* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
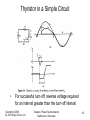
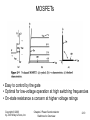
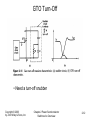
Chapter 2 Overview of Power Semiconductor Devices Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 Diodes • On and off states controlled by the power circuit Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-2 Diode Turn-Off • Fast-recovery diodes have a small reverse-recovery time Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-3 Thyristors • Semi-controlled device • Latches ON by a gate-current pulse if forward biased • Turns-off if current tries to reverse Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-4 Thyristor in a Simple Circuit • For successful turn-off, reverse voltage required for an interval greater than the turn-off interval Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-5 Generic Switch Symbol • Idealized switch symbol • When on, current can flow only in the direction of the arrow • Instantaneous switching from one state to the other • Zero voltage drop in on-state • Infinite voltage and current handling capabilities Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-6 Switching Characteristics (linearized) Switching Power Loss is proportional to: • switching frequency • turn-on and turn-off times Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-7 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) • Used commonly in the past • Now used in specific applications • Replaced by MOSFETs and IGBTs Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-8 Various Configurations of BJTs Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-9 MOSFETs • Easy to control by the gate • Optimal for low-voltage operation at high switching frequencies • On-state resistance a concern at higher voltage ratings Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-10 Gate-Turn-Off Thyristors (GTO) • Slow switching speeds • Used at very high power levels • Require elaborate gate control circuitry Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-11 GTO Turn-Off • Need a turn-off snubber Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-12 IGBT Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-13 MCT Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-14 Comparison of Controllable Switches Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-15 Summary of Device Capabilities Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-16