* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet #7
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
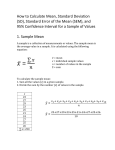
WORKSHEET #7 STA 291 Summer 2010 Confidence Intervals A confidence interval gives an estimated range of values which is likely to include an unknown population parameter, the estimated range being calculated from a given set of sample data. A confidence interval is based on three elements: (a) a value of a point estimator (the sample mean, etc.) (b) the standard error of the point estimator; and (c) the critical value of Z or t (e.g., the 95% confidence interval or the 99% confidence interval). Confidence Intervals for a single Mean (μ) for n≥30 𝑥̅ ± 𝑍𝛼/2 Sample Size 𝑠 √𝑛 Sample size needed to construct a 100(1-α)% confidence interval for μ or p with a margin of error of ME. 2 𝑍 𝛼/2 2 𝑛=𝑠 ( Examples 𝑀𝐸 ) A statistician wants to estimate the mean weekly family expenditure on clothes. He believes that the standard deviation of the weekly expenditure is $125. Determine with 95% confidence the number of families that must be sampled to estimate the mean weekly family expenditure on clothes to within $15. Suppose a sample with 50 observations yielded a mean of 30 and a variance of 100. What would be a 95% confidence interval for the true population mean? From a sample of 68 hot dogs it is found that Joey Chestnut can eat a hot dog and bun in 8.82 seconds. The standard deviation is 4.2 seconds. Determine with 99% confidence the average amount of time it takes him to each a hot dog and bun.