* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Graph Linear Equations Do Now Find the slope of each graph: 1. 2
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Median graph wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
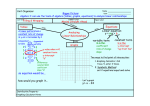
Graph Linear Equations Do Now Find the slope of each graph: 1. 2. Intercepts The place where a graph crosses over the x-axis is known as a x-intercept. Likewise, the place where a graph crosses over the y-axis is known as a y-intercept. Identify the x- and y-intercepts in the Do-Now graphs. Graph an Equation A linear equation can be written in slope-intercept form y = mx + b where m = slope and b is the y-intercept. Example: Find the slope and y-intercepts for the equations provided. Then graph the equation. y = 2x + 1 1 y = 3𝑥 – 3 y = -2x + 1 Graph Linear Equations Exercise: Graph a line with the information provided. Then state the equation of the line. 1. m = 1 and (-4, 2) Equation: 2 3 2. m = − and (-2, 1) Equation: 3. m = 3 and (2, 3) Equation: 2 Graph Linear Equations Notice that a linear equation in the slope-intercept form has a ‘y’ all by itself! Sometimes an equation needs to be rearranged so that we can reveal the true slope and y-intercept. Just like solving literal equations, keep your eye on the prize…get y by itself. Example: 2y + 3x = 8 Exercise: For each of the following, rearrange into y = mx + b form and then graph. 4. x + y = 4 5. x + 2y = 8 6. 3x – 4y = -4 7. 3y – 2x = -6 8. y = 4(x + 10) Graph Linear Equations Check points Sometimes a point won’t fit on the graph before you, but that doesn’t mean they don’t lie on the line (it does extend forever in both directions). Determine which points would 1 lie on the line 𝑦 = 2 𝑥 − 1 and which do not. (30, 14) (70, 28) (-30, -15) (-50, -26) Exercise: Circle all the ordered pairs (x, y) that are solutions to the provided equation. 9. 4x – y = 10 (3, 2) (2, 3) (-1, -14) (6, 0) (1, -6) Applications Gia had 25 songs in a playlist composed of songs from her two favorite artists, Beyonce and Jennifer Lopez. How many songs did she have by each on in the playlist? Equation: List three solutions: Exercise: Write an equation for each situation then graph it. 10. The sum of two numbers is 25. What are the numbers Graph Linear Equations Name: ___________________________________ Algebra I CC Date: ______ Exit Ticket 1 Consider the linear equation y = 3x – 1. 1. State the slope and y-intercept of this line. 2. Use the slope and the y-intercept to graph the line. Name: ___________________________________ Algebra I CC 1 Consider the linear equation y = 3x – 1. 1. State the slope and y-intercept of this line. 2. Use the slope and the y-intercept to graph the line. Date: ______ Exit Ticket Graph Linear Equations Name: ___________________________________ Algebra I CC Date: ______ HW #22 Lesson Summary An ordered pair is a solution to a two variable equation when each number substituted into its corresponding variable makes the equation a true number sentence. All of the solutions to a two variable equation are called a solution set. Directions: Graph the following linear equations. Be sure to state both the slope and yintercept. 1. y = − 3x + 3 4 2. 2y = x 3. 2x + y = 4 4. 3y + 12 = 2x Graph Linear Equations Review: 5. Solve for x: x4 – 1 = 15