* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kinesiology_Lab_files/Lab 5. The Knee
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
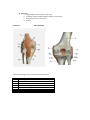
Lab 5 Anatomy of the Knee M ATERI ALS • human torso model • knee models • human skeleton • textbook and lecture notes for reference • Anatomage dissection table O BJECTIVES Upon the completion of these laboratory exercises, you should be able to: 1. Identify various anatomical structures of the knee joint. 2. Identify the muscles of the knee and thigh. 3. Apply biomechanical principles to the knee joint. 4. Identify origin, insertion, nerve innervation and actions of the knee joint. 5 . Apply kinisiological applications to common exercises. Key muscles of the thigh and knee joint iliacus sartorius pectineus rectus femoris(quad) vastus lateralis(quad) vastus medialis(quad) vastus intermedius(quad) biceps femoris (long head) biceps femoris (short head) semitendinosus semimembranosus Key boney landmarks of the thigh and knee joint. Femur: Head Neck Greater and lesser trochanter Linea aspera Medial and lateral condyles Intercodylar notch Medial and lateral epicondyles Adductor tubercle Patella: Anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments Medial and lateral meniscus Medial and lateral condyles: Tibial interarticular area Tibial tuberosity: medial condyle (pes anserine) Gerdy's tubercle Medial malleolus: Head Neck Lateral malleolus Tibia: Fibula: Anterior surface Articular surface: Facets Ligaments: Medial (tibial) lateral (Fibular) collateral ligaments Exercise 1. Review the following muscles on the Visible Body Application. Apply the proper nerve innervation and muscle actions. 1. Rectus femoris(quad) a. Origin:Anterior inferior iliac spine b. Insertion: tibial tuberosity c. Nerve innervation: femoral L2-4 d. Actions: 2. Vastus lateralis(quad) a. Origin: greater trochanter, linea aspera b. Insertion: lateral border of patella to tibial tuberosity c. Nerve innervation: femoral L2-4 d. Actions: 3. Vastus medialis (quad) a. Origin: lineas aspera b. Insertion: medial upper portion of patella to tibial tuberosity c. Nerve innervation: femoral L2-4 d. Actions: 4. Vastus intermedius (quad) a. Origin: upper 2/3 shaft of femur b. Insertion: tibial tuberosity c. Nerve innervation: femoral L2-4 d. Actions: 5. Biceps femoris (long head) a. Origin: ischial tuberosity b. Insertion: lateral condyle of tibia, head of fibula c. Nerve innervation: tibial part of sciatic(S1-3) d. Actions: 6. Biceps femoris (short head) a. Origin: linea aspera b. Insertion: lateral condyle of tibia, head of fibula c. Nerve innervation: common peroneal part of sciatic L5, S1,2) d. Actions: 7. Semitendinosus a. Origin: ischial tuberosity b. Insertion: anterior medial condyle of tibia ( pes anserine) Nerve innervation: tibial part of sciatic (L5, S1,2) c. d. Actions: 8. Semimembranosus a. Origin: ischial tuberosity b. Insertion: medial surface of shaft of tibia c. Nerve innervation: tibial part of sciatic (L5, S1,2) d. Actions: 10. Sartorius a. Origin: ASIS( anterior superior iliac spine b. Insertion: anterior medial condyle of tibia ( pes anserine) c. Nerve innervation: femoral L2,3 d. Actions Exercise 2. Knee Anatomy Label the following structures from the illustration above. Quadriceps tendon Patellar ligament Medial meniscus Lateral meniscus Medial collateral ligament (MCL) Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) Exercise 3. Muscles Sartorius Pectineus rectus femoris vastus lateralis biceps femoris (long head) biceps femoris (short head) semitendinosus iliacus Muscle Summary Table Joints effected Motion Created at Joints Anatomic plane of motions