* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War Two
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Weserübung wikipedia , lookup
War Front: Turning Point wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
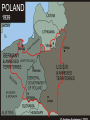
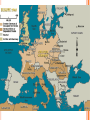
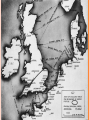
WORLD WAR TWO OUTBREAK OF WORLD WAR Britain & France prepare for Nazi-Soviet aggression . . . 1 Sept. 1939 = Germany invades Poland 3 Sept. 1939 = Britain & France declare war against Germany Nazis stage a Polish raid on a German radio tower “phony war” Tense relationship between Stalin and Hitler Stalin fortifies his new Polish border OUTBREAK OF WORLD WAR Britain & France prepare for Nazi-Soviet aggression . . . 1 Sept. 1939 = Germany invades Poland 3 Sept. 1939 = Britain & France declare war against Germany Nazis stage a Polish raid on a German radio tower “phony war” Tense relationship between Stalin and Hitler Stalin fortifies his new Polish border Invades Finland (“Winter War”, 1939-1940) HITLER’S MARCH THROUGH EUROPE “Blitzkrieg” = Germany’s new war-time strategy October 1939 = Poland defeated April 1940 = Germany invades Denmark & Norway Denmark puts up no resistance Norway defeated by June 1940 May 1940 = Hitler invades the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg May 1940 = Nazis invade France through Belgium Dunkirk evacuation 14 June 1940 = Nazis march through Paris HITLER’S MARCH THROUGH EUROPE “Blitzkrieg” = Germany’s new war-time strategy October 1939 = Poland defeated April 1940 = Germany invades Denmark & Norway Denmark puts up no resistance Norway defeated by June 1940 May 1940 = Hitler invades the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg May 1940 = Nazis invade France through Belgium Dunkirk evacuation 14 June 1940 = Nazis march through Paris 17 June 1940 = Pétain signs armistice with Germany France is split into an occupied zone and a Vichy zone THE BATTLE OF BRITAIN http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MkTw3_PmKtc Is Britain really “alone”? Sure, if you count Australia, New Zealand, Canada, South Africa, and India Operation Sea-Lion = the Germans plan to invade Britain August 1940 = Luftwaffe begin massive bombing campaign THE BATTLE OF BRITAIN http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MkTw3_PmKtc Is Britain really “alone”? Operation Sea-Lion = the Germans plan to invade Britain Sure, if you count Australia, New Zealand, Canada, South Africa, and India August 1940 = Luftwaffe begin massive bombing campaign August-September 1940 = “Battle of Britain” A fight for air supremacy over Britain 15 September = Royal Air Force finally beats back the Luftwaffe; Hitler puts the invasion on hold Luftwaffe continue to bomb Britain well into 1941 GROWING SOVIET-NAZI TENSION Hitler turns back toward the East . . . Mussolini had tried to invade Greece (1940) and was taking a beating Nazis wanted to control oil, agricultural, and mineral resources April 1941 = Nazis invade Yugoslavia Tito’s resistance! April & May 1941 = Nazis invade Greece Germans ordered to preserve cultural artifacts Germans defeat the Greeks and beat back the British Nazi brutality in the East . . . Massacres and “reprisal ratio” killings OPERATION BARBAROSSA: HITLER INVADES THE SOVIET UNION 22 June 1941 = Germany invades the Soviet Union Hitler wanted to completely annex its territory 3,000,000 soldiers = largest invasion force in history Soviets were unprepared Poor military leadership, experience, expectations Battle of Moscow (October 1941 – January 1942) Red Army rallies, stopping the German advance Germans were not prepared for the winter Gyorgi Zhukov leads a Soviet counterattack, pushing Germans back Summer of 1942 = Hitler tries the same tactic, but at Stalingrad Same result; Germans halted, winter comes, Germans pushed back “THE GREAT PATRIOTIC WAR” Russians were dedicated to winning WWII German arrogance and cruelty encouraged an enraged Soviet populace High cost of war for the Soviets . . . 1/3 of men born in 1906 died in war 20,000,000 Soviet people died (10% of population) Lots of starvation and poverty Eastern Front was the most brutal and the most deadly for both the Soviets and the Germans THE UNITED STATES ENTERS THE WAR Early efforts to help Britain and France Lend-Lease Act (1941) Problems in Japan . . . Historical tension between Japan and the West U.S. & Britain impose trade embargo on Japan In response, Japan invades Indochina (pisses off the U.S.) 7 December 1941 = Pearl Harbor U.S. immediately declares war against Japan 11 December 1941 = Germany declares war against the United States By 1943, American production has increased by 400% ALLIED VICTORY Different Allies, different strategies . . . Stalin wants help U.S. wants to beat Japan Britain wants back its influence in the Mediterranean Allied forces march through North Africa and land in mainland Italy by September 1943 November 1943 = Tehran Conference Stalin, Roosevelt, Churchill agree to work more in concert 6 June 1944 = D-Day General Eisenhower leads Allied troops onto the beaches of Normandy, France August 1944 = Paris is liberated ALLIED VICTORY Battle of the Bulge (December 1944 – January 1945) Germany’s final attempt to push back against the Allies April 1945 = Soviets invade Berlin Mass rape and sexual violence 30 April 1945 = Hitler commits suicide September 1945 = Japan surrenders Results of WWII . . . 50,000,000 people dead (including 6 million Jews) Soviets dominate Eastern Europe Europe is in shambles