* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download V 0
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
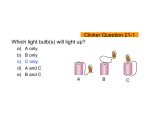
Clicker Questions for NEXUS/Physics Electric currents and circuits A. Yes B. No C. I have no idea NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions Is it possible to light a bulb with a battery using only one wire? Which of the arrangements shown will light the bulb? A. Only A C. Only C D. Only D E. Only E F. Only F G. A & C H. B & F I. D&E NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions B. Only B A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. A in #1 B in #1 A and B in #1 (equal) A in #2 B in #2 A and B in #2 (equal) All 4 equal Other NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions In the two cases shown here a battery is connected to a box containing some identical bulbs. The battery maintains a constant potential difference V0. across its terminals. Which bulbs will be brighter? Charge flows through a light bulb. Suppose a wire is connected across the bulb as shown. When the wire is connected, A. all the charge continues to flow through the bulb. B. half the charge flows through the wire, the other half continues through the bulb. C. all the charge flows through the wire. D. none of the above A. B. C. D. increases decreases decreases to 0 remains the same NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions This circuit has two identical light bulbs burning with equal brightness and a single 12 V battery. When the switch is closed, the brightness of bulb A A. B. C. D. increases decreases decreases to 0 remains the same NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions This circuit has two identical light bulbs burning with equal brightness and a single 12 V battery. When the switch is closed, the brightness of bulb B 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. A B C D B and C A and D Something else You can’t tell from the information given NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions Which of the bulbs in the following circuit is (are) the brightest? Sample Problem (R) (2R) (3R) (R) (V0) I0 = V0 /R NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions • How do the currents in resistors A and B compare? • How do the voltage drops across resistors A and B compare? • How does the current in and voltage drop across resistor C compare to those in A and B? • Find the current in resistor D. Sample Problem (R) (2R) (3R) (R) (V0) I0 = V0 /R NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions • If bulb D is removed from its socket, how does the brightness of the three bulbs A, B, and C change? Sample Problem (R) (2R) (3R) (R) (V0) I0 = V0 /R NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions • If bulb D is put back in its socket, and now bulb C is removed, rank the brightness of the three bulbs A, B, and D? #1 = 6V #2 = 3V A = B = C = 3Ω NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions Use Kirchhoff's principles to find: • the current through each of the bulbs and • the current through each of the batteries. What can you say about the voltage at the points A, B, and C? A. The magnitudes of the voltages at A and B add up to the magnitude of the voltage at C. B. The sum of the magnitudes of the voltages at two of the points adds up to the magnitude of the voltage at the third (but we can’t say which). C. The magnitude of the voltages at all three points are equal. D. There is not enough information to draw any of the above conclusions. E. Something else. What can you say about the currents at the points A, B, and C? A. The magnitudes of the currents flowing through A and B add up to the magnitude of the current flowing through C. B. The sum of the magnitudes of the currents at B and C add up to the magnitude of the current through A. C. The sum of the magnitudes of the currents at A and C add up to the magnitude of the current through B. D. The magnitude of the currents flowing through all three points are equal. E. There is not enough information to draw any of the above conclusions. F. Something else In what direction is the current at point C flowing? A. To the left. B. To the right. C. It is zero. D. There is not enough information to draw any of the above conclusions. E. Something else. What can you say about the voltage at the point C given that we take the voltage at the bottom of the battery to be 0? (V0 = 9 V; R = 3 Ω ) A. B. C. D. E. It is zero. It 9 Volts. It is 3 Volts. It is 4.5 Volts. There is not enough information to draw any of the above conclusions. F. Something else.