* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Equivalent circuits [Compatibility Mode].
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
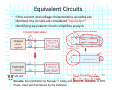
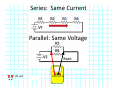
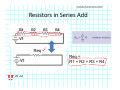
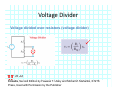
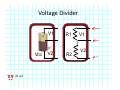
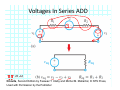
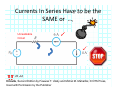
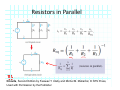
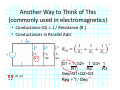
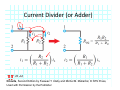
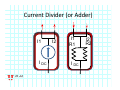
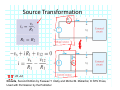
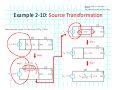
Introduction to Electrical & Computer Engineering Equivalent Circuits Dr. Cynthia Furse University of Utah 1 Equivalent Circuits • Equivalent V and I • Series & Parallel – Resistance & Conductance – Voltage & Current Sources • Voltage & Current Dividers • Equivalent Sources 2 Equivalent Circuits • If the current and voltage characteristics at nodes are identical, the circuits are considered “equivalent” • Identifying equivalent circuits simplifies analysis Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, Used with Permission by the Publisher Series: Same Current Parallel: Same Voltage VΩ com A All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Resistors in Series Add Req Req = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4 Voltage Divider Voltage divided over resistors (voltage divider) Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, Used with Permission by the Publisher Voltage Divider V1 VDC V2 R1 R2 V1 V2 Voltages In Series ADD Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, Used with Permission by the Publisher Currents In Series Have to be the SAME or …. Unrealizable Circuit Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, Used with Permission by the Publisher Resistors in Parallel Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, Used with Permission by the Publisher Another Way to Think of This (commonly used in electromagnetics) • Conductance (G) = 1 / Resistance (R ) • Conductances in Parallel Add G1 G2 G3 G1 = 1 G2= 1 G3= 1 R1 R2 R3 Geq=G1+G2+G3 Req = 1 / Geq 11 Current Divider (or Adder) Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, 12 Used with Permission by the Publisher Current Divider (or Adder) I1 I DC I2 I1 R1 I DC I2 R2 Voltages in Parallel Have to be the SAME or …. Unrealizable Circuit Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, Used with Permission by the Publisher Source Transformation Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, Used with Permission by the Publisher All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Example 2‐10: Source Transformation Equivalent Circuits • Equivalent V and I • Series & Parallel – Resistance & Conductance – Voltage & Current Sources • Voltage & Current Dividers • Equivalent Sources 17 Rim of Snow Canyon Saint George, Utah 18