* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4: Similarity Study Guide Simplifying ratios: be sure to convert to
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
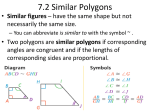
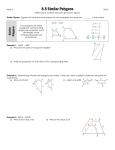
Unit 4: Similarity Study Guide Simplifying ratios: be sure to convert to the same units of measurement first Solving proportions for a variable: cross multiply then solve for the value of the variable Scale factor: ratio of the lengths of two corresponding sides of two similar polygons Properties of Proportions (1) a c b d is equivalent to . b d a c a c a b is equivalent to . b d c d a c ab c d (3) is equivalent to b d b d Theorem Similar polygons Description Two polygons are similar if corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding side lengths are proportional Angle-Angle Similarity (AA ~) If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the two triangles are similar. (2) How to Apply It (1) Take the reciprocal of each ratio “flip” each ratio (2) switch the means (3) add the denominator to the numerator Image K Y and J X Side-Angle-Side Similarity (SAS ~) If two sets of corresponding sides are proportional and the included angle is congruent, then the triangles are similar. AB AC and A Q QR QS Side-Side-Side Similarity (SSS ~) If all three corresponding sides are proportional, then the triangles are similar. AB AC BC QR QS BS Side-Splitter Theorem If a line is parallel to one side of a triangle and intersects the other two sides, then it divides those sides proportionally. XR YS RQ SQ Corollary to the Side-Splitter Theorem If three parallel lines intersect two transversals, then the on segments intercepted the transversals are proportional. AB WX BC XY Perimeters and Areas of Similar Figures Scale factor: ratio of the lengths of two corresponding sides of two similar polygons Ratio of Perimeters = Scale Factor Ratio of Areas = Scale Factor 2