* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TOPOLOGIES in COMPUTER NETWORKING
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Bus (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
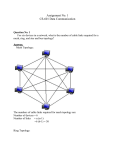
TOPOLOGIES in COMPUTER NETWORKING Refers to the physical layout of the network devices and cabling and how all the components communicate with each other. FOUR BASIC TYPES OF NETWORK TOPOLOGIES Mesh Bus Ring Star MESH TOPOLOGY Also called a point-to-point topology Each device is connected directly to all other devices on the network. Network of 4—each computer would need 3 connections and cables; Network of 30 computers, each would need 29 connections and cables. MESH MESH ADVANTAGES Provides fault tolerance The ability to overcome a failure. Fault tolerance allows the network to continue functioning in the event of a cable failure. Used in WANs to ensure that all sites continue to transmit in the event of a cable failure. DISADVANTAGES Rarely used in LANs. High expense to equip each computer with an individual connection. Large amount of cable required for all other computers on the network. Design a Mesh Topology BUS TOPOLOGY Multipoint topology Sharing Each computer has just one connection attached to a single cable that is shared by all other devices on the network. Single starting and ending point. At each end of the cable is a device known as a terminator. BUS TOPOLOGY PACKET Terminator An electrical signal that flows along the cable. BUS TOPOLOGY ADVANTAGES It is simple and reliable. It requires a small amount of cable. Adding more devices to the network is easy to do. DISADVANTAGES Troubleshooting problems is difficult to do. It becomes slower as more devices are added to the network. A cable problem can shut down the entire network. Design a Bus Topology RING TOPOLOGY Opposite of a bus, a bus has two end points. A ring is a circle with no ends. All devices on the network are connected to the ring. Packets travel in a loop in one direction. RING TOPOLOGY RING TOPOLOGY ADVANTAGES It is easy to manage. It is good for networks with many devices. Cable problems are easy to locate. DISADVANTAGES It can require more cable and special equipment. It is not as widely used as a bus topology. One malfunctioning computer can shut down the entire network. Design a Ring Topology STAR TOPOLOGY All devices are connected to a central device. The central device is known as a hub. A multipoint star topology resembles a star when viewed from above. STAR TOPOLOGY controller scanner STAR TOPOLOGY ADVANTAGES It is the easiest topology to manage and troubleshoot. Adding additional devices is easy to do. One malfunctioning computer or cable doesn’t stop the entire network. DISADVANTAGES If the hub fails, the entire network stops. It requires more cable. Cable installation can be more difficult. Design a Star Topology DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS How many devices will be attached to the network? What is the maximum distance between the devices? What is the predicted growth for the network? What degree of fault tolerance is necessary? How much money can be spent? What other networks will be connected to it?