* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sea Anemones
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
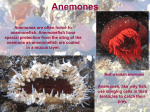
Sea Anemones Beaded Sea Anemone Zebra Anemone Red Anemones on Reef Classification/Identification • Anemones are cnidarians • Members of the class Anthozoa (meaning “flower animal”) • Stinging tentacles • Radial symmetry • Nerve net • sessile Habitat • Live in salt water environment • Found in coastal/shallow waters (coral reefs) and in deep ocean waters as well • Temperate and tropical areas worldwide • Do not change location from where they first planted themselves unless sense that their environment is unstable Nervous system • Very simple nervous and muscular system • Decentralized nervous system that controls • • functions in order to maintain homeostaysis As well biochemical and physical responses to stimuli For example, if you were to touch an anemone the entire animal contracts, withdrawing all of its tentacles into the polyp Movement • Usually have limited movement-as they are sessile • However can move if feel threatened in environment by muscular movements and plant themselves in a new area with substrate (muscular foot) Feeding • Uses nematocysts on tentacles to paralyze prey • Tiny fish swim into tentacles • After capturing food , brings it to its mouth and • • food is digested inside the digestive sac by enzymes Digestion is mostly extracellular Two –way digestive tract…Undigested food particles and wastes are eliminated through the mouth as well nematocysts • Each one contains a small vesicle filled with toxins called actinoporins • When the hair is touched mechanically triggers a cell explosion that injects poison into the prey • This is why anemones have a sticky feeling Life cycle • • • • • Dominant structure is polyp Are sessile so live attached to a substrate for life Reproduce sexually and asexually Sexually-Produce embryos that develop into planula larvae which settle and develop into adult polyps Asexually-regeneration from pieces of the polyp’s base Symbiosis • Symbiosis is a mutually beneficial relationship between two different species • Usually involves a mutual protection and or living habitat for each species • Anemone live in harmony with clownfish, hermit crabs, and algae • You can see this demonstrated in Finding Nemo! Exploitation • Part of global trade in marine ornamentals • 200 to 300 million dollar industry • Usually collected from the wild as juveniles or adults • Aquarium fishing activities significantly impact the populations of anemones • Are able to live in captivity but not as long as they can in the wild