* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oscilloscope - Tektronix TDS2000 Series Guide
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
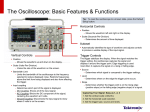
OSCILLOSCOPE
GUIDE
Tektronix TDS2000 Series
Department of
Electrical & Computer
Engineering
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Contents
1 – INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................................... 2
2 –OSCILLOSCOPE OVERVIEW ................................................................................... 2
3 – INSTRUMENT FRONT PANEL ................................................................................. 3
► Power Switch.......................................................................................................................... 3
► USB Drive Port ........................................................................................................................ 3
► Save Button ............................................................................................................................ 3
► Multipurpose Knob ................................................................................................................ 3
► LCD Screen ............................................................................................................................. 4
► Menu Option Buttons ............................................................................................................ 4
► VERTICAL Controls.................................................................................................................. 5
► HORIZONTAL Controls ............................................................................................................ 7
► TRIGGER Controls ................................................................................................................... 8
► Setup and Control Buttons..................................................................................................... 9
► Input Connectors.................................................................................................................. 14
4 – PASSIVE PROBES ................................................................................................. 15
5 – SIMPLIFIED MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE ........................................................ 18
6 – SAVING WAVEFORMS TO A USB DRIVE ............................................................. 19
7 – SAVING WAVEFORMS TO A COMPUTER ........................................................... 21
APPENDIX 1 – SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................... 23
APPENDIX 2 – REFERENCES ..................................................................................... 24
1
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
1 – Introduction
This guide provides basic instructions for operating the Tektronix TDS2000 Series Digital Phosphor
Oscilloscopes. These are some features of various models1 in the product line:
•
50 to 200 MHz bandwidth
•
Up to 2 GS/s sample rate
•
2 or 4 channels
•
Full color LCD with graphical user interface
•
USB I/O for data transfer and control
•
Built-in automated measurements
Copyright © Tektronix, Inc.
2 –Oscilloscope Overview
An oscilloscope is an instrument that measures a voltage signal and displays a graph of how the signal
varies over time. The vertical axis of the graph is the voltage, while the horizontal axis is time. Important
signal characteristics can be extracted from the graph, such as the shape and amplitude of the signal,
the frequency or period of a repetitive waveform, and the amount of noise or distortion.
A probe is used to connect the circuit being tested to the inputs of the oscilloscope. Each input, or
channel, can independently measure a signal. In a digital oscilloscope, an analog-to-digital converter
samples the input voltage signal and converts the analog values to digital form. The sampling is
performed repeatedly as part of the time sweep. The scope processes the incoming data and displays it
on the built-in monitor screen as a continuously updated graph of voltage versus time.
Important specifications of a digital oscilloscope include:
•
Bandwidth – Specifies the highest signal frequency that can be accurately measured
•
Sample rate – Determines how often the input signal can be sampled (samples per second)
•
Number of channels – Determines how many independent signals can be measured simultaneously
The front panel of a typical digital oscilloscope has these control sections:
•
Vertical – Adjusts the vertical (voltage) scaling and positioning of the waveform
•
Horizontal – Controls the horizontal (time) scaling and positioning of the waveform
•
Trigger – Provides a way to stabilize the display of repetitive signals on the screen
•
Acquisition – Controls how the input signal is acquired or sampled
1
The TDS2014C model has a 100 MHz bandwidth, 2 GS/s sampling rate, and four analog input channels.
2
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
3 – Instrument Front Panel
Power switch
(on top of chassis)
Option
buttons
Save/Print
button
Multipurpose
knob
Various setup
& control buttons
TRIGGER
controls
HORIZONTAL
controls
VERTICAL
controls
LCD
screen
Probe input
connectors
USB drive
port
Figure 1: Tektronix TDS2000C series front panel - Copyright © Tektronix, Inc.
► Power Switch
The switch located on top of the oscilloscope’s chassis turns the instrument either on or off.
Note: When the power is first applied, the oscilloscope performs a diagnostics test that lasts up to 30
seconds. When the test is done, an on-screen prompt asks if the current date or time needs to
be changed. To exit this display, simply push any button or wait for it to time out.
► USB Drive Port
This port is used to attach an external mass storage device. Screen images and waveform data can be
saved to or recalled from a USB flash drive (up to 64 GB in size) that is inserted in the port.
► Save Button
Pushing this button saves the waveform. Depending on how the button is configured, the waveform can
either be stored as a file on a USB drive or sent to an attached printer.
► Multipurpose Knob
The multipurpose knob is used to navigate the screen, select an item, or change a setting.
3
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
► LCD Screen
The screen shows a graph of the signal that is measured on an input channel. The oscilloscope provides
controls for making individual channels either active (waveform is displayed on the screen) or inactive
(waveform is omitted).
Trigger
status
Aquisition
mode
Graticle
divisions
(VERTICAL)
Voltage
Time
(HORIZONTAL)
Waveform
Waveform
Ground
reference
marker
Menu
options
Vertical scale
(voltage/div)
Channel
indicator
Trigger
values
Horizontal scale
(time/div)
Each channel is color coded: CH1=yellow, CH2=blue, CH3=purple, CH4=green
The main graph area is divided into a grid to aid in reading the amplitude and timing of the waveforms.
Dotted grid lines represent the major divisions on each axis. The vertical axis has units of voltage, while
the horizontal axis has units of time.
► Menu Option Buttons
The TDS2000C series support an on-screen menu for accessing various oscilloscope features that are not
assigned to a dedicated button.
If an oscilloscope function provides menu options, they are displayed in a column on the right side of the
LCD screen. The content of the menu will vary depending on the current function.
To the right of the menu column are the physical option buttons, which are located on the plastic bezel
that surrounds the LCD. By pressing a button, the menu option associated with the button is selected.
4
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
► VERTICAL Controls
The vertical section adjusts the vertical (voltage) configuration, scaling, and positioning of the waveform.
Each channel has its own independent vertical controls and settings.
1, 2, 3, 4 buttons
The 1 (yellow), 2 (blue), 3 (purple), 4 (green) buttons display on-screen menu options for a selected
channel (CH1 thru CH4). The menu options are applied only to the currently selected channel.
If a channel is not active when its button is pressed, then the channel becomes active, its measured
waveform is displayed on the screen, and its menu options appear.
If a channel is already active when its button is pressed, then the channel becomes inactive, and its
waveform stops being displayed.
The menu options are:
Coupling
Selects the channel’s input coupling. {DC, AC, Ground}
DC
Allows both AC and DC signals to get through.
AC
Filters out any DC signals, so only the AC variation is displayed.
Ground Temporarily replaces the waveform with a 0 V flat reference line.
BW Limit
Limits the bandwidth to filter out high frequency noise. {Off, 20 MHz}
Volts/Div
Selects the resolution of the vertical Scale knob. {Coarse, Fine}
Probe
Sets the scope to match the probe’s operating characteristics. {Type, Attenuation}
Type
Type of probe being used (either voltage or current).
Attenuation Sets the attenuation factor to match the probe’s factor. Press the
option button repeatedly or else use the multipurpose knob.
{1X, 10X, 20X, 50X, 100X, 200X, 500X, 1000X}
Invert
Flips the vertical polarity of the waveform.
5
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Math button
The Math (red) button allows math operations to be performed on waveforms. The result is
displayed as a separate red-colored waveform on the screen.
The menu options are:
Operation
Selects the math operation. {+, -, x, FFT}
+
Adds two waveforms
Subtracts two waveforms
x
Multiplies two waveforms
FFT
Fast Fourier Transform (magnitude vs frequency) of a single waveform
Sources
Selects source channels. {+,-,x: CH1&CH2 or CH3&CH4
FFT: CH1 thru CH4}
Position knob (vertical)
This knob moves the currently selected waveform up or down on the screen. It does not affect the
waveform’s vertical size. When multiple channels are active, the knob is useful for providing some
vertical separation among the waveforms, which are otherwise overlaid by default.
Scale knob (vertical)
This knob adjusts the vertical scale (size) of the currently selected waveform. The vertical voltage
scale is specified in units of volts per division (V/div).
Example: If the scale is 2 V/div, then each major division on the vertical axis represents a 2 V span.
6
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
► HORIZONTAL Controls
The horizontal section adjusts the horizontal (time) scaling and positioning of the waveform. All
channels share the same horizontal settings.
Horiz button
The button displays on-screen menu options for viewing a waveform across
the entire acquisition period, or just a windowed section of it.
The menu options are:
Main
Displays the original, complete waveform.
Window Zone
Sets the position of the window within the waveform. Use
the horizontal Position knob to move the window’s left (start)
and right (stop) markers to frame the zone boundaries.
Window
Displays only the part of the waveform that is within the
defined window zone. The contents of the window are
zoomed out to the full width of the screen.
Position knob (horizontal)
This knob moves all waveforms left or right on the screen. It does not affect the horizontal time
scale.
Set to Zero button
If waveforms have been horizontally shifted, this sets their position back to the zero reference point.
Scale knob (horizontal)
This knob adjusts the horizontal scale of all waveforms. The horizontal time scale is specified in units
of time per division (e.g., ms/div).
Example: If the scale is 5 ms/div, then each major division on the horizontal axis represents 5 ms.
7
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
► TRIGGER Controls
To show a stable image of a repeating waveform on the screen, the oscilloscope needs to acquire the
signal at the same point on the waveform during each sweep. This is done by setting a threshold voltage
value that, when the measured signal crosses the threshold, causes the oscilloscope to initiate an
acquisition sweep. This threshold is called the “trigger level”. The trigger source can be either the input
signal itself or an external trigger signal.
Note: If the measured input signal never crosses the threshold because the level was set too high or too
low, the displayed waveform will be unstable and jitter erratically on the screen.
Trig View button
As long as this button is pushed, a horizontal dashed line that represents the current trigger level is
superimposed on the trigger source’s waveform.
Force Trig button
Manually initiates acquisition regardless of an adequate trigger signal.
Set to 50% button
Automatically sets the trigger level to the midpoint between the trigger source’s minimum and
maximum voltage values.
Level knob
Manually adjusts the trigger level. An arrow marker on the right edge of the screen shows the level
relative to the waveform.
Trig Menu button
This is used to configure the trigger parameters.
The menu options are:
Type
Selects the type of trigger to detect. {Edge, Video, Pulse}
Edge
Triggers on the rising/falling edge of a signal that crosses the trigger level.
Pulse
Used when the trigger is a very fast pulse that the Edge mode would miss.
Source
Selects the trigger signal source. {CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4, Ext, Ext/5, AC Line}
CH1 … CH4 Uses one of the measurement channels as the trigger source.
Ext
An external trigger input is used as the source.
Slope
Determines whether to trigger on the rising or falling edge of a signal. {Rising, Falling}
Mode
Determines acquisition method if a valid trigger signal is not available. {Auto, Normal}
Coupling
Sets which components of the trigger signal are passed on to the trigger circuit.
{DC, Noise Reject, HF Reject, LF Reject, AC}
8
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
► Setup and Control Buttons
Buttons in this area provide additional control over waveform acquisition, measurement, and display.
AUTOSET button
Automatically adjusts the VERTICAL, HORIZONTAL, and TRIGGER controls to acquire a usable display.
The controls may need further manual adjustment for best results.
Single button
Enables a single sweep acquisition of a signal, after which the acquisition stops.
Run/Stop button
Allows the user to start and stop a continuous waveform acquisition.
Help button
This accesses the oscilloscope’s built-in help system. {Show Topic, Index, Help on Help, Back, Exit}
Default Setup button
Sets the oscilloscope back to its initial startup settings.
Acquire button
This sets up the acquisition parameters.
Menu options are:
Sample
Default mode for acquiring most waveforms.
Peak Detect
Used for detecting glitches and reducing the chance of aliasing.
Average
Used for reducing random or uncorrelated noise in the signal display.
Averages (X) Sets the number of averages to use if the Average option is active. {4, 16, 62, 128}
9
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
AutoRange button
This sets up automatic scaling of a waveform when it is displayed on the screen.
Menu options are:
Autoranging
Vertical and Horizontal
Vertical Only
Horizontal Only
Undo Autoranging
Determines if the acquired waveform is scaled to fit the screen. {On, Off}
Autoranges both the vertical and horizontal scales.
Autoranges just the vertical (voltage) scale.
Autoranges just the horizontal (time) scale.
Undos the last autorange.
Cursor button
This is used to superimpose a pair of movable vertical or horizontal bars on the screen to mark key
points on waveforms for measurement. The oscilloscope provides readouts of the cursors’ absolute
location values at the marked points, as well as relative deltas.
Menu options include:
Type
Sets the type of cursor to show (horizontal bars for amplitude, vertical bars for time).
{Off, Amplitude, Time}
Source
Selects which channel’s waveform the cursors will bound.
{CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4, MATH, …}
Cursor1
If selected, use the multipurpose knob to move cursor bar 1 (vertically when
Type=Amplitude or horizontally when Type=Time).
Cursor2
If selected, use the multipurpose knob to move cursor bar 2 (vertically when
Type=Amplitude or horizontally when Type=Time).
When activated, Cursor 1 and Cursor 2 display continuously updated readouts of their current
values (Amplitude mode: V, Time mode: t, V).
The center slot in the menu list shows a continuous readout of the difference between the two
cursors bars (Amplitude mode: ∆V, Time mode: ∆t, 1/∆t, ∆V).
Display button
The button is used to configure advanced display modes.
Menu options are:
Type
Controls how the waveform’s points are displayed. {Vectors, Dots}
Persistence Sets the length of time each sample point remains displayed.
{Off, 1 sec, 2 sec, 5 sec, Infinite}
Format
Determines the type of data displayed on each display axis. {YT, XY}
YT
Vertical axis is voltage and horizontal axis is time (default mode).
XY
CH1 determines the X coordinate (horizontal), while CH1 determines the Y
coordinate (vertical).
10
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Measure button
This controls access to the oscilloscope’s built-in automated measurements, such as calculating the
amplitude or frequency of a cyclic signal.
The menu slots on the right side of the screen can show up to five measurements simultaneously.
Each slot is labeled with the channel number, measurement type, and updated measured value.
By selecting a slot, these menu options appear to configure the measurement for that slot:
Source
Determines which channel will be measured. {CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4, Math}
Type
Type of measurement to be performed.
{None, Freq, Period, Mean, Pk-Pk, Cyc RMS, RMS, Min, Max, Cursor RMS, Rise Time, Fall
Time, Pos Width, Neg Width, Duty Cyc, Phase, Delay}
None
Freq
Period
Mean
Pk-Pk
Cyc RMS
RMS
Cursor RMS
Min
Max
Rise Time
Fall Time
Pos Width
Neg Width
Duty Cyc
Phase
Delay
Turns off automated measurement for the source channel
Frequency of the waveform
Period (time) of the waveform’s first complete cycle
Arithmetic mean amplitude over the entire record
Absolute difference between the maximum and minimum peaks of the
entire waveform
True RMS (root mean square) of the waveform’s first complete cycle
True RMS for all 2500 samples from one frame of the waveform data
True RMS of the waveform data from the selected starting to ending points
Minimum value of the entire 2500 point waveform record
Maximum value of the entire 2500 point waveform record
Time between 10% and 90% of the first rising edge of the waveform
Time between 90% and 10% of the first falling edge of the waveform
Time between first rising edge and next falling edge at waveform 50% level
Time between first falling edge and next rising edge at waveform 50% level
Ratio of positive pulse duration to the whole cycle
Phase angle difference from two different channels, using the rising edge of
the first signal compared to the rising edge of the second signal
Time difference from two different channels using the rising edge of the first
signal compared to the rising edge of the second signal
Ref button
This button recalls a waveform that was previously saved to the onboard reference memory and
displays it on the screen. It can then be compared to a waveform that is currently being measured.
Menu options include:
Ref A
Recall reference waveform A. {Off, On}
Ref B
Recall reference waveform B. {Off, On}
Ref C
Recall reference waveform C. {Off, On}
Ref D
Recall reference waveform D. {Off, On}
11
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Save/Recall button
This controls settings for saving and recalling screen images, waveform data, and setups.
Menu options2 are:
Action
Determines which save or recall function is active.
{Save All, Save Image, Save Setup, Save Waveform, Recall Setup, Recall Waveform}
Save All
Save Image
Save Setup
Configures the Save/Print button.
PRINT Button
Determines what the Save/Print button will do.
{Saves All To Files, Saves Images To File, Prints}
Select Folder
Selects the directory on the USB drive for saving files.
{Change Folder, New Folder}
Saves the screen image.
File Format
Selects the format for saving screen images.
{JPEG, PCX, RLE, TIFF, BMP, EPSIMAGE}
Select Folder
Selects the directory on the USB drive for saving files.
{Change Folder, New Folder}
Save …
Initiates saving the current screen image to a file.
Saves the current oscilloscope settings to a file named TEKnnnn.SET on
a USB flash drive or to non-volatile setup memory. {…}
Save Waveform Saves the current waveform in CSV text format to a file named
TEKnnnn.CSV on a USB drive or to reference memory.
Recall Setup
Save To
Selects the format for saving screen images.
{Ref, File}
Source
Selects the directory on the USB drive for saving files.
{CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4, Math}
To
Selects the directory on the USB drive for saving files.
{RefA, RefB, RefC, RefD}
Save
Initiates saving the current waveform.
Recalls previously saved oscilloscope settings either from a USB drive or
from non-volatile setup memory. {…}
Recall Waveform Recalls a previously saved waveform either from a USB drive or from
reference memory. {…}
2
The lesser-used functions will not be described in depth. Refer to the Tektronix reference manual for details.
12
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Utility button
This button gives access to system utility functions.
Menu options3 include:
Limit Test
Sets up limit testing of waveforms compared to a template. {…}
Data logging
Sets up logging of data over a long time span. {...}
System Status
Displays the current setup configuration of the oscilloscope.
{Horizontal, Vertical CH1 CH2, Vertical CH3 CH4, Trigger, Misc}
Options
Configures miscellaneous system options.
{Read USB Port, Printer Setup, GPIB Setup, Set Date and Time, Error Log}
Rear USB Port
Sets the type of device connected to the rear USB port.
{Autodetect, Printer, Computer}
Printer setup
Configures the Save/Print button.
{PRINT Button, Ink Saver, Layout, File Format}
PRINT Button Determines what the Save/Print button will do.
{Saves All To Files, Saves Image To File, Prints}
GPIB Setup
Ink Saver
Determines if saved screen images will have a
dark or light background color.
{Off, On}
Layout
Sets the orientation when saving screen images.
{Portrait, Landscape}
File Format
Sets the file type when saving screen images.
{JPEG, PCX, RLE, TIFF, BMP, EPSIMAGE}
Sets the address of the oscilloscope for GPIB data connection.
{Address}
Set Date and Time Sets the oscilloscope’s internal clock. {…}
Error Log
3
Displays a list of errors logged. {…}
Do Self Cal
Performs a self-calibration routine, which can take several minutes to complete.
{OK, Cancel}
File Utilities
If a FAT32-formatted USB flash drive is inserted in the oscilloscope’s front USB port,
this option gives access to basic file and directory operations on the drive.
{Change Folder, New Folder, Delete, Rename, Format}
Language
Sets the language used for prompts and help menus.
{English, French, German, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, Japanese, Korean, Chinese}
The lesser-used functions will not be described in depth. Refer to the Tektronix reference manual for details.
13
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
► Input Connectors
External probes are attached to the input connectors on the front panel of the oscilloscope.
1, 2, 3, 4 connector
Each channel has a dedicated female BNC connector. The input resistance is 1 MΩ and the input
capacitance is 20 pF.
Warning
The maximum allowed input voltage is 300 V. Do not exceed this limit!
Ext Trig connector
This female BNC connector is utilized when an external signal is required to trigger the waveform
acquisition. For example, a trigger signal can be either a single pulse or a periodic pulse train.
14
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
4 – Passive Probes
A typical passive probe consists of a cable with a male BNC connector on one end and a retractable hook
tip (or a pointed tip) with ground clip on the other. The BNC side attaches to one of the oscilloscope’s
inputs, while the probe tip is attached to a measurement point in the test circuit.
The probe tip is where the voltage signal enters the probe and is then carried through the cable to the
center pin of the BNC connector. The ground clip provides the ground reference from the test circuit to
the outer shield of the BNC connector.
Retractable Hook
Tip Adapter
Clip-on Ground
Lead
Probe
This end
attaches to the
oscilloscope
input
Cable
Adjustment
Tool
Figure 2: General purpose voltage probe with accessories – Copyright © Tektronix, Inc.
Circuit
Being
Measured
Probe
Cable
Oscilloscope
Input
Rprobe
9 MΩ
Tip
Ccable
Cprobe
Rin
1 MΩ
Cin
20 pF
GND
A 10X probe uses a 9 MΩ series
resistor to increase the total
input resistance “seen” by the
measured device to 10 MΩ.
All cables have some
amount of shunt
capacitance.
Input
TDS2000 series scopes
have a fixed input
resistance of 1 MΩ.
Input
Figure 3: Simplified circuit model of a 10X probe connected to an oscilloscope’s input channel
(For a 1X probe, Rprobe and Cprobe are omitted and replaced by a direct wire path.)
15
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
These are some important characteristics of a probe:
•
Bandwidth – This is the highest frequency signal that the probe can accurately pass through to the
oscilloscope for measurement. A common metric is the frequency at which the measured signal
amplitude has decreased by 3 dB from the original value.
•
Attenuation – The attenuation factor determines how much the probe reduces the amplitude of the
input signal before it enters the oscilloscope. Typical probes are either 1X (no attenuation at all) or
10X (amplitude is divided by 10). Some probes support manual switching between 1X and 10X
modes. Attenuation also affects the total input resistance that is “seen” by the circuit being tested.
Note: The attenuation factor setting in the vertical section of the oscilloscope should be changed to
match the attenuation factor of the probe. The displayed V/div value will be incorrect if the
factors do not match.
•
Loading Effect – As seen in the schematic diagram, the probe and oscilloscope are attached in
parallel with the test circuit. As a consequence, the measured voltage is influenced not only by the
circuit’s intrinsic characteristics, but also by the components of the probe and oscilloscope. In
particular, the effective input resistance and capacitance of the combined probe and oscilloscope
system affects the accuracy and fidelity of the voltage measurement.
Table 1: Typical characteristics of common probes
Probe
Description
Attenuation
Ratio
Total Input
Resistance
Total Input
Capacitance
10X probe
10:1
10 MΩ
1 to 25 pF
1X probe
1:1
1 MΩ
100 to 200 pF
Best Used For
Low-to-high amplitude
DC-to-high frequency
Very low-to-medium amplitude
DC-to-low frequency
For most measurements, the 10X probe is utilized because its high effective input resistance lessens
the load effect on the test circuit, and its low input capacitance allows higher frequencies to be
measured. On the other hand, the large attenuation factor makes measurements of very low
amplitude signals less accurate.
If the voltage level of the input signal is tiny, then a 1X probe may be a better choice because there
is no attenuation through the probe. However, the 1 MΩ input resistance imposes a larger loading
effect and the high input capacitance limits the frequency range.
16
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Probe Compensation
Some probes have a built-in compensation network that can be adjusted to better match a probe’s
unique operating characteristics to the oscilloscope’s inputs. Use the following procedure to
compensate a probe:
1. Connect the probe to the desired input channel on the oscilloscope.
2. On the front panel of the oscilloscope, attach the probe’s tip to the Probe Comp terminal and the
probe’s ground lead to the chassis ground terminal. On the TDS2000 series, the terminals are
located by the Channel 1 input connector. PROBE COMP generates a 5 volt square wave at 1 kHz.
3. Push the AUTOSET button to acquire the test signal.
4. Use the probe’s adjustment tool to make the square wave have a flat top.
Over compensated
Under compensated
Properly compensated
Figure 4: Effects of probe compensation on a square wave
17
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
5 – Simplified Measurement Procedure
1. Before making any connections, verify that the test circuit will not produce voltage or current levels
that could damage the oscilloscope.
2. Turn on the oscilloscope. The instrument is more accurate if allowed to warm up for a while.
3. Choose probes that are appropriate for the measurement. Each channel requires a separate probe.
4. For each channel that will be used:
a. Attach the probe’s BNC connector to an input connector on the oscilloscope.
b. If necessary, configure the coupling and attenuation factor for the channel.
c. If the probe has a built-in compensation network, then compensate the probe.
(Perform compensation whenever a probe is connected to the oscilloscope for the first
time.)
d. Connect the probe to the test circuit. If you will be working with static-sensitive parts, then
wear a grounding strap before making the connections.
i. Attach the ground clip of the probe to a ground point in the circuit.
ii. Attach the probe tip to the voltage measurement point in the circuit.
5. If the test circuit is not turned on yet, then apply power to the circuit.
6. Adjust the oscilloscope’s controls to achieve a stable display of the waveform.
(The Autoset button can be used to get a reasonable initial display.)
7. Voltage measurements are done by counting the number of graticle divisions that a waveform spans
in the vertical direction. Timing measurements are performed similarly in the horizontal direction.
(The Measure button can be used to automate common signal measurements.)
18
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
6 – Saving Waveforms to a USB Drive
Pressing the Save/Print button on the front panel of the oscilloscope can quickly save a measured
waveform to an attached USB drive. Depending on how the button is configured, it can store the data in
the following formats:
•
Screen image
A screen image is an exact copy of what is currently being shown on the LCD screen, including the
annotations around the perimeter of the graph and the menu options. Be sure to adjust everything
to your liking before saving. A captured screen image can be pasted directly into reports.
•
CSV file
A CSV file is just a text file with the data stored in Comma Separated Values format:
o
o
o
o
o
Column 1:
Column 2:
Column 3:
Column 4:
Column 5:
Defines labels for selected measurement setup parameters
Holds actual values of the parameters at the time of the screen capture
Empty
Holds the time axis (horizontal) values
Holds the voltage axis (vertical) values
The file can be imported into applications like Excel or MATLAB for further analysis.
Option 1: Configuring the Save/Print Button to save only screen images
1. Press: Utility button → Options → Printer Setup
2. Select PRINT Button multiple times until “Saves Image To File” appears.
3. Select File Format multiple times until the desired image type (e.g., JPEG) appears.
OPTIONAL:
4. Select Ink Saver and choose “On” to invert the saved image’s background from its normal black to
white, or choose “Off” to keep the background black.
5. Select Layout and choose either “Portrait” or “Landscape” orientation.
Option 2: Configuring the Save/Print Button to save both screen images and CSV data
1. Press: Utility button → Options → Printer Setup
2. Press: PRINT Button multiple times until “Saves All to Files” is selected.
3. Select the desired File Format, Ink Saver, and Layout settings (see previous section).
19
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Using the Save/Print Button to save waveforms
1. Insert a formatted USB drive into the oscilloscope’s front USB port.
2. Adjust the oscilloscope to get a good waveform displayed on the screen.
3. Press the Save/Print button to save the waveform to the USB drive.
Note: After a few seconds, a “clock” icon will appear on the screen. It will then take several more
seconds before the data is finally saved and the normal menu options reappear.
Warning: Wait until the clock disappears before removing the USB drive.
→ If the Save/Print button is configured to save only screen images
A file named TEKnnnn.xxx is created on the USB drive each time the Save/Print button is pressed. nnnn
is a number from 0000 to 9999. It starts at 0000 and is automatically incremented. xxx is the extension
of the image format, e.g., JPG.
→ If the Save/Print button is configured to save both screen images and CSV data
A directory named ALLnnnn is created on the USB drive each time the Save/Print button is pressed.
nnnn is a number from 0000 to 9999. It starts at 0000 and is automatically incremented.
These files are stored within the ALLxxxx directory:
•
FnnnnCHm.CSV (m is the channel number)
This is the CSV file containing the raw measured data. Each active channel is stored in its own file.
•
FnnnnTEK.xxx (xxx is the extension of the image format, e.g., JPG)
This is the actual screen image file.
•
FnnnnTEK.SET
This contains some additional oscilloscope settings.
20
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
7 – Saving Waveforms to a Computer
Although the TDS2000 series of oscilloscopes can save data to a USB drive, it also supports data transfer
to a computer over a USB cable. Tektronix makes software called OpenChoice Desktop that runs on a
Windows-based computer to control the oscilloscope and initiate screen image and/or data capture.
Starting OpenChoice Desktop
1. Verify that OpenChoice Desktop has been installed on the computer, along with the TekVISA driver.
2. Connect one end of a standard A/B USB cable to the USB port on back of the oscilloscope and the
other end to an available USB port on the computer4.
3. Turn on the oscilloscope and let it fully initialize before running OpenChoice Desktop.
4. Run the OpenChoice Desktop software.
The application window (Figure 6) presents an interface with tabs on top, command buttons on the left,
and the screen image/data area on the right. The default tab is “Screen Capture”.
Figure 6: OpenChoice Desktop startup window
Figure 5: Pop-up for selecting instrument
The upper left area of the window should display the name of the connected instrument that will
generate the screen image or waveform data.
Note: If the desired instrument name (e.g., TDS 2014C) is not shown, then follow this procedure:
1. In the main application window, click the [Select Instrument] button.
2. When the Select Instrument pop-up dialog (Figure 5) appears, look for an entry that starts with
“USB0::”. Select that item and click the OK button.
4
The computer communicates with the oscilloscope using the USBTMC-GPIB protocol and SCPI commands.
21
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Using OpenChoice Desktop to get a screen image
1. Click the “Screen Capture” tab.
2. Click the [Get Screen] button to initiate the screen image transfer to the computer.
3. Click [Save As] to save the screen image as a file (jpg, png, bmp, or tif) on the computer’s local drive.
Figure 7: Screen image capture
Using OpenChoice Desktop to get waveform data
1. Click the “Waveform Data Capture” tab.
2. Click the [Select Channels] button.
3. When the Select Channels pop-up dialog (Figure 8) appears, select the channels you want and click
the dialog box’s Get Data button to initiate the data transfer to the computer.
Note: To capture another waveform, click the [Get Data] button on the main application window.
4. Click [Save As] to save the waveform as a file (CSV or tab-delimited text) on the computer’s drive.
Figure 8: Pop-up for selecting channels
Figure 9: Waveform data capture
22
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Appendix 1 – Specifications
Table 2: Manufacturer’s instrument specifications
Model
Bandwidth
Channels
Sample rate on each channel
VERTICAL SYSTEM
Record length
Vertical resolution
Vertical sensitivity
DC vertical accuracy
Maximum input voltage
Position range
Bandwidth limit
Input impedance
Input coupling
HORIZONTAL SYSTEM
Time base accuracy
TRIGGER SYSTEM
Trigger modes
Trigger types
Trigger source
ACQUISITION SYSTEM
Acquisition modes
TDS2014C
100 MHz
4
2 GS/s
2.5K points
8 bits
2 mV to 5 V/div
±3%
300 VRMS CAT II; derated at 20 dB/decade above 100 kHz
to 13 Vp-pAC at 3 MHz
2 mV to 200 mV/div +2 V;
>200 mV to 5 V/div +50 V
20 MHz
1 MΩ in parallel with 20 pF
AC, DC, GND
50 ppm
Auto, Normal, Single Sequence
Edge (rising/falling), Video, Pulse width
CH1, Ch2, CH3, CH4, Ext, Ext/5, AC line
Peak detect, Sample, Average, Single sequence, Roll
mode
WAVEFORM MEASUREMENTS
Automatic measurements
Cursors
WAVEFORM MATH
Operators
Sources
FFT
Autoset menu
Period, Frequency, +Width, -Width, Rise Time, Fall Time,
Max, Min, Peak-to-Peak, Mean, RMS, Cycle RMS, Cursor
RMS, Duty Cycle, Phase, Delay
Types: Amplitude and time
Measurements: ∆T, 1/∆T, ∆V
Add, Subtract, Multiply, FFT
CH1-CH2, CH2-CH1, CH3-CH4, CH4-CH3,
CH1+CH2,CH3+CH4, CH1×CH2, CH3×CH4
Windows: Hanning, Flat Top, Rectangular
2048 sample points
Single-button, automatic setup of all channels for
vertical, horizontal, and trigger systems
23
Tektronix TDS2000 Series Oscilloscope Guide v1.0
Portland State University
Appendix 2 – References
[1]
Tektronix TDS2000C Series Data Sheet, Tektronix, Inc.
[2]
TDS2000C and TDS1000C-EDU Series Digital Storage Oscilloscope User Manual , Tektronix, Inc.
[3]
XYZs of Oscilloscopes - Primer, Tektronix, Inc.
[4]
ABCs of Probes - Primer, Tektronix, Inc.
24