* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Biomedical Imaging
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
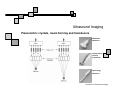
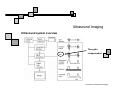
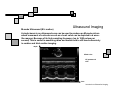
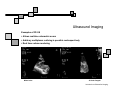
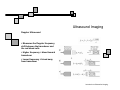
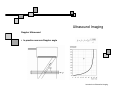
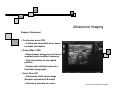
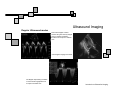
Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu Ultrasound Imaging Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Basic principles. Comparison to X-rays Ultrasound > 20kHz Medical/Diagnostic Ultrasound 1-15 MHz Sound spreads in all directions Ultrasound can be formed into a narrow beam (it is more “light-like”) Periodic motion yields pressure waves Speed of sound vs. speed of light Ultrasound requires a medium to propagate (no sound in vacuum) X-rays can be scattered. US can be reflected, refracted and focused Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasound pulse/continuous wave modes Pulsed Wave Mode Short DC pulse is applied to the crystal producing its instantaneous expansion an tissue compression Due to elastic tissue properties: high pressure wave front (compression) travels through the body at speed ν followed by a low wave front (decompression or rarefaction) Multiple frequencies are present in the signal and echo (bandwidth) Continuous Wave Mode AC voltage applied to crystal Periodic pattern of compression and rarefaction will travel across the body with speed ν and wavelength λ The frequency is given by the AC voltage applied to the transducer crystal: ν = λ f Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasound pulse/wave generation: transmission Ultrasound signal detection Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasound transducer frequency vs. resolution Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Piezoelectric crystals, beam forming and transducers Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Piezoelectric crystals, beam forming and transducers Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Piezoelectric crystals, beam forming and transducers Abdominal Obstetrics Intraoperative vascular (superficial) Gynecology Obstetrics Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasound system overview Time-gain compensation Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging A-mode Ultrasound (A = amplitude) Now obsolete in medical imaging. Wave spikes are represented when a single beam passes through objects of different consistency and hardness. The distance between these spikes (for example A and B ) can be measured accurately by dividing the speed of sound in tissue (1540 m/sec) by half the sound travel time. depth Introduction to Biomedical Imaging M-mode Ultrasound (M = motion) Ultrasound Imaging A single beam in an ultrasound scan can be used to produce an M-mode picture where movement of a structure such as a heart valve can be depicted in a wavelike manner. Because of its high sampling frequency (up to 1000 pulses per second) This is useful in assessing rates and motion and is still used extensively in cardiac and fetal cardiac imaging. depth Mitral valve LV (parasternal view time Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging B-mode Ultrasound (B = brightness) Same as A-mode, but one dimensional graphical display with brightness corresponding to amplitude of reflected sound 2D real-time ultrasound Most modern ultrasound devices are realtime 2D imaging systems. Multiple crystals (linear, curved or phased-array) or moving crystal Sequential B-mode pulses sweeping across a plane to display the image in either a linear or ‘sector’ format Displayed as real time imaging with up to 100 images per second. Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Summary A-, B-, M-mode ultrasound Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasound 2D piezoelectric arrays Allows real-time volumetric scans Arbitrary multiplanar reslicing is possible restrospectively Real time volume rendering Brest biopsy Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Examples of 3D US Allows real-time volumetric scans Arbitrary multiplanar reslicing is possible restrospectively Real time volume rendering Miltral valve 3D Color Doppler Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Doppler Ultrasound Measures the Doppler frequency shift between the transducer and the red blood cells Higher frequency = blood toward transducer Lower frequency = blood away from transducer Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Doppler Ultrasound In practice non zero Doppler angle Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Doppler Ultrasound Continuous wave (CW) Continuous sinusoidal wave, hence no depth information Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Doppler Ultrasound Continuous wave (CW) Continuous sinusoidal wave, hence no depth information Pulsed Wave (PW) Pulsed waves along one scan line at constant pulse repetition frequency Only information of one spatial position Sample each reflected pulse at a fixed time (range gate) Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Doppler Ultrasound Continuous wave (CW) Continuous sinusoidal wave, hence no depth information Pulsed Wave (PW) Pulsed waves along one scan line at constant pulse repetition frequency Only information of one spatial position Sample each reflected pulse at a fixed time (range gate) Color Flow (CF) Information of the whole image (Doppler equivalent of B-mode) Velocity is encoded as a color Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Doppler Ultrasound modes Pulse wave Doppler of mitral annulus using time-velocity integral (TVI) for analysis of diastolic function from an apical 4 chamber view. Color Doppler imaging of the heart CW Doppler representing moderate to severe mitral regurgitation from an apical 4 chamber view. Introduction to Biomedical Imaging Ultrasound Imaging Modern ultrasound systems GE Vivid7 GE Voluson 750 Introduction to Biomedical Imaging