* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fish Zoonoses
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
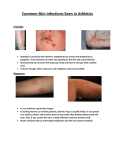
Zebrafish Zoonoses Mycobacterium Mycobacterium marinum and M. fortuitum are nontuberculous mycobacterium species that affect fish. Humans acquire infection by direct contact with infected animals or contaminated water. Infection is rare and more commonly occurs with exposure to minor trauma. A localized granulomatous nodule appears at the site of infection. In immunocompromised individuals, lymphadenopathy can occur followed by arthritis and osteomyelitis. Infection is treated with long-term oral antibiotics. Aeromonas Aeromonas hydrophila is a bacterium that occurs in freshwater and brackish environments. The disease is transmitted by infection of open wounds or ingestion of contaminated water or food. The bacteria causes septicemia in fish, and in humans most commonly causes gastroenteritis or local wound infections. The disease is treatable with oral antibiotics. Allergic Reactions to Fish Human sensitivity to fish proteins in the laboratory setting is rare. It remains possible however, to become sensitized to fish proteins through inhalation or skin contact. How to Protect Yourself Enroll in the UWM Occupational Health Program for Personnel with Laboratory Animal Contact. Follow posted Personal Protective Equipment requirements. Never wear protective equipment outside of animal areas. Wash your hands. The single most effective preventative measure that can be taken is regular hand washing. Wash hands and arms after handling any animal or any related equipment, and never drink or eat in the animal rooms. For more information: http://www.cdc.gov