* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inferior position in Eurasian Commerce
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
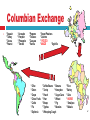
THE WEST AND THE WORLD The effects of Columbus’ Voyages European Empires in America Distinctive because they conquered territories located an ocean away From the voyages of Columbus to the mid-18th century, Europeans extended empires to encompass most of the Americas The European Advantage Geography Countries on the Atlantic rim (Portugal, Spain, France, and Britain) were closer than Asian competitors Used the fixed winds in the Atlantic which blew in same direction Need to Expand Population recovered from plague and needed more grain, sugar, meat, fish etc. “Europe needed a large land base to support the expansion of its own economy.” Chinese and Indian merchants were prosperous in the Indian Ocean trade so their wasn’t any incentive to go beyond Inferior position in Eurasian Commerce Europeans were aware of their inferior position in Eurasian commerce Muslim world controlled the Spice Trade They want to catch up Rivalry Intense rivalry drove rulers to compete Wealth and Status Colonies were an opportunity for impoverished nobles and commoners Religion Crusading zeal “We came here to serve God and the King, and also to get rich. Spanish conquistador Persecuted minorities looking for freedom European states mobilized resources Seafaring technology Iron, gunpowder weapons, and horses Rivalries within the Americas Divisions within and between societies provided the Europeans with allies Ex. Aztec Empire and Dona Marina Ex. Violent dispute for the Incan throne between Atahualpa and Huascar Meeting of Montezuma and Cortes with Dona Marina Germs and Disease Native Americans had no immunities Ex. Europeans outnumbered natives in Caribbean, Virginia, and New England within a few decades Vermeer’s Geographer A moment in time Look for objects from the Age of Discovery Conveys the excitement of scholarly inquiry and discovery Vermeer’s Astronomer Look for objects for the study of astronomy Who led the way in Exploration? Portugal Prince Henry the Navigator Bartolomeo Dias Founded navigational school Explore the West Coast of Africa 1st to round tip of Africa Vasco Da Gama 1st to find route to India around Africa Leads to 27,000 mile route Christopher Columbus Believed Earth was smaller Estimated Japan approximately 2,500 miles west of Canaries (actually 10,000 miles) Thought sailing west would be profitable Portuguese kings do not fund proposed westward trip Fernando and Isabel of Spain underwrite voyage Dias had already found the route Sailed south to Canary Islands, picked up supplies and turned west Discovers Bahamas and Cuba Called the natives, Tainos, “Indians” Insisted after 3rd voyage to South America that it was part of Asia Wind Patterns in the World’s Oceans How crucial was an understanding of the world’s wind patterns to the success of European overseas expansion? Amerigo Vespucci Italian explorer, financier, navigator, and cartographer who explored the coast of Brazil The 1st to demonstrate that Brazil and West Indies were a separate landmass from Asia Circumnavigation of the Globe Magellan Sailed for Spain Sails through Strait of Magellan, tip of South America Crew assailed by scurvy Sailed for 4 months before new provisions Ate worm-ridden biscuits, leather softened in the ocean, water that had gone foul Ate rats, ox hides dragged through the sea for 5 days, No fruit/veggies Rotting of gums, loss of teeth, abscesses, hemorrhaging, death 29 died from it Magellan and 29 crew members killed in local dispute in the Philippines Of his 5 ships and 280 men, 18 crew members return Establishment of the Trading-Post Empires Portugal is the 1st to establish one in W. Africa and E.Asia Afonso d’Alboquerque was the architect of trade duties policy Seized ports by force in Indian Ocean Forced merchant ships to buy safe-conduct passes Ships w/out passes were subject to confiscation and violators punished by Portuguese control declines in 16th century Although heavily armed, never had enough vessels to enforce orders England, Netherlands became most prominent in Indian Ocean trade Afonso d’Alboquerque Dutch and English Dutch and English were more important to spice trade in 17th c. 1. 2. Displace Portuguese by force as well as compete w/ each other Sailed faster, cheaper, and more powerful ships Conducted trade with joint-stock companies Why is this an advantage? The Dutch in 16th century Highly commercialized and urbanized Business and maritime shipping operations were envy of Europe Sought to control spice trade but also the production of cloves, cinnamon, nutmeg, and mace Control spice-producing islands, forcing the people to only sell to them Brutality over “nutmeg” Banda Islands of Indonesia Originally the only place nutmeg grew Used not only as spice, but as fragrance to get rid of smells EX. 17th c. plagues Dutch kill, enslave, or starve the population of 15,000 and replace them w/Dutch planters and slave labor Workers are harvesting mace, a spice derived from nutmeg trees that are indigenous to the Banda Islands of Indonesia. Until the 19th c., these islands were the world's only source of this valuable spice. The Columbian Exchange Named for Christopher Columbus Global diffusion: Plants and crops Animals Human populations Disease pathogens Permanently alters human geography, natural environment Tobacco was long used for religious and spiritual purposes in the Americas. After their arrival in the Americas, Europeans quickly popularized tobacco as a trade item and as a recreational drug to be smoked, snuffed, or chewed. Columbian Exchange * Squash * Turkey * Cocoa * Peanut * Avocado * Pumpkin * Pineapple * Tomato * Peppers * Tobacco * Cassava * Vanilla * Sweet Potatoes * Quinine * POTATO * MAIZE * Syphilis * Olive * Coffee Beans * Banana * Onion * Turnip * Honeybee * Grape * Peach * Sugar Cane * Citrus Fruits * Pear * Wheat * Cattle * Sheep * Pig * Flu * Typhus * Measles * Diptheria * Whooping Cough * Rice * Barley * Oats * HORSE * Smallpox * Malaria World Population Growth, 1500-1800 CE 900 800 700 600 500 Millions 400 300 200 100 0 1500 1600 1700 1800 Epidemic Disease and Population Decline Smallpox Also measles, diphtheria, whooping cough, influenza No prior exposure, no immunity to these diseases in western hemisphere or Oceania Ex. 1519 smallpox in Aztec Empire Population declines 90% within 100 years (17 million to 1.3 million) Human Population Migrations Largest forced migration in history: Atlantic Slave Trade European Pioneers