* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TLS Exam Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
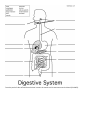
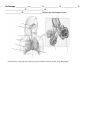
Name:_________________________________________________________________ Date:_____________ TLS Final Exam Review Sheet Anatomy, Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary System The levels of organization in the body include: ______________ ______________ _______________ _________________. At each level of organization, these parts of the body work together to carry out the major body functions. __________ - basic unit of structure and function in living things, are specialized in multicellular organisms and have parts called organelles (YOU SHOULD KNOW THESE….mitochondria, ribosomes…...) __________– a group of cells that perform a single function. There are 4 basic types in the human body Tissue _______________ ______________ ______________ _____________ Definition How to Remember Tissue that supports and connects body parts – most abundant and diverse tissue in the body. Connective tissue CONNECTS Tissue that lines the interior and exterior body surfaces (coverings and linings) Epithelial tissue covers all the edges Tissue responsible for movement (contracts). Movement and Muscle begin with M Tissue that receives, processes, and transmits messages. Nerves are long fibers in the body that carry messages, similar to long phone lines that carry sound _________- group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a single function _______________ – group of organs that perform closely related functions. Organ systems interact to maintain homeostasis in the body as a whole Body Cavities Many organs and organ systems in the human body are housed in compartments called __________________ These cavities _______________ internal organs There are _____ main body cavities: _________________: contains, supports, and protects the brain _________________: contains, supports, and protects the spinal cord _________________: contains, supports, and protects the heart, esophagus, and the organs of the respiratory system _________________: contains, supports, and protects the digestive system _________________: contains, supports, and protects the organs of the reproductive and excretory systems Label all the bones on the skeleton Word Bank: Sternum Vertebra Skull Humerus Patella Carpals Pelvis Tibia Ulan Tarsals Metatarsals Clavicle 1. List two functions of the skeletal system: Ribs Metacarpals Fibula Mandible Femur Phalanges Radius Scapula 2. List and describe the two parts of the skeletal system: 3. The tough membrane that covers bones is called the __________________________. 4. _______________ ________________ are a network of tubes running through compact bone that contain blood vessels and nerves. 5. Bone cells are called _______________________. 6. _________________ marrow contains blood vessels, nerves, and fat cells. 7. _________________ marrow produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. 8. The process by which bone is formed called _______________________. 9. The _____________________ ___________________is a region of a long bone where new cartilage is formed, lengthening the bone. 10. Two places where cartilage remains after 18-20 years are: ______________________ 11. Complete the following table: JOINT TYPES Fixed Semimovable Movable Hinge Ball & Socket Pivot Angular Gliding 13. ______________________ hold bones of a joint in place. EXAMPLE Muscular System: Label the muscles on the diagram below Word Bank: (use letters) Tricpes A Biceps B Deltoid C Quadriceps F Hamstrings G Gastrocnemius H Pectorals K Obliques L Can you identify any additional muscles??? Trapezius D Rectus abdominis I Lattimus dorsi E Gluteus maximus J 1. List two functions of the muscular system: 2. Complete the following table with regard to muscle types: Muscle Type Striated or Voluntary or Single or Non-striated Involuntary Multinucleated Where Found Skeletal Cardiac Smooth 3. Distinguish between voluntary and involuntary with regard to muscle control. 4. Distinguish between flexor and extensor with regard to muscle action. 5. What connects muscles to bone? 6. What is the pair of muscles involved in lifting a dumbbell from the sides of your body to your shoulders and back again? Integumentary System 1. What are some of the functions of the integumentary system? 2. What is the name of the pigment that determines skin color? ____________________ 3. What are hair and nails primarily composed of? __________________ 4. What are exocrine glands? 5. What are the main exocrine glands of the skin, and what is the function of each? 12. Please label the following skin diagram: Word Bank: Sweat gland Hair shaft Epidermis Oil gland Dermis Subcutaneous tissue Hair follicle Digestion and Excretion Question 1. Nutrients provide the body with the energy and materials it needs for 2. Most of the body’s energy needs should be supplied by dietary 3. What is the common passage way for both food and air and where is it located? 4. What are the functions of the digestive system? 5. What do we call the ball of food that is swallowed? 6. Where does chemical digestion begin? 7. What enzyme begins to chemically break down carbohydrates? 8. What are the wavelike contractions of muscle that move food through the digestive system? 9. What is bile? 10. Where is it made? Where is it stored? 11. Pepsin and HCL begin the digestion of ________ in the _______. 12. What are the fingerlike projections of the small intestine called? 13. What do they do? 14. Where is urea formed? 15. What is the functional unit of the kidney? 16. What is the first stage of urine formation called? 17. How does urine leave the body? 18. Where is it stored until it can leave? 19. What connects the kidneys to the bladder? 20. What organs do food actually pass through? 21. What are the accessory organs of digestion? Answer Trace the path of a bite of food from the time it enters the mouth until its nutrients enter the blood (5 POINTS). Kidney Bladder Urethra Ureter Starting with the kidney trace the path of urine out of the body (2 POINTS). Circulatory and Respiratory System Review Sheet 1. What is the function of the circulatory system? 2. Distinguish between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. 3. Fill in the chart below to describe the types of blood cells and the function of each Cell Type Description Function Erythrocytes Leukocytes Platelets 4. Explain what blood plasma is, what it is made of, and its major functions. 5. Identify each of the blood vessels below and tell the function of each: C A B 6. Label the picture of the heart below: D E C F G B H I A J 7. Tell which of the structures above carry oxygen-rich blood and which carry oxygen-poor blood. 8. Trace the path of a drop of blood, starting from the superior vena cave until it returns to the superior vena cava. (Assume that it passes through the head at one point.). Name all the major structures through which it passes. Use RED for oxygenated blood and BLUE for deoxygenated blood Superior vena cava ________________ ______________ ________________ __________________ ________________ _________________ __________________ _________________ ________________ __________________ _________________ _____________ _________________ _______________ _______________ . Question 1. Pumping chambers of the heart 2. Vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs? 3. Heart chamber that receives blood from the vena cava 4. Vessels that carry blood away from the heart 5. Vessles that contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood 6. Blood cells that do not contain a nucleus 7. Circulation from the heart to the? 8. Blood cells that transport gases 9. Blood cells that fight infections 10. Involved in the clotting process 11. Blood cells that contain hemoglobin 12. Alveoli are connected to the bronchi by the ? 13. Muscle below the lungs 14. Site of gas exchange 15. Tiny air sacs in the lungs Answer Air Passage: ____________or___________ ______________ _______________ __________________ ________________ _______________ __________________ (where gas exchange occurs) Label all parts: nose, pharynx, trachea, larynx, bronchiole, bronchi, alveoli, lungs, diaphragm