* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacterial Growth Requirements
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
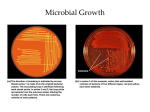
Bacterial Growth Growth Requirements Environmental Effects Bacterial Growth Characteristics Culture Media – Chemicals » Carbon » Nitrogen » Micronutrients (S, P, Fe, Mg, K, Na, etc.) – Solid or Liquid » Agar for solid support – Sterilization usually using an autoclave Bacterial Growth Characteristics Agar – Extract of seaweed (red algae) a polysaccharide of galactose and galacturonic acid – In 1881, Fannie Hesse, who was working as a technician for her husband in the laboratory of Robert Koch, suggested agar – Used as setting agent in jam making for some time – Replaced gelatin (poor temperature characteristics and supports growth) – Dissolves at 90°C and solidifies at 40°C Bacterial Growth Characteristics Culture Media – Selective and Differential Media – Complex vs. chemically defined Bacterial Growth Characteristics Selective and Differential Media – Differential - differentiates between organisms based upon colony morphology (especially color) on media – Selective - permits only certain organisms to grow (e.g. high salt or other inhibitors) Bacterial Growth Characteristics Complex vs. chemically defined – Chemically defined – each component has a know chemical formula and/or structure, e.g. minimal media (glucose, ammonium nitrate, and a defined mixture of salts) – Complex media (undefined) – components come from non defined sources, e.g. tryptone, peptone, yeast extract, oatmeal Bacterial Growth/Environmental Energy sources Carbon sources Physical influences on growth Bacterial Growth/Environmental Energy sources – Organisms acquire energy as a result of oxidation/reduction reactions – Light energy - phototroph – Chemical energy - chemotroph » organic (reduced forms of carbon) » inorganic (reduced metals) Bacterial Growth/Environmental Carbon sources – autotrophs use carbon dioxide – heterotrophs use reduced organic carbon sources: » sugars » organic acids » alcohols Bacterial Growth/Environmental Nitrogen sources – Reduced (ammonia) – Nitrates and Nitrites – Nitrogen Fixation Bacterial Growth/Environmental Nutritional Classifications - based upon energy & carbon source – photoautotroph - uses light energy and carbon dioxide as carbon source – photoheterotroph - uses light energy and an organic carbon source – chemoautotroph - uses an inorganic chemical as energy and carbon dioxide – chemoheterotroph - uses an organic chemical as energy and an organic carbon source Bacterial Growth - Physical Physical Influences on Growth – – – – – Temperature pH Osmotic pressure Oxygen availability Oxygen toxicity Bacterial Growth - Physical Temperature – psychrophillic - an organism that exhibits optimal growth at about 15 deg. C and does not grow above 20 deg. C – mesophillic - an organism that exhibits optimal growth at about 30-37 deg. C and does not grow below 10 or above 50 deg. C – thermophillic - an organism that exhibits optimal growth between 50-60 deg. C and does not grow below 40 deg. C or above 70 deg. C – Hyperthermophillic – growth between 70 and 110 deg C Bacterial Growth - Physical pH – most bacterial prefer pH 7 or slightly acidic – can tolerate to pH 4 due to production of organic acids during glucose metabolism Bacterial Growth - Physical Osmotic Pressure – ideal seems to be about 0.5% to 1.0% NaCl – some organisms tolerate much higher salt, e.g. Staphylococcus will go to 10% NaCl – halophiles - adapted to high salt concentrations many belong to Archea bacteria Bacterial Growth - Physical Toxic Oxygen - Forms – – – – Singlet oxygen Superoxide free radicals Peroxides Hydroxyl free radicals Bacterial Growth - Physical Toxic Oxygen - Neutralization – Catalase: » 2 H2O2 2 H2O + O2 – Superoxide dismutase: » 2 O2 - + 2 H+ O2 + H2O2 – Peroxidases: » H2O2 H+ + H2O Bacterial Growth - Physical Oxygen Classification – – – – Aerobic - grows in presence of oxygen Obligate aerobe - requires oxygen Anaerobic - grows in absence of oxygen Obligate anaerobe - will only grow in absence of oxygen – Facultative anaerobe - will grow both anaerobically or aerobically Bacterial Growth - Physical Oxygen Classification – Aerotolerant - only grow anaerobically but will tolerate oxygen – Microaerophillic - growth occurs only in presence of low concentrations of oxygen Bacterial Growth - Physical Catalase SOD Obligate Aerobe + + Faculatative Anaerobe + + Obligate Anaerobe - - Aerotolerant Anaerobe - + Microaerophiles - -