* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tonsillitis
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
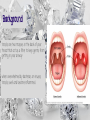
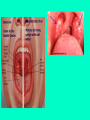
Tonsillitis By: Kendle Kossie and Kelsey Pett Outline ● vocabulary ● background ● Diagnosis ● How it occurs ● treatment ● Population Affected ● Conclusion Vocabulary Tonsillitis- excessive swelling of your tonsils CBS- complete blood cell count EBV- ebstain-barr virus or mono Tonsils- clusters of lymphatic tissue in the pharynx that functions as the first line of defense against infection Background tonsils are two masses in the back of your throat that act as a filter to keep germs from getting in your airway when overwhelmed by bacterias or viruses, tonsils swell and become inflammed. Symptoms Red, swollen tonsils White or yellow coating or patches on the tonsils Sore throat Difficult or painful swallowing Fever Enlarged, tender glands (lymph nodes) in the neck A scratchy, muffled or throaty voice Bad breath Stomachache, particularly in younger children Stiff neck Headache diagnosis physical exam including: other diagnosing methods include: light instrument to exam throat throat swab sent to a lab checking neck for swollen glands CBS- to indicate an infection or not checking for enlargement of spleen other diagnosing methods include: throat swab sent to a lab CBS- to indicate an infection or not (complete blood cell count) how it occurs -most common cause is viruses (ex: cold, flu, ebv or mono) -caused by strep throat about 30% of the time these germs are transmitted by casual contact with others sometimes transmission occurs by oral contact, especially in the case of EBV. the tonsils try to fight viruses and bacteria that enter through our mouth and nose, the result is an infection in the tonsils which can then swell, becoming inflamed and painful. Treatment Bacterial Antibiotics Viral Surgery Techniques to cut, burn, evaporate enlarged tonsils scalpel (common) self treatment Common lots of rest drink plenty of both warm and cool fluid eat smooths foods Gargle warm salt water laser radiowaves ultrasonic energy electrocautery Post Surgery difficulty breathing and swallowing Population Affected & Prevention ● affects young children ● between 5 and 15 years of age ● CONTAGIOUS good hygiene such as frequently hand washing avoid sharing food and drinks replace your toothbrush after being diagnosed with tonsilitis Conclusion tonsillitis occurs when bacteria or viruses infect the tonsils causing them to swell. This is most common in young children. Doctors typically diagnose tonsillitis by physical exams, throat swabs, or if needed, a CBC test. It can be treated with antibiotics or self treatment and in extreme cases surgery. Works Cited http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/tonsillitis-symptoms-causes-and-treatments http://www.medicinenet.com/adenoids_and_tonsils/article.htm http://patient.info/health/tonsillitis-leaflet http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tonsillitis/basics/definition/con-20023538