* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DEVELOPING A UBIQUITOUS ACCESS OF E-CONTENT
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
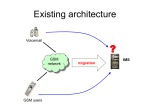
PROPOSAL SUBMITTED TO MHRD GOVERNMENT OF INDIA, UNDER THE NME-ICT DEVELOPING A UBIQUITOUS ACCESS OF e-CONTENT BY DEPLOYING A WiMAX APPLICATION WITH IMS PROPOSAL SUBMITTED BY PROF. V. PRITHIVIRAJ, PRINCIPAL PONDICHERRY ENGINEERING COLLEGE, PUDUCHERRY. OUTLINE Overview Proposed architecture Soft switches Migration from soft switch to IMS IMS WiMax Wireless Mesh Justification and importance of the project Time Frame Estimated budget OBJECTIVES To develop IMS application on Laptops, PDAs and Cell phones. To Develop and implement IMS network. To interwork WiMAX with IMS as core network for accessing the eContents. To install and test the performance of the WiMAX - IMS setup. To integrate Wireless mesh network with IMS and Wimax in the foliage environment To achieve seamless connectivity for the accessing the e-Content material by establishing WiMAX. OVERVIEW OF THE PROPOSAL IMS(IP Multimedia Subsystem) is used to deliver the e-Contents to the user equipment. It acts as the core network. Wireless Mesh Network is used to deliver the e-Contents at last mile since it will reach the mobile devices even in the dense foliage environment. To deliver this e-Content to a extension center located far away from the university, Wimax is used. Wimax has high bandwidth and can be transmitted over long distances. PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE FEATURES OF THE PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE Open source User-centric services Extensive to stay ahead Linked with the operator environment Soft switch A softswitch is a central device in a telecommunications network which connects calls from one phone line to another Soft switches run on commercial computers and operating systems, and they provide open applications programming interfaces. Soft switch architecture separates service control from service access and uses an IP-based core layer in the switching network SOFT SWITCH vs IMS Features of soft switch Integration/Incorporation Convergence of voice and data Combination of telecom & internet technologies Reuse PSTN database & IN services in packet networks Multiple sources for app development & deployment Decreased operating costs Standardization Standard interfaces (protocols) for communications Open standards (APIs) for service creation Customized services created by users themselves Better scalability Migration from Soft switch to IMS Step 1: The softswitch is decomposed into two logical components subscriber facing unit to AGCF PSTN facing unit to MGCF By separating the softswitch into these components, the network can be more easily scaled for better overall network efficiencies Migration from Soft switch to IMS Step 2: Addition of SIP based services by deploying AS. Step 3: SIP end points are added to provide the users with high QOS. SIP end points are connected with PCSCF which is connected to policy server. Policy server provide the required Qos and Security. Migration from Soft switch to IMS Step 4: Fixed/Mobile convergence FMC will address the business needs relating to Triple play service. HSS is added to the network to maintain the user database. It maintains the subscribers data uniformly between cellular and ip network. IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM(IMS) IMS defines a complete architecture and framework that enables the convergence of voice, video, data and mobile network technology over an IP-based infrastructure It fills the gap between the two most successful communication paradigms, cellular and Internet technology IMS ARCHITECTURE Applications Services IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Sh AS Operator 2 HSS HLR Mw Si IM-SSF Presence Mk Dh Sh BGCF SLF Cx OSA-SCS Dx Mi Mj Mm IM Mg Gq Ut Gm IMS Terminal PDF Gr Gc MRFC Mn Mp MRFP Wx MGW „Mb/Gi-Cloud“ Uu UTRAN / GERAN Mr Go CAP WLAN Access, WAG MGCF CSCF ISC Ww, Wu Multimedia IP Networks BGCF CSCF AAA GGSN Wm Gn Iu SGSN CS-Domain -orPSTN -orLegacy -orExternal PS-Domain PDGW Wu, Wp WLAN (Home) IMS Based Video Telephony HS S Cx Cx Mw ICSCF SCSCF Mw Mw PCSCF OK SIP Request WiMAX Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access Killer’ technology in every sense of the word! Non-line-of-sight standard and can cover tens of miles Advantages of QoS in WiMax Low latency for mission-critical and mission-non critical applications Data prioritization (Bandwidth management) Optimized transmission of specific applications such as video, and voice PROPOSED ARCHITECTUREFor University Extention Centre WIRELESS MESH WMN consists of access points and clients. The clients connect through these access points either directly or in multi hop fashion which enables the network to have a wide coverage compared to the traditional networks. Provides an excellent solution for last mile connectivity in difficult terrain like dense foliage Highly reliable and robust in nature. Wireless Mesh Network Proposal IMS can provide access to multimedia content. Wireless Mesh can be used in a dense foliage environment so that a user can access the e-Contents even if he is sitting under the tree or in the foliage environmet or in any place in the university campus. Wimax can be used to transmit it for longer distances. So it is possible to access the e-Contents from the university extention centres. With the use of technologies ie., integrating IMS, WiMax and the Wireless Mesh, the e-Contents can be delivered to the any user equipment such as laptop, PDA and other devices. Feasibility of IMS The IMS technology has been implemented and tested by many service enablers such as Ericsson, Nokia Siemens, Alcatel Lucent, etc. Many testing procedures are also introduced to check their working and they are quite successful. Since IMS can be interfaced with any access network, the issue of incompatibility would not arise. Justification & importance of project With WiMAX as the access network a wide coverage area of about 50 kms is possible. Hence access to the econtent is made available to everyone. Interworking WiMAX with IMS as the core network provides the end user with access equipment independent service The mesh network provides an excellent solution for last mile connectivity in difficult terrain like dense foliage. Hence the user can access the e-content with different equipments such as Laptop, Mobiles, PDAs, iPOD, etc. Year wise contribution to the project I year: Interface between server with desktops, laptops in a seamless fashion using the IMS interface for multimedia e-Content within in the University building premises. II year: To deliver the same content over laptops, tablet pc's, PDA's and cell phones with suitable communication software interface within the 800acres campus situated in the midst off very robust foliage environment for seamless operation and delivery of multimedia content with appropriate content. Extention of the e-Content delivery to a remote station(University extention centre located 25 to 50 kms away from the main campus) using WiMax. Year wise contribution to the project-Contd., III year: Using the modellling and simulation attempted in the second year for IMS content delivery on several laptos, tablet pcs, PDA's etc., it is proposed to interface IMS with WiMax at the remote station(University extention centre) for last mile delivery. IV year: As there is a distinct possibility of extention centre being situated in a totally different environment from the university premesis it is proposed to model the surrounding terrain and the environment for accessing the multimedia e-Content in a seamless fashion. V year: To integrate the entire activity( I,II, III, IV) in a holistic manner and complete the entire system model. Time frame for development Case study - 5 months Procuring Equipment - 10 months Installing - 4 months Testing - 5 months Implementation - 12 months In addition, testing of the implemented system in real time environment would be done for a period of two years. Hence the total required time period is about five years approximately. NON RECURRING BUDGET S.No. Equipment Name 1. IMS Hardware Sun V890 machine, Ultra SPARC IV Processor Ultra SPARC IV+ Processor, External Cache per Processor Memory ,10,000 RPM FCAL Disk Drive, 16X DVD-ROM Drive, Gigabit Ethernet Port Ethernet Port 1@10/100 Base-T1@10/100, Serial Port RS232C/RS-423 via splitter cable SB Port , PCI Slots , Power Supply 2. 3. IMS Software Solaris OS CFX 5000 Cost in Rs. (In lakhs) 600 60 WiMAX (Hardware & Software) 400 4. Gadgets and Equipments 500 Total 1560 RECURING BUDGET S.No. Item 1. Engagement of Human resources and materials 4 years 10 2. Travel 4 years 10 3. Contingency 4 years 10 4. Miscellaneous 4 years 10 Total Duration Cost in Rs.(In lakhs) 40 Total: Recurring + Non recurring = 1600lakhs. Estimated budget for implementing Soft switch: Sl.No 1. Item Approx. Cost (In Lakhs) IBM Server and Software 60 (For Soft switch) 2. Wimax and WiFi 50 3. Wireless Mesh Access Points and Routers 30 4. Tablet PC 2.1 5. Laptops 1.2 6. Desktops 0.6 7. PDA 0.8 8. Cell Phone ipod 0.3 9. HR and other expenses 5 Total 150 Work already done by Principal Investigator Five Research Projects between the two IITs involving DRDO, ISRO and Department of Electronics, Three MHRD / AICTE projects are undertaken at PEC and one grant in research project on “Secure Communication Using Chaotic Cryptography” sponsored by Department of Information Technology, Ministry of Communication and Information Technology, New Delhi to the tune of Rs.16.75 lakhs Govt. of India. Publications of PI JOURNALS Thenmozhi K, Prithiviraj V, “Suitability of Coded Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (COFDM) for Multimedia Data Transmission in Wireless Telemedicine Applications” IEEE Computer Society 2007, ISBN 0-7695-30508. 288-292 Gerardine Immaculate Mary, Prithiviraj V, “An effective approach for precision automobile parking system” International of systemic, cybernetics and informatics, 2007: 29-32 Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Prithiviraj V, “IEEE 802.11a Physical layer implementation using OFDM” International Journal of Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics (IJSCI), October 2006, 57-60. Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Devasena L, Prithiviraj V, “DSP based implementation of Space Time Coded OFDM Systems” ,IEEE Explore, ISBN 1-4244-0322-7/06. Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Prithiviraj V , Shweta S, “MC-CDMA promises wireless broad band beyond 3G”, Electronic Engineering Times –Asia, August 2006(eetindia.com) Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R , Prithiviraj V, “COFDM Transceiver for Mobile Multimedia Communications”, BES Review, Vol XII, No.2 April-June,2006, 30-34.[This article was selected for EDI Award by Broadcast Engineering Society(I) Award Committee for the year 2007 for significant contribution in the field of art, science or technology of Radio & TV broadcasting ] Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Prithiviraj V, “COFDM for Multimedia Applications”, ACCST Research Journal, Vol. 111, No. 2, April 2005. Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Prithiviraj V,“FPGA implementation of COFDM Transmitter”, ACCST Research journal (in press) . Aravind T, Chandana Nilavan S, Prithiviraj V, “Security in computer communication using chaotic cryptography”, Proceedings of the 15th international conference on computer communication,2002, 643-653, Published in Handbook of Cryptography, CRC Press 2003(Citation). INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCES Thenmozhi K, Prithiviraj V, Hemalatha M, Bharadwaj D, Vignesh R, “Diversity reception for CDMA based mobile communication systems” 1st international conference on Wireless VITAE, 2009, 660-664 Manikandan K, Prasanna C, Saranesh S, Subramanian R,Prithiviraj V, “Front end design of software defined BTS for interoperability between GSM and CDMA”, 1st international conference on Wireless VITAE, 2009, 655-659 Immaaculate Mary G, Prithiviraj V, “Test measurements of improved localization technique for precision automobile parking” International conference on Recent advances in Microwave theory and applications, Microwave 2008, 550-553 Gerardine Immaculate Mary, Prithiviraj V, “ UWB localization techniques for precision automobile parking system”, 10th international conference on Electromagnetic interference and compatibility, INCEMIC 2008: 621-626 Gerardine Immaculate Mary, Prithiviraj V, “Improved UWB localization for precision automobile parking system”, IEEE region 10th conference TENCON 2008, 1-4 Gerardine Immaculate Mary, Prithiviraj V, “Smart electronic display using Bluetooth technology”, IEEE region 10th conference TENCON 2008 Thenmozhi K, Prithiviraj V, “ Suitability of Coded Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (COFDM) for Multimedia Data Transmission in Wireless Telemedicine Applications” International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Application (ICCIMA 2007), Mepco Schlenk Engineering College, Sivakasi, co-sponsored by IEEE Madras section, Tamil Nadu, December 2007. Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Devasena L, Prithiviraj V, “DSP based implementation of Space Time Coded OFDM Systems” International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS2006), University of Peradeniya, Sponsored by IEEE Sri Lanka Section, Sri Lanka, August 2006. Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Prithiviraj V, “Multi Carrier Code Division Multiple Access (MC-CDMA) Implementation Using Orthogonal Frequency Division Mutiplexing (OFDM)”, International Conference on Wireless Networking & Mobile Computing (ICWNMC ‘05), Velammal Engineering College in Association with IEEE Madras Section, December –2005. Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Prithiviraj V, “Suitability of Multicarrier Code Division Multiple Access (MCCDMA) for Broad band Wireless Communication Systems”, accepted for International Conference on Intelligent Systems (ICIS 2005) University Technology, PETRONAS, Malaysia, December-2005. Meenakshi pavithra V, Sakthipriya G, Prithiviraj V, “Real time guidance for indoor navigation using Bluetooth technology”, 44th Annual symposium on Engineering Trends in Wireless Networks, IEEE Bangalore section, 2005 Thenmozhi K, Varadarajan R, Prithiviraj V, Venkatesh V, “OFDM / COFDM for Wireless Telemedicine Application”, International conference on Telemedicine, ISRO, Bangalore, March-2005. Thenmozhi K, Karthighairasan M, Prithiviraj V,“Performance Analysis of OFDM/COFDM MODEM in Wireless Environment”, Conference on Wireless Communication and Sensor Networks, IEEE UP chapter, IIIT Allahabad, March2005 NATIONAL CONFERENCES Prithiviraj V, “Government Process Reform through Reengineering and Standardization for e-Governance - Implemented in Planning and Research Department, Government of Puducherry (GOP)”, 10th National Conference on eGovernance, Bhopal,2007 Thenmozhi K, Karthighairasan M, Prithviraj V, “OFDM/COFDM transceiver in Wireless Communication”, National Conference on Advances in Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Jayam College of Engineering & Tech., Dharmapuri, April-2005. Thenmozhi K, Karthighairasan M, Prithiviraj V, “VLSI Implementation of COFDM MODEM”, 36th Mid-term symposium “Emerging & Futuristic Communication Systems” IETE, Bangalore, April-2005. Karthighairasan M, Thenmozhi K, Prithiviraj V, “OFDM/COFDM Modem for Wireless Broadband Communication”, Second National Conference on Advances in Electronic Communications (ADELCO 2005), National Engineering College, Kovilpatti, April -2005. Thank you