good environment for the growth of bacteria. 2nd Type: • Secondary: Caused by the entry of bacteria or enzymes into the peritoneum from the gastrointestinal or biliary tract. • This can be caused due to an ulcer eating its way through stomach wall or intestine when there is a rupture of the appendix or a ruptured diverticulum. • Also, it can occur due to an intestine to burst or injury to an internal organ which bleeds into the internal cavity. Both cases are very serious & can be life threatening if not treated properly!!! • Hollow organs are more susceptible to athletic injury when they are full of waste & food products. • Injury to a hollow organ may so signs of: > black tarry stool >bright red blood in the fecal discharge >bloody vomitus * Always remember there may be referred pain. Signs & Symptoms • Swelling & tenderness in • the abdomen • • Fever & Chills • • Loss of Appetite • • Nausea & Vomiting • ^ Breathing & Heart Rates Shallow Breaths Low BP Limited Urine Production Inability to pass gas or feces Symptoms Con’t: • An acutely ill patient tends to lie “very” still because any movement causes excruciating pain. • They will lie with there knees bent to decrease strain on the tender peritoneum. Exam & Evaluation • Feel & press the abdomen to detect any swelling & tenderness in the area as well as signs of fluid has collected in the area. • Listen to the bowel sounds & check for difficulty breathing, low blood pressure & signs of dehydration. Evaluation con’t: • The usual sounds made by the active intestine and heard during examination with a stethoscope will be absent, because the intestine usually stops functioning. • The abdom may be rigid and boardlike • Accumulations of fluid will be notable in primary due to ascites. Exams con’t: • Blood Test • Samples of fluid from the abdomen • CT Scan • Chest X-rays • Peritoneal lavage. Treatment Approach • Hospitalization is common. • Surgery is often necessary to remove the source of infection. • Antibiotics are prescribed to control the infection & intravenous therapy (IV) is used to restore hydration. TX Con’t: • Morphine for pain. • Dietary supplements (omega 3, omega 6 fatty acids, vitamin A, E, C, and zinc) Prognosis • Untreated peritonitis is poor, usually resulting in death. • With Tx, prognosis is variable, dependent on the underlying causes. Preventive Care • There is “NO WAY” to prevent peritonitis, since the diseases it accompanies are usually not under the voluntary control of an individual. • However, the best way to prevent serious complications is to seek medical attention as soon as symptoms appear. Histopathology of typical flask-shaped ulcer of intestine This occurs in acute pancreatitis References: • “Evaluation and Management of Secondary Peritonitis.” American Family Physician 54 (October 1996): 1724+. • “Subacute Bacterial Peritonitis: Diagnosis and Treatment.” American Family Physician 52 (August 1995): 645. • Isselbacher, Kurt J., and Alan Epstein. “Diverticular, Vascular, and Other Disorders of the Intestinal and Peritoneum.” In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, ed. Anthony S. Fauci, et al. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1997. References con’t: • Platell C., Papadimitiriou J M., Hall J.C. The Influence of Lavage Fluid on Peritonitis. Journal of American College Surg 2000; 191: 672-680. • Boeschoten, EW. Long-Term Consequences of Peritonitis. Perit Dial Int. 1996;16(suppl 1): S349-S354.