* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thermions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
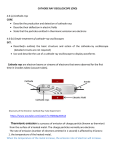
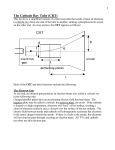
Thermionic Emission •When a metal is heated up the electrons more kinetic energy. •During heating electrons in the piece of metal leap out into its surroundings. •The metal, having lost an electron, gets a positive charge. •The result is an electrostatic attraction between the (negatively charged) electrons that have leapt out of the metal and the (positively charged) metal they have left. •This tends to pull them back. Thermionic Emission •The result of the above is to produce what is called a “space charge effect”. •The hot metal becomes surrounded by a “cloud” of electrons, that have jumped out of the metal, but are then drawn back by the attraction between the electron and the metal. •Taken overall, the system is still electrically neutral since we have the negative electrons and the positive metal. •The usual practice with valves is to use the heated metal as a cathode This allows us to pass a current though the cathode and heat it up. When we heat up the metal we get a cloud of electrons that are ‘boiling’ off the metal surface and then falling back again. This property of ‘boiling off’ electrons is called ‘Thermionic Emission’ as the emission of electrons is produced by the heat. Thermionic Emission Emission of electrons or ions by substances that are highly heated The driving force of this process is the thermal energy The charged particles are called thermions The number of thermions emitted increases rapidly as the temperature of the substance rises. The heated material may be in the form of a metal filament or of some compound that coats and is heated by the filament. If the heated body carries a positive or negative charge, the thermions will be of the same charge. Thermionic valves Devices which allow electron flow in one direction only & work using heat Thermionic Diode The anode and cathode are made of good conductors (e.g. metals), but are separated by an insulating envelope and the vacuum inside. •heat the cathode by applying a voltage between the two cathode heater leads, H1 and H2. •The anode develops a negative potential with respect to the cathode, and some current will flow through the resistor •The amount of current depends on the temperature of the cathode, its surface area, the distance to the anode, etc Diode Valves •A diode consists of an evacuated glass tube into which are sealed into two separate electrodes. •The cathode or filament is constructed so that as current flows through it, a space charge of electrons developed around it as result of thermal effect of the current •The anode or the plate is the other electrode •When positive it attracts electrons across the valve •Electrons can pass only from cathode to anode as there is no space charge around the cold anode •Thermionic valve allows electrons to flow in one direction, but not in the reverse direction Triode Valves •Works on exactly the same principle as the diode valve, but has a third electrode (grid) placed between the cathode & the anode •It is possible, using an external circuit, to make the grid negative, positive or neutral •If neutral, the grid will not affect electron flow across the valve •If positive, it will attract electrons away from the cathode & thus amplify the electron flow through the valve •If negative, the grid will repel electrons & reduce or stop the electron flow •In the above case valve can act as a switch or a regulator Thank You..