* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECON 2201 A – Mock Midterm – Week 10
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
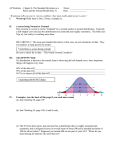
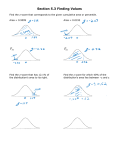
Peter Brown [email protected] ECON 2201 A 9 4th floor MacOdrum Library Thursdays 11:00 – 12:00 Short Answer Questions 1) Compare and contrast simple standard deviation and sample standard errors. What notation is used for each term? 2) Determine the confidence interval estimate using the following information. A sample of 500 with, σ = 0.5, x̅ = 15, with a confidence interval of 95%. Please draw out your findings! 3) Determine the common critical values (ie the z-scores of the critical values) for 80%, 90%, 95%, 99% 4) Determine the required sample size using the following information: Confidence level 95% (convert this into z-score); population proportion 0.85; standard error 0.05 Application The average height of a women in Canada, between the ages of 25-49, is 158.1 cm. The standard deviation is 5.7 cm. 1) The height is considered to be normally distributed. What is the probability that a women would be in between 175 and 185 cm tall? 2) Taking a random sample of 10 people from the population, what would expect the standard deviation of the sample distribution to be? (hint think back to the formula where we know the population standard deviation) 3) Using our sample of 10 people, what is the probability of getting a sample mean between 150 and 155 cm? Peter Brown [email protected] ECON 2201 A 9 4th floor MacOdrum Library Thursdays 11:00 – 12:00 Application Using Z-Scores, ensure to include a picture of the drawing! Use a Z-score table to determine the answer. 1) What is the probability that -1.5 ≤ z ≤ 1.5? 2) What is the probability that z ≥ 1.75? 3) What is the probability that z ≤ -1.68? 4) What is the probability that -2.1 ≤ z ≤ - 0.9? Application – Confidence Interval Unknown σ (using the Student t-Distribution) When using t-distribution, this means we do not know the population standard deviation (go back and look at the 2 formulas for confidence interval). Here, we will have to use t-distributions instead of z-scores). We have a sample of 25 males aged 25-49, and of the number of hours they sleep in a given night. The sample mean has been determined to be 6.75 hours. We do not know the population mean, but we know the standard deviation to be 1.5. Determine the confidence interval with a confidence level of 95%. Peter Brown 9 [email protected] ECON 2201 A 4th floor MacOdrum Library Thursdays 11:00 – 12:00 Application - z-score for sample distribution of p These help us determine if the information we have in a sample match the information we have from a population. A hotel brand determined they have a 90% approval rate with its customers. In a random sample of 50 people, it received only an 80% approval rate. How likely is it that a sample of 50 people will have an approval rating of only 80%? p is the sample proportion, and σ𝑝 is the standard error of the sample distribution. Use the z-score formula, and solve to find the chance that the approval rate would be 80% or less.