* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PX810501_NT-proBNP-27May2015
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
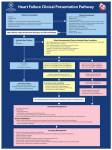
N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) Date of SC final approval About the Measure Domain: Measure: Definition: Purpose: Sickle Cell Disease: Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, and Renal N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) A bioassay to determine an individual’s level of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-pro-BNP) is released from the right or left ventricle of the heart when it is under increased strain related to volume or pressure overload. Levels of NT-pro-BNP can be used as a screening tool to evaluate an individual’s left and right ventricular function. Elevated NT-pro-BNP levels can be used diagnostically in decompensated congestive heart failure and they can be followed longitudinally to understand response to therapy. In patients with pulmonary hypertension and acute pulmonary embolism, elevated levels reflect an increased risk of morbidity and mortality. Additionally, in patients with sickle cell disease, levels of NT-proBNP levels > 160 pg/ml predict increased mortality risk About the Protocol Description of Protocol: Selection Rationale: Specific Instructions: This protocol provides instructions for drawing, processing, and storing blood according to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) methods. Because there are many comparable assays for ascertaining levels of Nterminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), the protocol also provides basic guidelines to aid comparability among different studies. The Sickle Cell Disease Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, and Renal Working Group selected N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) measurement because it is a validated, specific, low-burden, and non-invasive alternative to echocardiography for differentiating patients with ventricular dysfunction. Additionally, this assay does not require sample extraction and there is no detectable cross reactivity with atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), N-terminal pro-atrial natriuretic peptide (NT-proANP), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), or urodilatin. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) instructions for drawing, processing, and storing blood provide a standard methodology used successfully for many years to ensure comparable results across study sites. However, the Sickle Cell Disease Working Group 1 (Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, and Renal) notes that certain aspects (e.g., exclusion criteria) of the NHANES protocol are study specific and might not be applicable to all types of studies (e.g., sickle cell disease). N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) analysis is performed by plasma assay. Protocol Text: Summary of the N-terminal Pro-brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) Assay The following is a summary version of the full National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2012 protocol. Exclusion Criteria Persons will be excluded from this component if they: Version 10 – 10/21/09 N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) Date of SC final approval • Report that they have hemophilia; or • Report that they have received cancer chemotherapy in the last 4 weeks SP = Sample Person. 1. Do you have hemophilia? 1[] 2[] 7[] 9[] Yes No Refused Don’t Know If the SP answers "Yes," the SP is excluded from the blood draw. If SP answers "No" or "Don’t Know," blood is drawn from the SP. 2. Have you received cancer chemotherapy in the past four weeks or do you anticipate such therapy in the next four weeks? 1 [ ] Yes 2 [ ] No 7 [ ] Refused 9 [ ] Don’t Know If the SP answers "Yes," the SP is excluded from the blood draw. If SP answers "No" or "Don’t Know," blood is drawn from the SP. Venipuncture Procedures Editor’s Note: Please review chapter 4 of the Laboratory Procedures Manual from the 2011-2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) for a full description of phlebotomy procedures. This manual is posted here, and is also available at the NHANES website: 2011-2012 NHANES Laboratory Procedures Manual Venipuncture should generally be performed using the median cubital, cephalic, or basilic veins in the left arm unless this arm is unsuitable. If the veins in the left arm are unsuitable, look for suitable veins on the right arm. If the veins in the antecubital space on both arms are not suitable, then look for veins in the forearm or dorsal side of the hand on the left arm/hand and then the right arm/hand. Recording the Results of the Venipuncture Procedure Immediately after completing the venipuncture, record the results of the blood draw, the reasons for a tube not being drawn according to the protocol, and any comments about the venipuncture. Blood Processing Please review chapter 8 of the Laboratory Procedures Manual from the National Version 10 – 10/21/09 N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) Date of SC final approval Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2012 for a full description of blood processing procedures: 2011-2012 NHANES Laboratory Procedures Manual • • Centrifuge the tube at room temperature to separate the plasma and aliquot into an appropriate storage tube. Determine if the plasma is hemolyzed, turbid, lipemic, or icteric. If so, enter a comment to describe the plasma. Laboratory Assay for NT-proBNP NT-proBNP can be measured using a two-step sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in streptavidin-coated microtitre plates. The Sickle Cell Disease Working Group 1 (Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, and Renal) notes that there are a number of different reagents and instruments that are appropriate to measure the concentration of NT-proBNP. Once an assay is chosen for a particular study, the Working Group recommends that no changes in the protocol be made over the course of the study. To aid comparability, the Working Group recommends that the investigator record the make and manufacturer of equipment used and the repeatability and coefficients of variation for the assay. Reference Ranges Participant: Source: Language of Source: Personnel and Training Required: Equipment Needs: Protocol Type: Age < 50 years old 50-75 years old >75 years old Adults Range (pg/mL) 300 - 450 300 - 900 300 – 1800 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2011). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Questionnaire, Laboratory Procedures Manual. Hyattsville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Bay, M., Kirk, V., Parner, J., Hassager, C., Nielsen, H., Krogsgaard, K., Trawinski, J., Boesgaard, S., & Aldershvile, J. (2003). NT-proBNP: A new diagnostic screening tool to differentiate between patients with normal and reduced left ventricular systolic function. Heart, 89, 150–154. English A phlebotomist, nursing staff, or other health care professional who is trained to draw blood and laboratory staff who are trained to perform this assay. Phlebotomy supplies, centrifuge for serum separation, and freezer for sample storage is required. Bioassay Requirements: Requirements Category Major equipment Required (Yes/No): No Version 10 – 10/21/09 N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) Date of SC final approval Common Data Elements: General References: Specialized training No Specialized requirements for biospecimen collection Average time of greater than 15 minutes in an unaffected individual TBD by PhenX Team No No Machado, R. F., Hildesheim, M., Mendelsohn, L., Remaley, A. T., Kato, G. J., & Gladwin, M. T. (2011). NT-pro brain natriuretic peptide levels and the risk of death in the cooperative study of sickle cell disease. British Journal of Haematology, 154(4), 512-520. Machado, R. F., Anthi, A., Steinberg, M. H., Bonds, D., Sachdev, V., Kato, G. J., Taveira-DaSilva, A. M., Ballas, S. K., Blackwelder, W., Xu, X., Hunter, L., Barton, B., Waclawiw, M., Castro,O., Gladwin, M. T., & MSH Investigators. (2006). N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels and Risk of Death in Sickle Cell Disease. JAMA, 296(3), 310-318. doi:10.1001/jama.296.3.310 Karl, J., Borgya, A., Gallusser, A., Huber, E., Krueger, K., Rollinger, W. & Schenk, J. (1999). Development of a novel, N-terminal-proBNP (NT-proBNP) assay with a low detection limit. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation, 59(Suppl230), 177-181. Tamizifar, B., & Rismankarzadeh, M. (2012). Using NT-proBNP as a criterion for heart failure hospitalization. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 17(1): 111-113. Pfister, R., & Schneider, C. A. (2008). ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: application of natriuretic peptides. European Heart Journal, 382-383. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehn560 382-383 Additional Information About the Measure Essential Data: Current Age, Race, Ethnicity Related PhenX Measures: Derived Variables: Keywords/Related Concepts: Heart Valve Function, Pulmonary Hypertension, Blood Pressure None N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, NT-proBNP, left ventricular ejection fraction, LVEF, sickle cell disease, SCD, chronic heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, PH, biomarkers, immunoassay Version 10 – 10/21/09