* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Layered Network
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Communication protocol wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
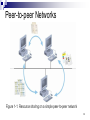
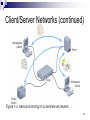
Layered Protocol Types of Networks by Logical Connectivity Peer to Peer and Client-Server Peer-to-peer Networks Every computer can communicate directly with every other computer By default, no computer has more authority than another Every computer is capable of sending and receiving information to and from every other computer 2 Peer-to-peer Networks Figure 1-1: Resource sharing on a simple peer-to-peer network 3 Type of Networks Client/Server Server: central computer used to facilitate communication and resource sharing between other computers on the network (called clients) Client/server network: uses a server to enable clients to share data, data storage space, and devices To function as a server, a computer must be running a network operating system (NOS) 4 Client/Server Networks (continued) Figure 1-2: Resource sharing on a client/server network 5 Client/Server Networks Advantages of using client/server networks over peer-to-peer networks: User logon accounts and passwords can be assigned in one place Access to multiple shared resources can be centrally granted to a single user or groups of users Problems can be tracked, diagnosed, and often fixed from one location 6 Client/Server Networks Advantages of using client/server networks over peer-to-peer networks (continued): Servers are optimized to handle heavy processing loads and dedicated to handling requests from clients, enabling faster response time Because of their efficient processing and larger disk storage, servers can connect more than a handful of computers on a network 7 Network Classification by Area PAN (Personal Area Network) Local area network (LAN): confined to a relatively small space, such as a building or an office Metropolitan area network (MAN): larger than a LAN; connects clients and servers from multiple buildings Wide area network (WAN): connects two or more geographically distinct LANs or MANs 8 LANs, MANs, and WANs Figure 1-4: A simple WAN 9 Network Topology 12 What is Communication Communication is successful when the message May have to agree on the Agree on the method used already received andlanguage confirmedused 13 Protocols Driving Force: need for different proprietary networking system to communicate Protocol: set of rules for acceptable behaviour to enable communication Specifically: the set of rules used by communicating parties for that communication to be successful Suite of protocols cover all required behaviour Mostly implemented in software Complexity demands that protocols are ‘layered’ 14 ISO/OSI Reference Model ISO in 1984 Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) A design guideline for network layering Abstract layers provide different services Defines 7 layers of service Each layer provides service to adjacent layers Each layer communicates with same layer in remote machine. 15 OSI Reference Model Application Layer Application Layer Presentation Layer Presentation Layer Session Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Transport Layer Network Layer Network Layer Link Layer Link Layer Physical Layer Physical Layer 16 OSI Model 17 OSI Layers 18 OSI Layers 19 OSI Layers 20 OSI Layers 21 OSI Layers 22 OSI Layers 23 OSI Layers 24 TCP/IP Model 25 Data Encapsulation 26 Data Encapsulation 27 OSI Layer vs. TCP/IP Layer 28 5-7 4 3 1-2 FTP – File Transfer Protocol HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol WAP – Wireless Application Protocol SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol TCP UDP IP e.g. IEEE 802.x 29 Packet Tracer Example of packet data unit (PDU) in layered network 30 Movie GoodWarriors 31 Quiz What are the differences between Circuit switching and packet switching Connection oriented and connectionless oriented Protocols What are they? Why do we layer protocols? ISO/OSI – 7 layer reference model How does the OSI abstract services? How does TCP/IP stack relate to OSI? 33 Topik IM & SIP protocol Dhcp & e-mail protocol p2p protocol ipv6 & packettracer Vlan rip & ospf Ns2, contoh aplikasi omnet++, contoh aplikasi 34