* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SERIAL BUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS
Industry Standard Architecture wikipedia , lookup
Serial Peripheral Interface Bus wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Low-voltage differential signaling wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Serial port wikipedia , lookup
Low Pin Count wikipedia , lookup
Bus (computing) wikipedia , lookup
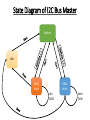
SERIAL BUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS 𝟐 𝐈 𝐂 & CAN SERIAL BUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS 𝟐 𝐈 𝐂 Protocol Introduction to I2C I2C is well known bus invented by PHILIPS. I2C stands for INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT. These type of bus is famous in TV circuit board and then it come to computer environment. It has speed of 100kbs but it can be extended to 450kbps. But only the problem is our processor has a capability of I2C protocol bus inbuilt. Technical Specifications The I2C Bus has two lines that carry its signals − one line is for clock named as SCL and second is for data named as SDL. By using I2C protocol the master can address 127 slaves at an instances. It has a processing element functionally as a bus controller or a microcontroller with I2C bus interface circuits. Bit format of I2C Brief introduction by video session State Diagram of I2C Bus Master Address Idle DATA Read DATA Write Get DATA Send DATA SERIAL BUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS CAN Protocol Serial Communication Distributed Control Area Network (CAN) Bus Distributed Control Area Network Example - a network of embedded systems in automobile It has a speed of 1 Mbps as a data rate It uses Multi-master bus. CAN Module are required CANBUS and the OSI Model CAN is a closed network – no need for security, sessions or logins. - no user interface requirements. Physical and Data Link layers in silicon. OSI:-> Open Systems Interconnection 10 CANBUS Physical Layer Physical medium – two wires terminated at both ends by resistors. Differential signal - better noise immunity. Benefits: Reduced weight, Reduced cost Fewer wires = Increased reliability Conventional multi-wire looms CAN bus network vs. http://canbuskit.com/what.php 11 Message Oriented Transmission Protocol Each node – receiver & transmitter A sender of information transmits to all devices on the bus All nodes read message, then decide if it is relevant to them All nodes verify reception was error-free All nodes acknowledge reception CAN bus © 2005 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. 12 Message Format Each message has an ID, Data and overhead. Data –8 bytes max Overhead – start, end, CRC, ACK 13 Bus Arbitration Arbitration – needed when multiple nodes try to transmit at the same time Only one transmitter is allowed to transmit at a time. A node waits for bus to become idle Nodes with more important messages continue transmitting CAN bus © 2005 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. 14 Bus Arbitration Message importance is encoded in message ID. Lower value = More important As a node transmits each bit, it verifies that it sees the same bit value on the bus that it transmitted. A “0” on the bus wins over a “1” on the bus. Losing node stops transmitting, winner continues. 15 CAN protocol There is a CAN controller between the CAN line and the host node. CAN controller ─BIU (Bus Interface Unit) consisting of a buffer and driver Method for arbitration─ CSMA/AMP (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Arbitration on Message Priority basis) Each Distributed Node Uses: Twisted Pair Connection up to 40 m – for bidirectional data. Line, which pulls to Logic 1 through a resistor between the line and + 4.5V to +12V. : Line Idle state Logic 1 (Recessive state) Detects Input Presence at the CAN line pulled down to dominant (active) state logic 0 (ground ~ 0V) by a sender to the CAN line Physical Layer It has two states 1. Dominant State(Logic 0) 2. Recessive State(Logic 1) Data Link Layer Bit Format of CAN Bus START 1 BIT 12 BITS ARBITRATION FIELD 6 BITS CONTROL FIELD 0 TO 64 BITS 16 BITS 2 BITS DATA FIELD CRC FIELD 7 BITS ACK END FIELD FRAME There are 5-fields in CAN data Frame Format and START & STOP Bits 1. Arbitration field 2. Control Field [Specifies the number of bytes of data to follow (0-8)] 3. Data Field 4. CRC Field [cyclic redundancy check code] 5. Acknowledge Field Protocol defined First field in frame bits First field of 12 bits ─ “Arbitration field”. 11-bit destination address and RTR bit (Remote Transmission Request) Destination device address specified in an 11-bit subfield and whether the data byte being sent is a data for the device or a request to the device in 1-bit sub-field. Maximum 211 devices can connect a CAN controller in case of 11-bit address field standard Arbitration Field Identifies(11 bits) the device to which data is being sent or request is being made. When RTR bit is at '1', it means this packet is for the device at destination address. If this bit is at '0' (dominant state) it means, this packet is a request for the data from the device. Control Field (6 bits) Second field of 6 bits- control field. The first bit is for the identifier’s extension. The second bit is always '1'. The last 4 bits specify code for data length Data Field (up-to 8 bytes data) Third field of 0 to 64 bits Its length depends on the data length code in the control field. CRC Field Fourth field (third if data field has no bit present) of 16 bits─ CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) bits. The receiver node uses it to detect the errors, if any, during the transmission ACK Field Fifth field of 2 bits─ First bit 'ACK slot' ACK = '1 BIT' and receiver sends back '0' in this slot when the receiver detects an error in the reception. Sender after sensing '0' in the ACK slot, generally retransmits the data frame. Second bit 'ACK delimiter' bit. It signals the end of ACK field. If the transmitting node does not receive any acknowledgement of data frame within a specified time slot, it should retransmit. EOF Field Sixth field of 7-bits end- of- the frame specification and has seven '0's Summary CAN bus – Controller Area Network bus Primarily used for building ECU (Engine control unit) networks in automotive applications. Two wires OSI - Physical and Data link layers Differential signal - noise immunity 1Mbit/s, 120’ Messages contain up to 8 bytes of data 27 Self Study USB Protocol…………………..!!!